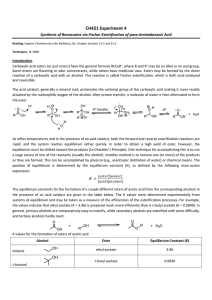
Open questions (66 points total
... 2p 17 How does the value of equilibrium constant Kp change with temperature? The industrial production can take place without a catalyst at atmospheric pressure and high temperature. At equilibrium, usually 0.20 volume% methane gas remains. 7p 18 Calculate the value of Kp for this industrial pro ...
... 2p 17 How does the value of equilibrium constant Kp change with temperature? The industrial production can take place without a catalyst at atmospheric pressure and high temperature. At equilibrium, usually 0.20 volume% methane gas remains. 7p 18 Calculate the value of Kp for this industrial pro ...
Rate and Equilibrium
... Distribution of gas and the effect of temperature: All gases are in random motion. This is caused by the collision of gaseous particles in air. The collisions are occurs randomly. Collisions may result in a loss or gain of kinetic energy and an uneven distribution of speed amount gaseous particles. ...
... Distribution of gas and the effect of temperature: All gases are in random motion. This is caused by the collision of gaseous particles in air. The collisions are occurs randomly. Collisions may result in a loss or gain of kinetic energy and an uneven distribution of speed amount gaseous particles. ...
ME 533 Lecture 7 Pla..
... • typical value of vibrational quantum (about 0.1-0.2eV) occurs in a very interesting energy interval. • From one hand this energy is relatively low WRT typical electron energies in electric discharges (1-3 eV) and for this reason vibrational excitation by electron impact is very effective. • From ...
... • typical value of vibrational quantum (about 0.1-0.2eV) occurs in a very interesting energy interval. • From one hand this energy is relatively low WRT typical electron energies in electric discharges (1-3 eV) and for this reason vibrational excitation by electron impact is very effective. • From ...
chm 103 general chemistry
... 2. Carboxylic Acids: Organics containing –COOH (carboxyl) groups a. Carboxyl structure ...
... 2. Carboxylic Acids: Organics containing –COOH (carboxyl) groups a. Carboxyl structure ...
슬라이드 1
... In solution, lithium dimethylcuprate exists as a dimer, [LiCu(CH3)2]2. Four methyl groups are attached to a tetrahedral cluster of lithium and copper atoms. However, in the presence of LiI, the compound seems to be a monomer of compostition (CH3)2CuLi. ...
... In solution, lithium dimethylcuprate exists as a dimer, [LiCu(CH3)2]2. Four methyl groups are attached to a tetrahedral cluster of lithium and copper atoms. However, in the presence of LiI, the compound seems to be a monomer of compostition (CH3)2CuLi. ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry and
... Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals from p Atomic Orbitals Figure 10.24 - shows interaction to form • σ bonds when atomic orbitals approach end to end • π bonds when atomic orbitals approach side to side ...
... Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals from p Atomic Orbitals Figure 10.24 - shows interaction to form • σ bonds when atomic orbitals approach end to end • π bonds when atomic orbitals approach side to side ...
practice unit #2 exam
... A. increases as temperature decreases. B. decreases when a catalyst is added. C. increases as reactant concentration increases. D. decreases as reactant concentration increases. ...
... A. increases as temperature decreases. B. decreases when a catalyst is added. C. increases as reactant concentration increases. D. decreases as reactant concentration increases. ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts Answer Key
... a) Quantitative analysis determines that a compound has an empirical formula of CH and a molecular mass of 26 grams/mole. Determine the molecular formula of this compound, showing all work: (Molecular Mass / Empirical Mass) X Empirical Formula = (26 g / 13.0 g) = 2 X CH = C2H2 ...
... a) Quantitative analysis determines that a compound has an empirical formula of CH and a molecular mass of 26 grams/mole. Determine the molecular formula of this compound, showing all work: (Molecular Mass / Empirical Mass) X Empirical Formula = (26 g / 13.0 g) = 2 X CH = C2H2 ...
Benzocaine Synthesis via Esterification
... a large excess of one of the reactants (usually the alcohol). Another method is to remove one (or more) of the products as they are formed. This can be accomplished by physical (e.g., azeotropic distillation of water) or chemical means. The position of equilibrium is determined by the equilibrium co ...
... a large excess of one of the reactants (usually the alcohol). Another method is to remove one (or more) of the products as they are formed. This can be accomplished by physical (e.g., azeotropic distillation of water) or chemical means. The position of equilibrium is determined by the equilibrium co ...
South Pasadena • Chemistry Name Period Date 5 · Chemical
... Find the volume of O2 (g) produced at STP when 42.0 grams of KClO3 (s) decomposes. GIVEN: ...
... Find the volume of O2 (g) produced at STP when 42.0 grams of KClO3 (s) decomposes. GIVEN: ...
Organic Reactions
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
New Title
... 6. What do you read the arrow in a chemical equation as meaning? 7. Label each formula in the chemical equation below as either a reactant or a product. ...
... 6. What do you read the arrow in a chemical equation as meaning? 7. Label each formula in the chemical equation below as either a reactant or a product. ...
Dissociation energy of the C-H bond in chloroform Cl3C
... Start the JASCO V-670 uv-vis-nir instrument and its software, if they are not already running. Set the NIR bandwidth to 8.0 nm. Set scanning speed to 100 nm/min and response to slow. Install the long-path cell holder, if it is not already in the instrument. ◦ To switch cell holders, first turn of th ...
... Start the JASCO V-670 uv-vis-nir instrument and its software, if they are not already running. Set the NIR bandwidth to 8.0 nm. Set scanning speed to 100 nm/min and response to slow. Install the long-path cell holder, if it is not already in the instrument. ◦ To switch cell holders, first turn of th ...
chemical reaction
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... A formula equation is an equation in which the reactants and products are represented by symbols and formulas. It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equ ...
... A formula equation is an equation in which the reactants and products are represented by symbols and formulas. It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equ ...
Solved Guess Paper – 3 Q1. Define the term molarity . Ans
... India’s Leadings smart learning campus for 10th 11th 12th , IIT ,AIEEE, AIPMT ( All Engineering and Medical Entrance courses ) ...
... India’s Leadings smart learning campus for 10th 11th 12th , IIT ,AIEEE, AIPMT ( All Engineering and Medical Entrance courses ) ...
Study Guide
... 49. In the compound CH3Cl the bond between carbon and chlorine is A) intermolecular B) ionic C) nonpolar covalent D) polar covalent 50. Which one of the following is NOT true about elements that form cations? A) The atoms lose electrons in forming ions. B) The elements are metals. C) They are locate ...
... 49. In the compound CH3Cl the bond between carbon and chlorine is A) intermolecular B) ionic C) nonpolar covalent D) polar covalent 50. Which one of the following is NOT true about elements that form cations? A) The atoms lose electrons in forming ions. B) The elements are metals. C) They are locate ...