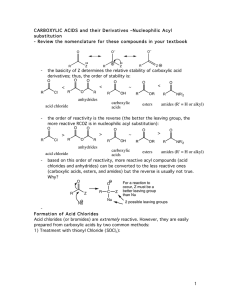
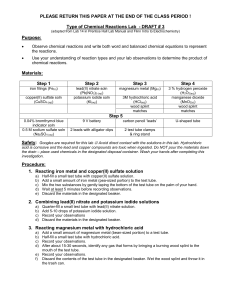
Chem 150 Unit 4 - Chemical Properties I Chemical Reactions
... within and between molecules that results in the formation of new molecules. • This process involves the making and breaking of covalent bonds. • An important concept in these processes is that all of the atoms present before a reaction are also present after the reaction ...
... within and between molecules that results in the formation of new molecules. • This process involves the making and breaking of covalent bonds. • An important concept in these processes is that all of the atoms present before a reaction are also present after the reaction ...
Chapter 7 Covalent Bonding Outline Covalent Bonding Introduction
... • Recall that atoms may form ions that are isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas • Na forms Na+ 1s22s22p63s1 1s22s22p6 • F forms F1s22s22p5 1s22s22p6 • Some atoms share electrons rather than ionize • Sharing results in atoms becoming isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas, as they do in for ...
... • Recall that atoms may form ions that are isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas • Na forms Na+ 1s22s22p63s1 1s22s22p6 • F forms F1s22s22p5 1s22s22p6 • Some atoms share electrons rather than ionize • Sharing results in atoms becoming isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas, as they do in for ...
Chemistry of Cars unit_7_chemistry_of_cars
... copper(II) hydroxide + acetic acid → calcium hydroxide + phosphoric acid → calcium bromide + potassium hydroxide → ...
... copper(II) hydroxide + acetic acid → calcium hydroxide + phosphoric acid → calcium bromide + potassium hydroxide → ...
Exam 2 Review A
... process, i.e., the acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes. 4. Be able to explain how alkenes can be hydrated in a Markovnikov fashion using oxymercuration-demercuration, using an arrow-pushing mechanism for first step of this process. 5. Be able to explain how alkenes can be hydrated ...
... process, i.e., the acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes. 4. Be able to explain how alkenes can be hydrated in a Markovnikov fashion using oxymercuration-demercuration, using an arrow-pushing mechanism for first step of this process. 5. Be able to explain how alkenes can be hydrated ...
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90933) 2014
... Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid vigorously to form a salt and hydrogen gas. The magnesium reacts and disappears into solution; the solution warms up and there is fizzing due to production of hydrogen gas. Magnesium is high up on the activity series (above H), so will easily react. Copper is ...
... Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid vigorously to form a salt and hydrogen gas. The magnesium reacts and disappears into solution; the solution warms up and there is fizzing due to production of hydrogen gas. Magnesium is high up on the activity series (above H), so will easily react. Copper is ...
Introduction - Blanche Ely High School
... The process of storing light energy from the sun in the form of glucose The process of making sugar (glucose) using light energy Photo--”light” Synthesis--”make” ; ...
... The process of storing light energy from the sun in the form of glucose The process of making sugar (glucose) using light energy Photo--”light” Synthesis--”make” ; ...
File
... are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
... are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
Name ionic compounds containing main group or
... A chemist has a 100-gram sample of a compound that contains 17.073 grams of carbon, 2.168 grams of hydrogen, 10.840 grams of oxygen, 8.5366 grams of nitrogen, 28.8618 grams of chlorine and the rest is bromine. What is the empirical formula of the compound? Refer to Question # 27 to answer this quest ...
... A chemist has a 100-gram sample of a compound that contains 17.073 grams of carbon, 2.168 grams of hydrogen, 10.840 grams of oxygen, 8.5366 grams of nitrogen, 28.8618 grams of chlorine and the rest is bromine. What is the empirical formula of the compound? Refer to Question # 27 to answer this quest ...
Honors Biology General Chemistry Questions 2016 Name Most of
... B. number of protons C. mass number. D. only A and B are correct. E. A, B, and C are correct. 5. The image above indicates that 3. An oxygen atom has an atomic number of 8. Therefore, it must have A. 8 protons. B. 8 electrons. ...
... B. number of protons C. mass number. D. only A and B are correct. E. A, B, and C are correct. 5. The image above indicates that 3. An oxygen atom has an atomic number of 8. Therefore, it must have A. 8 protons. B. 8 electrons. ...
Chemistry Stoichiometry Standard Set 3 Review
... The mole concept is often difficult at first, but the concept is convenient in chemistry just as a dozen is a convenient concept, or measurement unit, in the grocery store. The mole is a number 6.02 x 1023. Specifically, a mole is defined as the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. When atomic ...
