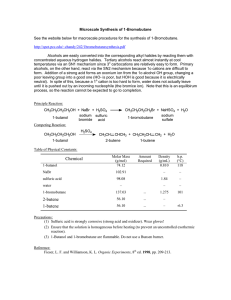
纳米结构体系物理化学性质的理论研究方法与实例
... • In the IUPAC system ketone names are derived from the names of alkanes which have the same number of C atoms(including the carbonyl C atom) by dropping the –e from alkane and adding –one to form the name alkanone. • The name of the ketone having three C atoms is derived from propane and is propano ...
... • In the IUPAC system ketone names are derived from the names of alkanes which have the same number of C atoms(including the carbonyl C atom) by dropping the –e from alkane and adding –one to form the name alkanone. • The name of the ketone having three C atoms is derived from propane and is propano ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... − (4) the reason why the melting and boiling points of quartz is so high – (a) melting point 1700oC – (b) boiling point 2230oC ...
... − (4) the reason why the melting and boiling points of quartz is so high – (a) melting point 1700oC – (b) boiling point 2230oC ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number 原子序 is the number of protons in its nucleus (ex. 2He) • An element’s mass number 質量數 is the sum of protons + neutrons in the nucleus ...
... Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number 原子序 is the number of protons in its nucleus (ex. 2He) • An element’s mass number 質量數 is the sum of protons + neutrons in the nucleus ...
The Chemical Earth
... The name of the element closer to the bottom or left-hand side of the periodic table is written first. The the suffix ‘-ide’ is added to the end of the name of the second element. The number of atoms of each element is indicated by the prefixes ‘mono-’, ‘di-’, ‘tri-’, ‘tetra-’, ‘penta-’ or hexa-’, w ...
... The name of the element closer to the bottom or left-hand side of the periodic table is written first. The the suffix ‘-ide’ is added to the end of the name of the second element. The number of atoms of each element is indicated by the prefixes ‘mono-’, ‘di-’, ‘tri-’, ‘tetra-’, ‘penta-’ or hexa-’, w ...
5073 Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
SCH 3U - Norbraten
... in the condensed phases. Since energy is directly proportional to the temperature, the above trends ought to hold true. In addition, there are energies associated with making these phase transitions: Each of these processes are considered to be endothermic, and scale with the magnitude of the interm ...
... in the condensed phases. Since energy is directly proportional to the temperature, the above trends ought to hold true. In addition, there are energies associated with making these phase transitions: Each of these processes are considered to be endothermic, and scale with the magnitude of the interm ...
Functional Groups and nomenclature Major concepts Stable
... LA; the dipole arrow points to oxygen because it’s more electronegative d. The nitrogen atom of an amine LB; nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon e. The carbon attached to chlorine of an alkyl halide LA; chlorine is more electronegative, so the dipole points away from carbon 6. Application t ...
... LA; the dipole arrow points to oxygen because it’s more electronegative d. The nitrogen atom of an amine LB; nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon e. The carbon attached to chlorine of an alkyl halide LA; chlorine is more electronegative, so the dipole points away from carbon 6. Application t ...
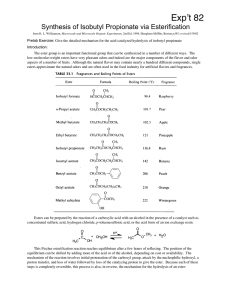
Synthesis of 1
... temperatures via an SN1 mechanism since 3o carbocations are relatively easy to form. Primary alcohols, on the other hand, react via the SN2 mechanism because 1o cations are difficult to form. Addition of a strong acid forms an oxonium ion from the 1o alcohol OH group, changing a poor leaving group i ...
... temperatures via an SN1 mechanism since 3o carbocations are relatively easy to form. Primary alcohols, on the other hand, react via the SN2 mechanism because 1o cations are difficult to form. Addition of a strong acid forms an oxonium ion from the 1o alcohol OH group, changing a poor leaving group i ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Equilibrium
... 10. Consider the following system, which is at equilibrium, CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g). The result of removing some CH4(g) and H2O(g) from the system is that * a. more CH4(g) and H2O(g) are produced to replace that which is removed b. Kc decreases c. more CO(g) is produced d. more H2O(g) is cons ...
... 10. Consider the following system, which is at equilibrium, CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g). The result of removing some CH4(g) and H2O(g) from the system is that * a. more CH4(g) and H2O(g) are produced to replace that which is removed b. Kc decreases c. more CO(g) is produced d. more H2O(g) is cons ...
Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data
... The direct conversion of graphite to diamond is not easily carried out (or we would all be doing it) and hence it is also not easy to measure the enthalpy change associated with this phase change. It is, however, fairly straight forward to burn (combust) either graphite or diamond (there may be some ...
... The direct conversion of graphite to diamond is not easily carried out (or we would all be doing it) and hence it is also not easy to measure the enthalpy change associated with this phase change. It is, however, fairly straight forward to burn (combust) either graphite or diamond (there may be some ...
