IGCSE® Chemistry - Hodder Plus Home
... 10 (a) (i) an agent that causes colourless [1] substances on a chromatogram to become coloured [1] (ii) the ratio of the distance travelled by the solute [1] to the distance travelled by the solvent [1] in chromatography (b) ninhydrin [1] (c) (i) sample 1 = alanine [1], sample 2 = lysine ...
... 10 (a) (i) an agent that causes colourless [1] substances on a chromatogram to become coloured [1] (ii) the ratio of the distance travelled by the solute [1] to the distance travelled by the solvent [1] in chromatography (b) ninhydrin [1] (c) (i) sample 1 = alanine [1], sample 2 = lysine ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... Alcohols from Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with Grignard Reagents • Alkyl, aryl, and vinylic halides react with magnesium in ether or tetrahydrofuran to generate Grignard reagents, RMgX • Grignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds to yield alcohols ...
... Alcohols from Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with Grignard Reagents • Alkyl, aryl, and vinylic halides react with magnesium in ether or tetrahydrofuran to generate Grignard reagents, RMgX • Grignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds to yield alcohols ...
Document
... reagents with nitroarenes was a very useful synthetic tool. He rationalised the mechanism on the basis of a SET pathway, where the geometry of the alkyl radical influences the site of collapse on the nitroarene radical anion viz: alkyl radicals on the ring, allyl radicals on the nitrogen atom and vi ...
... reagents with nitroarenes was a very useful synthetic tool. He rationalised the mechanism on the basis of a SET pathway, where the geometry of the alkyl radical influences the site of collapse on the nitroarene radical anion viz: alkyl radicals on the ring, allyl radicals on the nitrogen atom and vi ...
Alkenes 3 - ChemWeb (UCC)
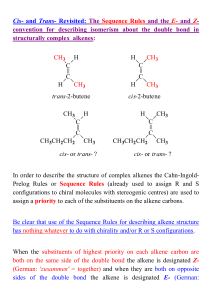
... This reaction illustrated above is called a 1,2- or -elimination to indicate that the groups being eliminated are located on adjacent atoms in the starting material as compared to a 1,1- or -elimination where both are located on the same carbon atom This, in itself, tells you nothing about the act ...
... This reaction illustrated above is called a 1,2- or -elimination to indicate that the groups being eliminated are located on adjacent atoms in the starting material as compared to a 1,1- or -elimination where both are located on the same carbon atom This, in itself, tells you nothing about the act ...
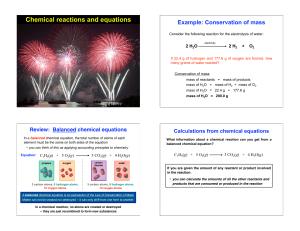
Chapter 12: Chemical Equilibrium • Chemical Equilibrium
... Forward and Reverse Reactions • At the start of a chemical reaction, the reactant concentrations decrease over time, with a corresponding decrease in rate of the forward reaction. • As the reactants are being consumed, the product concentration increases, with a corresponding increase in the rate of ...
... Forward and Reverse Reactions • At the start of a chemical reaction, the reactant concentrations decrease over time, with a corresponding decrease in rate of the forward reaction. • As the reactants are being consumed, the product concentration increases, with a corresponding increase in the rate of ...
Reactions of alcohols File
... Reaction of an alcohol (R-OH) with sodium metal an alkoxide (R-O- Na+) + hydrogen gas (H2) ...
... Reaction of an alcohol (R-OH) with sodium metal an alkoxide (R-O- Na+) + hydrogen gas (H2) ...
Organic Chemistry
... • of the two carbons of the mercurinium ion intermediate, the more substituted carbon has the greater degree of partial positive character • alternatively, computer modeling indicates that the CHg bond to the more substituted carbon of the bridged intermediate is longer than the one to the less subs ...
... • of the two carbons of the mercurinium ion intermediate, the more substituted carbon has the greater degree of partial positive character • alternatively, computer modeling indicates that the CHg bond to the more substituted carbon of the bridged intermediate is longer than the one to the less subs ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact. Ans: Due to hydrogen bond with water molecules 17. Preparation of ethers by dehydration of alcohols is not suitable for the using of secondary and tertiary alcohols give reason. Ans: dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohols to give corresponding ...
... comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact. Ans: Due to hydrogen bond with water molecules 17. Preparation of ethers by dehydration of alcohols is not suitable for the using of secondary and tertiary alcohols give reason. Ans: dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohols to give corresponding ...
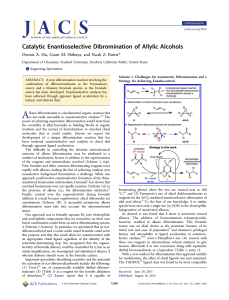
Catalytic Enantioselective Dibromination of Allylic Alcohols
... dibromination must take into account the aforementioned issues. Our approach was to formally separate Br2 into electrophilic and nucleophilic components that are unreactive on their own but in combination would form an active dibrominating species, 1 (Scheme 1, bottom). In particular, we speculated ...
... dibromination must take into account the aforementioned issues. Our approach was to formally separate Br2 into electrophilic and nucleophilic components that are unreactive on their own but in combination would form an active dibrominating species, 1 (Scheme 1, bottom). In particular, we speculated ...
File
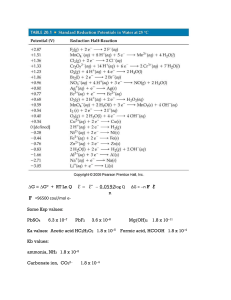
... a student wishes to use the Nernst equation to find the equilibrium constant. What number should the student use for “n” in the Nernst equation? ________16. Which of the following solutions would form a buffer when added to 50.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH3? I. 25.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH4Cl II. 25.0 mL of 2.0 ...
... a student wishes to use the Nernst equation to find the equilibrium constant. What number should the student use for “n” in the Nernst equation? ________16. Which of the following solutions would form a buffer when added to 50.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH3? I. 25.0 mL of 2.00 molar NH4Cl II. 25.0 mL of 2.0 ...
CHE 1031 Lab Manual
... Knowledge in chemistry, as in all the physical sciences, is obtained initially from performing experiments in a laboratory. It is in the laboratory that facts are discovered and concepts, ideas and theorie ...
... Knowledge in chemistry, as in all the physical sciences, is obtained initially from performing experiments in a laboratory. It is in the laboratory that facts are discovered and concepts, ideas and theorie ...
Biochemistry Powepoint
... atoms and are found in living things. Most inorganic compounds do not contain carbon atoms. Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. Cha ...
... atoms and are found in living things. Most inorganic compounds do not contain carbon atoms. Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. Cha ...
odd - WWW2
... but (x + y) = 5, the sum of the iron ions. Hence by substitution, x = 3 and y = 2. Thus there are three Fe2+ ions and two Fe3+ ions per formula. 14.29 Zeolites are used as ion exchangers for water; as adsorption agents, particularly for water in organic solvents; for gas separation, particularly dio ...
... but (x + y) = 5, the sum of the iron ions. Hence by substitution, x = 3 and y = 2. Thus there are three Fe2+ ions and two Fe3+ ions per formula. 14.29 Zeolites are used as ion exchangers for water; as adsorption agents, particularly for water in organic solvents; for gas separation, particularly dio ...
Chapter 20 Organic Chemistry
... as polluted air or spoiled food. • Odorants must be volatile. • However, many volatile substances have no scent at all. • Most common smells are caused by organic molecules. • The study of compounds containing carbon combined with one or more of the elements hydrogen(H), nitrogen(N), oxygen(O), and ...
... as polluted air or spoiled food. • Odorants must be volatile. • However, many volatile substances have no scent at all. • Most common smells are caused by organic molecules. • The study of compounds containing carbon combined with one or more of the elements hydrogen(H), nitrogen(N), oxygen(O), and ...
Synthesis of Amide Bond Isosteres Incorporated
... It has been observed that vaccination of mice with the galactosylated CII256-270 peptide can protect them from CIA, and those that still develop arthritis are not affected as severely.15 This implies a possibility of using glycopeptides in the treatment of RA since mice transgenic for the RA associa ...
... It has been observed that vaccination of mice with the galactosylated CII256-270 peptide can protect them from CIA, and those that still develop arthritis are not affected as severely.15 This implies a possibility of using glycopeptides in the treatment of RA since mice transgenic for the RA associa ...