... The mole concept is often difficult at first, but the concept is convenient in chemistry just as a dozen is a convenient concept, or measurement unit, in the grocery store. The mole is a number 6.02 x 1023. Specifically, a mole is defined as the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. When atomic ...
Document
... b. Liquid: definite volume without a definite shape; particles are close together but can move past one another – particles in a liquid move more rapidly than those in a solid. ...
... b. Liquid: definite volume without a definite shape; particles are close together but can move past one another – particles in a liquid move more rapidly than those in a solid. ...
Biochemistry Week 3: Macromolecules
... 1) What does it mean for a molecule to be a polymer? What polymers are found in nature? 2) How can simple biological molecules, like a monosaccharide, form a polymer and then how can that polymer be broken down into simple monomers? 3) Discuss how carbohydrates are formed, their chemical composition ...
... 1) What does it mean for a molecule to be a polymer? What polymers are found in nature? 2) How can simple biological molecules, like a monosaccharide, form a polymer and then how can that polymer be broken down into simple monomers? 3) Discuss how carbohydrates are formed, their chemical composition ...
chemistry important question i
... (b) Draw the structures of the following : (i) H4P2O7 (Pyrophosphoric acid) (ii) XeF2 8.(a) Draw the structures of the following : (i) XeF4 (ii) H2S2O7 (b) Account for the following : (i) Iron on reaction with HCl forms FeCl2 and not FeCl3. (ii) HClO4 is a stronger acid than HClO. (iii) BiH3 is the ...
... (b) Draw the structures of the following : (i) H4P2O7 (Pyrophosphoric acid) (ii) XeF2 8.(a) Draw the structures of the following : (i) XeF4 (ii) H2S2O7 (b) Account for the following : (i) Iron on reaction with HCl forms FeCl2 and not FeCl3. (ii) HClO4 is a stronger acid than HClO. (iii) BiH3 is the ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... traditional unit, the debye (D, 1 D = 3.34 x 10–30 C·m), is often used. Depending on the spatial arrangement of the bonds, a molecule containing highly polar bonds can be nonpolar … the vector addition of the dipole moments yields a net dipole moment of zero for the overall molecule. Bond order is t ...
... traditional unit, the debye (D, 1 D = 3.34 x 10–30 C·m), is often used. Depending on the spatial arrangement of the bonds, a molecule containing highly polar bonds can be nonpolar … the vector addition of the dipole moments yields a net dipole moment of zero for the overall molecule. Bond order is t ...
What is a property?
... Volume Units are grams/ml or grams/cm3 where mass is measured in grams and volume is measured in ml or cm3 ...
... Volume Units are grams/ml or grams/cm3 where mass is measured in grams and volume is measured in ml or cm3 ...
PowerPoint for Part 1 - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... • As you might expect, as you increase the number of C atoms in the alkane, there is more to burn, and more heat is given off. ...
... • As you might expect, as you increase the number of C atoms in the alkane, there is more to burn, and more heat is given off. ...
HighFour Chemistry Round 1 Category C: Grades 9 – 10 Thursday
... Bromine (Br) has an atomic number of 35, its electric configuration is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5. The outermost shell, n = 4, has 7 electrons. Therefore, the number of valence electrons of bromine (Br) is 7. ...
... Bromine (Br) has an atomic number of 35, its electric configuration is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5. The outermost shell, n = 4, has 7 electrons. Therefore, the number of valence electrons of bromine (Br) is 7. ...
Chapter 2 - Cloudfront.net
... Use the general characteristics of each to distinguish a mixture from a substance. This is the harder way to go. Fixed composition = Substance Varied composition = Mixture We can physically separate mixtures into their component parts. We cannot do so with ...
... Use the general characteristics of each to distinguish a mixture from a substance. This is the harder way to go. Fixed composition = Substance Varied composition = Mixture We can physically separate mixtures into their component parts. We cannot do so with ...
king fahd university of petroleum and minerals chemistry
... 17. An electrochemical cell consists of a nickel metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ni2+] = 1.0 M connected through a salt bridge to an aluminum electrode immersed in a solution with [Al3+] = 1.0 M. An amount of sodium hydroxide is added to the aluminum solution half-cell, causing Al(OH)3 ...
... 17. An electrochemical cell consists of a nickel metal electrode immersed in a solution with [Ni2+] = 1.0 M connected through a salt bridge to an aluminum electrode immersed in a solution with [Al3+] = 1.0 M. An amount of sodium hydroxide is added to the aluminum solution half-cell, causing Al(OH)3 ...