* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Depletion force wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
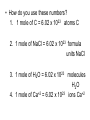
Chapter 7 Chemical Quantities The Mole (Friend or foe) What is a mole? 1. SI base unit to measure the amount of a substance 2. The amount of a substance that contains the same number of particles as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon-12 What is Avogadro’s number? 1. the number of particles in a mole 2. 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles 3. particles are: atoms, ions, molecules, formula units • How do you use these numbers? 1. 1 mole of C = 6.02 x 1023 atoms C 2. 1 mole of NaCl = 6.02 x 1023 formula units NaCl 3. 1 mole of H2O = 6.02 x 1023 molecules H 2O 4. 1 mole of Ca+2 = 6.02 x 1023 ions Ca+2 • What is molar mass? 1. the mass in grams of one mole of a pure substance (element or compound) 2. use the periodic table to find the mass 3. What is the molar mass of helium? 4.0 g He mole 4. will be used as a conversion factor 5. Examples: a. What is the molar mass of 1 mole of Al? 27.0 g Al mole b. What is the molar mass of 1 mole of CO2? C = (1)(12.0) = 12.0 O = (2)(16.0) = 32.0 44.0 g/mole Converting from moles to grams 1. What is the grams of 3.50 mole of Cu? 2. There are 11.9 g of Al, how many moles of Al are there? 3. How many moles are in 25.0 grams of H3PO4? • Converting moles to molecules 1. How many molecules are in 5.2 moles of NaCl? 2. How many moles are in 3.12 x 1015 Mg+2 ions? • Convert grams to molecules. 1. How many molecules are in 3.14 grams of NaOH? 2. How many grams are in 4.12 x 1012 molecules of Rh? 3. How many molecules are in 523 g of KI? Percent Composition 1. Definition – the percent by mass of each element in the compound 2. Formula: % composition = mass of element 100 mass of compound 3. Ex. Find the percent composition of copper (I) sulfide. Cu2S Cu = 2(63.5) = 127.0 S = 1(32.1) = 32.1 159.1g/mole %Cu = 127.0 100 = 79.8% 159.1 %S = Empirical Formula 1.Shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms in a compound 2. Examples: a.) C2H8 = b.) Al2O3 = 3. Examples: Analysis shows a compound to contain 26.56% K, 35.41% Cr, 38.03% O. Find the empirical formula. Molecular Formula 1. Indicates the ratio of the atoms 2. Indicates the actual number of atoms 3. n = Molecular mass empirical mass 4. (empirical formula)n = molecular formula 5. Examples: An organic compound is found to contains 92.25% C and 7.75% H. If the molecular mass is 78, what is the molecular formula?