2(#pi bonds)
... electrons have a lower energy than they would have in isolated atomic orbitals. • Sigma (s) bonding molecular orbital: A MO in which electron density is concentrated between two nuclei along the axis joining them and is cylindrically symmetrical. ...
... electrons have a lower energy than they would have in isolated atomic orbitals. • Sigma (s) bonding molecular orbital: A MO in which electron density is concentrated between two nuclei along the axis joining them and is cylindrically symmetrical. ...
physical setting chemistry
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then blacken the corre ...
... Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then blacken the corre ...
BSc/MSci Course Unit Examination - QMplus
... (c) Use the crystal field approach to show how the d-orbital splitting patterns change on axial elongation of the ligands along the hypothetical z-axis in an octahedral complex. Include discussion of square planar complexes in your answer. [8 marks] (d) Account for the fact that trans-[NiCl2(en)2] h ...
... (c) Use the crystal field approach to show how the d-orbital splitting patterns change on axial elongation of the ligands along the hypothetical z-axis in an octahedral complex. Include discussion of square planar complexes in your answer. [8 marks] (d) Account for the fact that trans-[NiCl2(en)2] h ...
IR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectroscopy
... ¾ Carbon-nitrogen bonds are more polar than carbon-carbon bonds, thus give stronger absorption. ¾ C-N single bonds absorb around 1200 cm-1. • Close to C-C and C-O absorptions ...
... ¾ Carbon-nitrogen bonds are more polar than carbon-carbon bonds, thus give stronger absorption. ¾ C-N single bonds absorb around 1200 cm-1. • Close to C-C and C-O absorptions ...
what are acyl chlorides?
... Acyl chlorides can't be said to dissolve in water because they react (often violently) with it. The strong reaction means that it is impossible to get a simple aqueous solution of an acyl chloride. ...
... Acyl chlorides can't be said to dissolve in water because they react (often violently) with it. The strong reaction means that it is impossible to get a simple aqueous solution of an acyl chloride. ...
formic (methanoic) acid
... Produced by the action of Lactobacillus bacteria on the milk sugar lactose. Lactic acid is formed in the body as an intermediate product in carbohydrate metabolism and is produced by muscle metabolism. Blood-lactate levels rise after strenuous exercise and the stiff sore feelings of muscles as the r ...
... Produced by the action of Lactobacillus bacteria on the milk sugar lactose. Lactic acid is formed in the body as an intermediate product in carbohydrate metabolism and is produced by muscle metabolism. Blood-lactate levels rise after strenuous exercise and the stiff sore feelings of muscles as the r ...
The Complete Notes - Joliet Junior College
... the course. Thus, it is important that the student does not let any ‘gaps’ in their knowledge develop. This fact exemplifies the differences in philosophy between the sciences and arts, as art courses are often more modular in nature. Example: I overhead a student tell another: “Yeah, I blew off rea ...
... the course. Thus, it is important that the student does not let any ‘gaps’ in their knowledge develop. This fact exemplifies the differences in philosophy between the sciences and arts, as art courses are often more modular in nature. Example: I overhead a student tell another: “Yeah, I blew off rea ...
The Chemistry of Excited States
... M* → M + light However, some molecules are capable of relaxing back to their ground state by also emitting a photon. Luminescence, the emission of light from an excited-state molecule, is a most dramatic example of the fascinating colors of chemistry. The measurement of luminescence can be one of th ...
... M* → M + light However, some molecules are capable of relaxing back to their ground state by also emitting a photon. Luminescence, the emission of light from an excited-state molecule, is a most dramatic example of the fascinating colors of chemistry. The measurement of luminescence can be one of th ...
Lecture 2
... SALC can now be treated similarly to the atomic orbitals and combined with appropriate AO’s from H 1s(H) is Ag so it matches two SALC. The interaction can be bonding or antibonding. ...
... SALC can now be treated similarly to the atomic orbitals and combined with appropriate AO’s from H 1s(H) is Ag so it matches two SALC. The interaction can be bonding or antibonding. ...
Regiospecificity according to Markovnikov
... Alkyne Acidity: Formation of Acetylide Anions • Terminal alkynes are weak Brønsted acids (alkenes and alkanes are much less acidic (pKa ~ 25. See Table 8.1 for comparisons)) • Reaction of strong anhydrous bases with a terminal acetylene produces an acetylide ion • The sp-hydbridization at carbon ho ...
... Alkyne Acidity: Formation of Acetylide Anions • Terminal alkynes are weak Brønsted acids (alkenes and alkanes are much less acidic (pKa ~ 25. See Table 8.1 for comparisons)) • Reaction of strong anhydrous bases with a terminal acetylene produces an acetylide ion • The sp-hydbridization at carbon ho ...
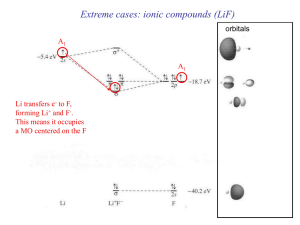
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY AND BONDING NOTES
... these molecular orbitals is part of the key to gaining an understand of bonding in molecules. The Nature of Molecular Orbitals “A molecular orbital is the wavefunction of an electron in a molecule moving under the influence of the nuclear attraction and the average repulsion of all other electrons.” ...
