Matter - Clayton State University
... - Strength of forces holding the structural particles together ...
... - Strength of forces holding the structural particles together ...
Limiting reactant - Dr. Gregory Chemistry
... Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants used and amounts of products formed in a chemical reaction. It is based on the law of conservation of mass. ...
... Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants used and amounts of products formed in a chemical reaction. It is based on the law of conservation of mass. ...
Ex: -F, -Cl, -Br
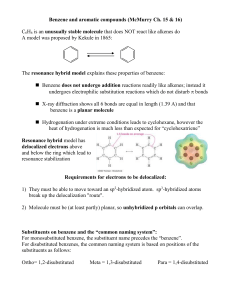
... The resonance hybrid model explains these properties of benzene: Benzene does not undergo addition reactions readily like alkenes; instead it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions which do not disturb bonds X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benz ...
... The resonance hybrid model explains these properties of benzene: Benzene does not undergo addition reactions readily like alkenes; instead it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions which do not disturb bonds X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benz ...
Unit 3
... • Reversible reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium • The rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal. • At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, although not necessarily equal. ...
... • Reversible reactions reach a state of dynamic equilibrium • The rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal. • At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, although not necessarily equal. ...
Order and Half-life Equations
... The order (and thus the rate law) is determined by linear regression analysis of three graphs. The graph with the best straight line (r2 closest to 1) determines the order. Note that the absolute value of the slope is the value of the rate constant. The graphs (y vs x): - Zeroeth Order: [A] vs. t ha ...
... The order (and thus the rate law) is determined by linear regression analysis of three graphs. The graph with the best straight line (r2 closest to 1) determines the order. Note that the absolute value of the slope is the value of the rate constant. The graphs (y vs x): - Zeroeth Order: [A] vs. t ha ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Directions (51–57): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 On a field trip, Student X and Student Y collected two rock samples. Analysis revealed that both rocks contained lead a ...
... Directions (51–57): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 On a field trip, Student X and Student Y collected two rock samples. Analysis revealed that both rocks contained lead a ...
Haloalkanes
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
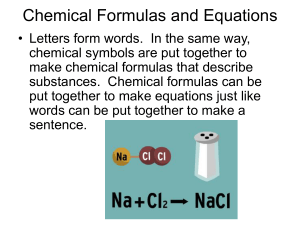
Chapter 9 Balancing Equations
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... atoms as the right side for EACH element. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
1. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, boron–10 and
... 62. Hydrogen gas is collected over water at 29oC. The total pressure of the system is 773 torr. If the vapor pressure of water at 29oC is 30 torr, what is the partial pressure 67. Under which conditions does a real gas most closely of the hydrogen gas? approximate an ideal gas? A) 803 torr C) 743 to ...
... 62. Hydrogen gas is collected over water at 29oC. The total pressure of the system is 773 torr. If the vapor pressure of water at 29oC is 30 torr, what is the partial pressure 67. Under which conditions does a real gas most closely of the hydrogen gas? approximate an ideal gas? A) 803 torr C) 743 to ...
notes - ap unit 1 matter_meas_blank
... 2. Leading zeros are those that precede all of the non-zero digits and are never counted as significant figures. 3. Captive zeros are those that fall between non-zero digits and are always counted as significant figures. 4. Trailing zeros are those at the end of a number and are only significant if ...
... 2. Leading zeros are those that precede all of the non-zero digits and are never counted as significant figures. 3. Captive zeros are those that fall between non-zero digits and are always counted as significant figures. 4. Trailing zeros are those at the end of a number and are only significant if ...
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... C) Most important kind of bond in chemistry. 3) Metallic Bonding a) Occurs in metals. b) Electron Sea Model: we will not focus on this at all. II) Nature & Strength of Covalent Bonds 1) Associated terminology A) Bond Energy - energy required to break a bond (also called bond dissociation energy). B) ...
... C) Most important kind of bond in chemistry. 3) Metallic Bonding a) Occurs in metals. b) Electron Sea Model: we will not focus on this at all. II) Nature & Strength of Covalent Bonds 1) Associated terminology A) Bond Energy - energy required to break a bond (also called bond dissociation energy). B) ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 3. What 2 temperatures measure the same amount during a phase change of a liquid pure solvent to a solid? 4. Know how to read phase diagrams. Sketch a quick diagram locating the triple point, critical point, the melting point /freezing point line and the boiling point/condensation point line. Also l ...
... 3. What 2 temperatures measure the same amount during a phase change of a liquid pure solvent to a solid? 4. Know how to read phase diagrams. Sketch a quick diagram locating the triple point, critical point, the melting point /freezing point line and the boiling point/condensation point line. Also l ...
Slide 1 of 24
... Propane gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor and carbon dioxide. Choose the correct word equation for this reaction. A. propane + carbon dioxide → water + oxygen B. propane + oxygen + water → carbon dioxide C. propane + oxygen + water + carbon dioxide D. propane + oxygen → water + carbon ...
... Propane gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor and carbon dioxide. Choose the correct word equation for this reaction. A. propane + carbon dioxide → water + oxygen B. propane + oxygen + water → carbon dioxide C. propane + oxygen + water + carbon dioxide D. propane + oxygen → water + carbon ...
Grignard Reactions - faculty at Chemeketa
... In the Grignard reagent, the bonding electrons between carbon and magnesium are shifted away from the electropositive Mg to form a strongly polar covalent bond. As a result the charge distribution in the Grignard reagent is such that the organic group (R) is partially negative and the –MgX group is ...
... In the Grignard reagent, the bonding electrons between carbon and magnesium are shifted away from the electropositive Mg to form a strongly polar covalent bond. As a result the charge distribution in the Grignard reagent is such that the organic group (R) is partially negative and the –MgX group is ...
Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring `00 What product is formed when
... e) addtion of a hydride ion and a proton more or less at the same time 18. Which of the following describes “reductive amination?” a) an aldehyde or a ketone + a tertiary amine + H2/zeolite b) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + ...
... e) addtion of a hydride ion and a proton more or less at the same time 18. Which of the following describes “reductive amination?” a) an aldehyde or a ketone + a tertiary amine + H2/zeolite b) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + ...
5073 Chemistry IGCSE ordinary level for 2016
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...