Chapter 8
... Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. ...
... Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... • Carbon has many allotropes • most common are graphite and diamond ...
... • Carbon has many allotropes • most common are graphite and diamond ...
AP CHEMISTRY 2005/2006
... The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atom ...
... The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atom ...
CST Review Part 2
... State Standard #3 The conservation of atoms in chemical reactions leads to the principle of conservation of matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equat ...
... State Standard #3 The conservation of atoms in chemical reactions leads to the principle of conservation of matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equat ...
pdfInt 2 Homework Unit 2 1 MB
... Name the type of chemical reaction which takes place when iodine (2.22) reacts with propene. ...
... Name the type of chemical reaction which takes place when iodine (2.22) reacts with propene. ...
Document
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
Topic 1: Quantitative Chemistry
... 4.1.5: State that transition elements can form more than one ion. 4.1.6: Predict whether a compound of two elements would be ionic from the position of the elements in the periodic table or negativity values.4.1.7: State the formula of common polyatomic ions formed by non-metals in periods 2 and 3. ...
... 4.1.5: State that transition elements can form more than one ion. 4.1.6: Predict whether a compound of two elements would be ionic from the position of the elements in the periodic table or negativity values.4.1.7: State the formula of common polyatomic ions formed by non-metals in periods 2 and 3. ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... of an atom was a) in the electrons. b) concentrated in the nucleus. c) evenly spread throughout d) in rings around the atom. the atom 18. A nuclear particle that has about the same mass as a proton, but with no electrical charge, is called a(n) a) nuclide. b) neutron. c) electron. d) isotope. ...
... of an atom was a) in the electrons. b) concentrated in the nucleus. c) evenly spread throughout d) in rings around the atom. the atom 18. A nuclear particle that has about the same mass as a proton, but with no electrical charge, is called a(n) a) nuclide. b) neutron. c) electron. d) isotope. ...
Chemical Bonding
... shape of the molecule about each carbon. Determine the hybridization of each carbon atom and draw an valence orbital diagram to represent the carbon atoms. Sketch how the orbitals of carbon and hydrogen overlap to form sigma bonds. Sketch separately the delocalized Π bonding and draw an energy level ...
... shape of the molecule about each carbon. Determine the hybridization of each carbon atom and draw an valence orbital diagram to represent the carbon atoms. Sketch how the orbitals of carbon and hydrogen overlap to form sigma bonds. Sketch separately the delocalized Π bonding and draw an energy level ...
I - Holland Public Schools
... * collision theory - idea that in order for a reaction to occur, the molecules must come in physical contact with one another (they must collide) *When you look at the equations above on paper, there is no way to tell which one is faster It can only be determined by experiment * reaction rate is aff ...
... * collision theory - idea that in order for a reaction to occur, the molecules must come in physical contact with one another (they must collide) *When you look at the equations above on paper, there is no way to tell which one is faster It can only be determined by experiment * reaction rate is aff ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a dotted line. Because they occur between two different molecules and not within one molecule (like ionic or covalent bonds) and they occur between partial (not full) charges, hydrogen bonds are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. 16. Chemical re ...
... (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a dotted line. Because they occur between two different molecules and not within one molecule (like ionic or covalent bonds) and they occur between partial (not full) charges, hydrogen bonds are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds. 16. Chemical re ...
Chapter 1-
... the type of carbon the hydrogen is attached to C-H bonds where the carbon has more s character are shorter, stronger and stiffer and thus vibrate at higher frequency C-H bonds at sp centers appear at 3000-3100 cm -1 C-H bonds at sp2 centers appear at about 3080 cm-1 C-H bonds at sp3 centers ...
... the type of carbon the hydrogen is attached to C-H bonds where the carbon has more s character are shorter, stronger and stiffer and thus vibrate at higher frequency C-H bonds at sp centers appear at 3000-3100 cm -1 C-H bonds at sp2 centers appear at about 3080 cm-1 C-H bonds at sp3 centers ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... Chemical reactions change the way atoms are grouped but atoms are not changed. Thomson/Plum Pudding Model o Most of the atom consisted of one large positive charge and small negative charges embedded that balances out the charges. Rutherford/Nuclear Model o Atom contained a positive central core ...
... Chemical reactions change the way atoms are grouped but atoms are not changed. Thomson/Plum Pudding Model o Most of the atom consisted of one large positive charge and small negative charges embedded that balances out the charges. Rutherford/Nuclear Model o Atom contained a positive central core ...
Describing Chemical Reactions
... products. In an open system, matter can enter from or escape to the surroundings. A match burning in the air is an example of an open system. You cannot measure the mass of all the reactants and products in an open system. A closed system is a system in which matter cannot enter from or escape to th ...
... products. In an open system, matter can enter from or escape to the surroundings. A match burning in the air is an example of an open system. You cannot measure the mass of all the reactants and products in an open system. A closed system is a system in which matter cannot enter from or escape to th ...
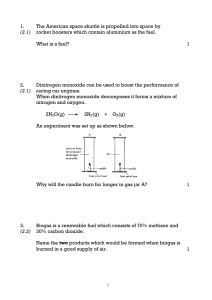
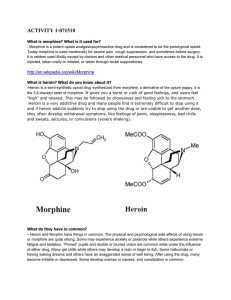
activity 1-071510 - ids
... a functional group, the acyl with chemical formula COCH3. It is sometimes abbreviated as Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl. The carbonyl center of an acyl radical has one nonbonded electron with which it forms a ch ...
... a functional group, the acyl with chemical formula COCH3. It is sometimes abbreviated as Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl. The carbonyl center of an acyl radical has one nonbonded electron with which it forms a ch ...
Chapter 1 Student Notes
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
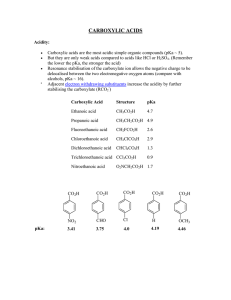
carboxylic acids - La Salle University
... Carboxylic acids are the most acidic simple organic compounds (pKa ~ 5). But they are only weak acids compared to acids like HCl or H2SO4. (Remember the lower the pKa, the stronger the acid) Resonance stabilisation of the carboxylate ion allows the negative charge to be delocalised between the two e ...
... Carboxylic acids are the most acidic simple organic compounds (pKa ~ 5). But they are only weak acids compared to acids like HCl or H2SO4. (Remember the lower the pKa, the stronger the acid) Resonance stabilisation of the carboxylate ion allows the negative charge to be delocalised between the two e ...
Chapter 7
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...
... 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 ...