... these molecular orbitals is part of the key to gaining an understand of bonding in molecules. The Nature of Molecular Orbitals “A molecular orbital is the wavefunction of an electron in a molecule moving under the influence of the nuclear attraction and the average repulsion of all other electrons.” ...
Homework Booklet [4,S]
... How many of each of the fundamental particles are present in the nucleus of Ne-22? What is the electron configuration of Ne-20? Why is neon a very unreactive element? Explain the meaning of the word isotope. What is the difference between the two isotopes of Neon? Calculate the relative atomic mass ...
... How many of each of the fundamental particles are present in the nucleus of Ne-22? What is the electron configuration of Ne-20? Why is neon a very unreactive element? Explain the meaning of the word isotope. What is the difference between the two isotopes of Neon? Calculate the relative atomic mass ...
Retrosynthesis - Organic Chemistry
... Do NOT start studying by trying to memorize the reactions here! Work as many problems as you can, with this list of reactions in front of you if necessary, so that you can get through as many problems as you can without getting stuck on eth reagents/conditions, and so that you can learn and practice ...
... Do NOT start studying by trying to memorize the reactions here! Work as many problems as you can, with this list of reactions in front of you if necessary, so that you can get through as many problems as you can without getting stuck on eth reagents/conditions, and so that you can learn and practice ...
Exam Review_Key_All Topics.082
... 1. Provide an example for each of the following solution types a) ...
... 1. Provide an example for each of the following solution types a) ...
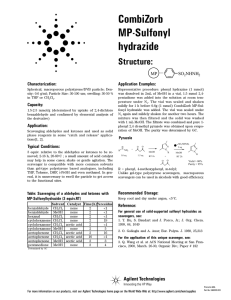
CombiZorb MP-Sulfonyl hydrazide
... with 1 mL MeOH. The filtrate was combined and pure 1phenyl 2,4 di-methyl pyrazole was obtained upon evaporation of MeOH. The purity was determined by GC. ...
... with 1 mL MeOH. The filtrate was combined and pure 1phenyl 2,4 di-methyl pyrazole was obtained upon evaporation of MeOH. The purity was determined by GC. ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides - City University of New York
... But how does a nitrile group behave? What could be happening? We are breaking the CN bond; bond order goes from 3 to 0. Probably stepwise. Chemically speaking: the nitrogen of the nitrile is basic (lone pair) and can be protonated. This makes it a better electrophile (cf. carbonyl). Multiple bond ca ...
... But how does a nitrile group behave? What could be happening? We are breaking the CN bond; bond order goes from 3 to 0. Probably stepwise. Chemically speaking: the nitrogen of the nitrile is basic (lone pair) and can be protonated. This makes it a better electrophile (cf. carbonyl). Multiple bond ca ...
lect 7
... • When the pH is initially low, H+ consumption in the reduction reactions increases the pH. For example: MnO2 (s) + 4 H+ + 2e- = Mn2+ + 2H2O • If the pH is initially basic, then the liberation and reprecipitation of metal ions such as Fe and Mn as hydroxides, carbonates, or sulfides tends to lower t ...
... • When the pH is initially low, H+ consumption in the reduction reactions increases the pH. For example: MnO2 (s) + 4 H+ + 2e- = Mn2+ + 2H2O • If the pH is initially basic, then the liberation and reprecipitation of metal ions such as Fe and Mn as hydroxides, carbonates, or sulfides tends to lower t ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... 11. A cylinder of unknown volume contains neon gas, Ne(g), at 4.0 atm and 400 K. The neon gas is then transferred to a 10.0 L gas cylinder containing Ar(g), at 6.0 atm and 400 K. If the final total pressure at 400 K is 9.0 atm, then what is the volume of the cylinder that initially contained the neo ...
... 11. A cylinder of unknown volume contains neon gas, Ne(g), at 4.0 atm and 400 K. The neon gas is then transferred to a 10.0 L gas cylinder containing Ar(g), at 6.0 atm and 400 K. If the final total pressure at 400 K is 9.0 atm, then what is the volume of the cylinder that initially contained the neo ...
CHAPTER II. A Facile Synthesis of Arylacetic Acid Derivatives via
... determined against standard strain H37Rv and with 2 human strains of mycobacterium tuberculosis. The in vitro anti tubercular activity of the compounds were evaluated on Lowenstein-Jensen medium. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the compounds were also determined by agar ...
... determined against standard strain H37Rv and with 2 human strains of mycobacterium tuberculosis. The in vitro anti tubercular activity of the compounds were evaluated on Lowenstein-Jensen medium. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the compounds were also determined by agar ...
9. The Copigmentation Interactions between Strawberry
... temperature at heating and at cooling. Obtained results confirmed that the interaction between pigment:copigment complex was destroyed at heating to 50 oC”and with following cooling to 20oC was not seen reversibility of the copigmentation process. Practical applications The copigmentation process co ...
... temperature at heating and at cooling. Obtained results confirmed that the interaction between pigment:copigment complex was destroyed at heating to 50 oC”and with following cooling to 20oC was not seen reversibility of the copigmentation process. Practical applications The copigmentation process co ...
Spotlight 106 Oxalic Acid: A Very Useful Brønsted Acid in Organic Synthesis SYNLETT
... stereoelectronic effects in the area of amide chemistry. ...
... stereoelectronic effects in the area of amide chemistry. ...











![Homework Booklet [4,S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010355871_1-63c750e3d1b58eaaebbb3f5d45651c44-300x300.png)