Separation of a Mixture
... A physical change is a change in a materials size, shape, or state of matter, but it is still the same material. It changes its physical appearance but not its composition. A mixture is a combination of different pure substances that still retains its own chemical identity and its own properties ...
... A physical change is a change in a materials size, shape, or state of matter, but it is still the same material. It changes its physical appearance but not its composition. A mixture is a combination of different pure substances that still retains its own chemical identity and its own properties ...
APEF – Equilibrium and Reaction Rate Multiple Choice Answers
... 33. Analysis of a sample of HCl gas showed that when equilibrium was reached at a certain temperature, one half of the HCl molecules had dissociated into H2 and Cl2 molecules: 2HCl(g) ' H2(g) + Cl2(g) What is numerical value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature? A. 0.25 B. 0.50 C. 1.0 D. ...
... 33. Analysis of a sample of HCl gas showed that when equilibrium was reached at a certain temperature, one half of the HCl molecules had dissociated into H2 and Cl2 molecules: 2HCl(g) ' H2(g) + Cl2(g) What is numerical value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature? A. 0.25 B. 0.50 C. 1.0 D. ...
Lab Grade 250 pts - Western Illinois University
... Homework: Homework assignments will be provided on Western Online, and will not be distributed in class. Due dates are posted on the top of all homework assignments. Five homework problem sets (20 pts each) will be given throughout the semester and are due at the beginning of class on their due date ...
... Homework: Homework assignments will be provided on Western Online, and will not be distributed in class. Due dates are posted on the top of all homework assignments. Five homework problem sets (20 pts each) will be given throughout the semester and are due at the beginning of class on their due date ...
Chapter 8
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
... • The four regions of high electron density surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen ...
Stoichiometry intro
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
Functional Groups
... Functional Groups functional group: an atom, or group of atoms (with specific connectivity), exhibiting identical chemical reactivity regardless of the molecule containing it; the reactivity of individual functional groups dictates the reactivity of the molecule of which they are a part ...
... Functional Groups functional group: an atom, or group of atoms (with specific connectivity), exhibiting identical chemical reactivity regardless of the molecule containing it; the reactivity of individual functional groups dictates the reactivity of the molecule of which they are a part ...
C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... An electron in which of these orbitals would have the highest energy in a multi-electron atom? a. 4s b. 4p c. 4d d. 4f e. all of these orbitals have the same energy in a multielectron atom 33. If the empirical formula for a compound is HO, which molecular formula is not possible based on this inform ...
... An electron in which of these orbitals would have the highest energy in a multi-electron atom? a. 4s b. 4p c. 4d d. 4f e. all of these orbitals have the same energy in a multielectron atom 33. If the empirical formula for a compound is HO, which molecular formula is not possible based on this inform ...
Catalyst Notes - University of Idaho
... where these energy barriers are small. A poor catalyst may be such a strong absorber for a species that the species is rendered immobile. This strongly adsorbed species may not desorb, thus ‘poisoning’ the catalyst by blocking the site from mobile species. Sulfur and lead are common catalyst poisons ...
... where these energy barriers are small. A poor catalyst may be such a strong absorber for a species that the species is rendered immobile. This strongly adsorbed species may not desorb, thus ‘poisoning’ the catalyst by blocking the site from mobile species. Sulfur and lead are common catalyst poisons ...
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... acetic acid are allowed to react, at equilibrium the theoretical yield of ester is only 67%. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When ...
... acetic acid are allowed to react, at equilibrium the theoretical yield of ester is only 67%. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When ...
Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions
... and phosphorus. Atoms of these elements occur in organic substances as parts of functional groups. In an organic molecule, a functional group is an atom or group of atoms that always reacts in a certain way. The addition of a functional group to a hydrocarbon structure always produces a substance wi ...
... and phosphorus. Atoms of these elements occur in organic substances as parts of functional groups. In an organic molecule, a functional group is an atom or group of atoms that always reacts in a certain way. The addition of a functional group to a hydrocarbon structure always produces a substance wi ...
Atmospheric Chemistry: CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151
... (b) An experimentalist (let’s call him Matthew) wants to measure this rate coefficient. For a source of IO, he uses the laser photolysis of N2O to produce O atoms, followed by the reaction of O + CF3I. Given the rate coefficient for this reaction of kO+ CF3I = (7.9 ± 0.8) × 10-12 exp[-(175 ± 40)/T] ...
... (b) An experimentalist (let’s call him Matthew) wants to measure this rate coefficient. For a source of IO, he uses the laser photolysis of N2O to produce O atoms, followed by the reaction of O + CF3I. Given the rate coefficient for this reaction of kO+ CF3I = (7.9 ± 0.8) × 10-12 exp[-(175 ± 40)/T] ...
Thermochemistry only Sp 12 unit I
... ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction that are not conveniently measured directly Example 1: For the reaction: Fe2O3 (s) + 3 CO(g) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) , the value of ΔHrxn is -23.5 kj. The sta ...
... ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction that are not conveniently measured directly Example 1: For the reaction: Fe2O3 (s) + 3 CO(g) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) , the value of ΔHrxn is -23.5 kj. The sta ...