Use the following answers for questions 1
... 59. When 70. milliliter of 3.0-molar Na2CO3 is added to 30. milliliters of 1.0-molar NaHCO3 the resulting concentration of Na+ is (A) 2.0 M (B) 2.4 M (C) 4.0 M (D) 4.5 M (E) 7.0 M 67. A student wishes to prepare 2.00 liters of 0.100-molar KIO3 (molecular weight 214). The proper procedure is to weigh ...
... 59. When 70. milliliter of 3.0-molar Na2CO3 is added to 30. milliliters of 1.0-molar NaHCO3 the resulting concentration of Na+ is (A) 2.0 M (B) 2.4 M (C) 4.0 M (D) 4.5 M (E) 7.0 M 67. A student wishes to prepare 2.00 liters of 0.100-molar KIO3 (molecular weight 214). The proper procedure is to weigh ...
ammines ncert solution
... N−atom is delocalized over the benzene ring. In C6H5CH2NH2, N is not directly attached to the benzene ring. Thus, its lone pair is not delocalized over the benzene ring. Therefore, the electrons on the N atom are more easily available for protonation in C6H5CH2NH2 than in C6H5NH2 i.e., C6H5CH2NH2 is ...
... N−atom is delocalized over the benzene ring. In C6H5CH2NH2, N is not directly attached to the benzene ring. Thus, its lone pair is not delocalized over the benzene ring. Therefore, the electrons on the N atom are more easily available for protonation in C6H5CH2NH2 than in C6H5NH2 i.e., C6H5CH2NH2 is ...
Asymmetric Glycine Enolate Aldol Reactions
... transformation of these adducts to the enantiomerically pure N-methyl @-hydroxyamino acids 1. This reaction methodology (la), an important constituent has been applied to the asymmetric synthesis of (4R)-4-((E)-2-butenyI)-4,N-dimethyl-~-threonine in the immunosuppressant peptide cyclosporine. Severa ...
... transformation of these adducts to the enantiomerically pure N-methyl @-hydroxyamino acids 1. This reaction methodology (la), an important constituent has been applied to the asymmetric synthesis of (4R)-4-((E)-2-butenyI)-4,N-dimethyl-~-threonine in the immunosuppressant peptide cyclosporine. Severa ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... and [isobutane] = 2.18 M? If it is not at equilibrium, in which direction will the reaction proceed in order to achieve equilibrium? Is the system at equilibrium when [butane] = 0.75 M and [isobutane] = 2.60 M? If it is not at equilibrium, in which direction will the reaction proceed in order to ach ...
... and [isobutane] = 2.18 M? If it is not at equilibrium, in which direction will the reaction proceed in order to achieve equilibrium? Is the system at equilibrium when [butane] = 0.75 M and [isobutane] = 2.60 M? If it is not at equilibrium, in which direction will the reaction proceed in order to ach ...
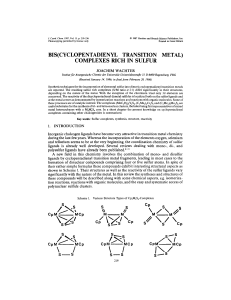
Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society
... In the title compound, [Hg (C14H13N4O3)2], the central Hg atom is sixcoordinated by two tridentate triazenide ligands through two N and one O atoms. Spectrophotometric study of complex formation between this ligand and Hg2+ in DMF solution indicated a large stability constant for the mercury ion com ...
... In the title compound, [Hg (C14H13N4O3)2], the central Hg atom is sixcoordinated by two tridentate triazenide ligands through two N and one O atoms. Spectrophotometric study of complex formation between this ligand and Hg2+ in DMF solution indicated a large stability constant for the mercury ion com ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Solution Chemistry • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e. solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions ...
... Solution Chemistry • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e. solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... • For similar reasons, other reactive groups like ester, nitriles, carbonyl (other than the one intended to react), cannot be present in the organometallic or carbonyl components. ...
... • For similar reasons, other reactive groups like ester, nitriles, carbonyl (other than the one intended to react), cannot be present in the organometallic or carbonyl components. ...
- Mendeley Data
... In the Schiff base compounds which are among the privileged ligands, the carbonyl group of ketone or aldehyde are replaced by an imine group due to simple one-pot condensation synthesis in an alcoholic solvent. For more than a century, metal complexes of the Schiff base ligands have been rigorously ...
... In the Schiff base compounds which are among the privileged ligands, the carbonyl group of ketone or aldehyde are replaced by an imine group due to simple one-pot condensation synthesis in an alcoholic solvent. For more than a century, metal complexes of the Schiff base ligands have been rigorously ...
hong kong diploma of secondary education examination
... X, Y and Z are three different elements. X2+ ion, Y– ion and argon atom have the same electronic arrangement. Z belongs to the same period as X and the same group as Y in the ...
... X, Y and Z are three different elements. X2+ ion, Y– ion and argon atom have the same electronic arrangement. Z belongs to the same period as X and the same group as Y in the ...
Disproportionation of Monolithium Acetylide into
... most widely used ethynylation and alkynylation reaction.1 Monolithium acetylide (1) disproportionates readily above -25 °C into the more stable dilithium carbide (2) and acetylene.2 Liquid ammonia which is utilized in processes claimed to have industrial economics1,3 serves not only as a solvent but ...
... most widely used ethynylation and alkynylation reaction.1 Monolithium acetylide (1) disproportionates readily above -25 °C into the more stable dilithium carbide (2) and acetylene.2 Liquid ammonia which is utilized in processes claimed to have industrial economics1,3 serves not only as a solvent but ...
electrical energy and capacitance
... Example 1. A compound is discovered with a 58.12 g/mol molar mass. Its empirical formula is C2H5. What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) ( ...
... Example 1. A compound is discovered with a 58.12 g/mol molar mass. Its empirical formula is C2H5. What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) ( ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in very strong acid ...
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in very strong acid ...
the chemical and physical properties of condensed
... several polyphosphates. In these transitions a second phosphate anion and a melt are formed. All known intermediate chain length polyphosphates formed as phase diagram entities are of this type3032. Yet another type of transformation occurs during the dehydration of a crystalline hydrate. In most sy ...
... several polyphosphates. In these transitions a second phosphate anion and a melt are formed. All known intermediate chain length polyphosphates formed as phase diagram entities are of this type3032. Yet another type of transformation occurs during the dehydration of a crystalline hydrate. In most sy ...