ALDEHYDES , KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
... • The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers due to dipole dipoe interaction and lower than those of alcohols due to absence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. • The lower members of aldehydes and ketones are miscible with water due to hydrogen bonding. 1. C ...
... • The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers due to dipole dipoe interaction and lower than those of alcohols due to absence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. • The lower members of aldehydes and ketones are miscible with water due to hydrogen bonding. 1. C ...
1. Bromine exists naturally as a mixture of bromine
... When 125.0 g of ethylene (C2H4) burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide and water, how many grams of CO2 are formed? ...
... When 125.0 g of ethylene (C2H4) burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide and water, how many grams of CO2 are formed? ...
WEEK
... Students will be able to use the Periodic Table to investigate properties of atoms and the formation of ions Students will be able to identify nuclear reactions as nuclear decay, nuclear fission, or nuclear fusion. Students will be able to describe the relative amounts of energy produced in nuclear ...
... Students will be able to use the Periodic Table to investigate properties of atoms and the formation of ions Students will be able to identify nuclear reactions as nuclear decay, nuclear fission, or nuclear fusion. Students will be able to describe the relative amounts of energy produced in nuclear ...
Before RNA and After: Geophysical and Geochemical
... (Sect. 2.3). Atomic nitrogen reacting with small amounts of methane in the upper atmosphere was also proposed by Zahnle (1986) as a potential source for hydrogen cyanide. Subsequent to Löb’s (1906) work, several authors have continued to investigate the formation of aldehydes from CO2, crucial for a ...
... (Sect. 2.3). Atomic nitrogen reacting with small amounts of methane in the upper atmosphere was also proposed by Zahnle (1986) as a potential source for hydrogen cyanide. Subsequent to Löb’s (1906) work, several authors have continued to investigate the formation of aldehydes from CO2, crucial for a ...
Document
... 1. Write the reaction. NixCyOy -> X Ni + Y CO 2. Use conservation of mass to find the mass of CO. 97.4 mg (mass tot) – 33.5 mg (mass Ni) = 63.9 g (mass CO) 3. Find the number of moles of CO and of Ni. CO : 63.9 mg / (12.0+16.0 g/mol) = 2.28 mmol Ni : 33.5 mg / 58.7 g / mol) = 0.57 mmol 4. Find the r ...
... 1. Write the reaction. NixCyOy -> X Ni + Y CO 2. Use conservation of mass to find the mass of CO. 97.4 mg (mass tot) – 33.5 mg (mass Ni) = 63.9 g (mass CO) 3. Find the number of moles of CO and of Ni. CO : 63.9 mg / (12.0+16.0 g/mol) = 2.28 mmol Ni : 33.5 mg / 58.7 g / mol) = 0.57 mmol 4. Find the r ...
CH 2
... 1. Name the longest continuous chain of carbons as the main chain 2. Number the carbon atoms in the main chain starting on the end nearest a substituent -Where there are 2 or more substituents, the main chain should be numbered to give the lowest ...
... 1. Name the longest continuous chain of carbons as the main chain 2. Number the carbon atoms in the main chain starting on the end nearest a substituent -Where there are 2 or more substituents, the main chain should be numbered to give the lowest ...
An Introduction to Redox
... The students will develop an understanding of the structure of atoms, compounds, chemical reactions, and the interactions of energy and matter. Benchmark 3: The student will gain a basic concept of chemical reactions. The student … 1. understands a chemical reaction occurs when one or more subs ...
... The students will develop an understanding of the structure of atoms, compounds, chemical reactions, and the interactions of energy and matter. Benchmark 3: The student will gain a basic concept of chemical reactions. The student … 1. understands a chemical reaction occurs when one or more subs ...
Chapter 19.1 Balancing Redox Equations
... If we perform a reaction at a higher temperature compared the same reaction at a lower temperature, which sentence best describes what happens to the rate of reaction? a) The reaction at the higher temperature will always have a slower rate. b) The reaction at the higher temperature will always have ...
... If we perform a reaction at a higher temperature compared the same reaction at a lower temperature, which sentence best describes what happens to the rate of reaction? a) The reaction at the higher temperature will always have a slower rate. b) The reaction at the higher temperature will always have ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... their relatively small size and small number of valence orbitals. Lithium is the only element in Period 2 that forms a simple oxide and nitride. All beryllium compounds exhibit covalent bonding. Be2+ does not exist as a discrete ion due to its extremely high charge density. ...
... their relatively small size and small number of valence orbitals. Lithium is the only element in Period 2 that forms a simple oxide and nitride. All beryllium compounds exhibit covalent bonding. Be2+ does not exist as a discrete ion due to its extremely high charge density. ...
Ch 6 LAN 7th Intro Chem Chemical Reactions
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
... dioxide and water as indicated in the following reaction 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) When 26.0 g of acetylene is burned in sufficient oxygen for complete reaction, the theoretical yield of CO2 is 88.0 g Calculate the percent yield for this reaction if the actual yield is only 72.4 ...
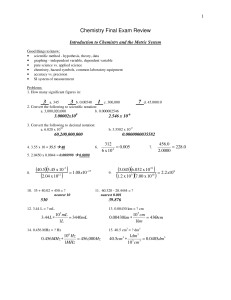
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... • basic characteristics and names of the major groups • metals, nonmetals, metalloids – “staircase” • ionization energy, electronegativity, atomic radius, trends shown in these properties on the periodic table Problems: 1. Give the number of valence electrons, physical state (metal, nonmetal, or met ...
... • basic characteristics and names of the major groups • metals, nonmetals, metalloids – “staircase” • ionization energy, electronegativity, atomic radius, trends shown in these properties on the periodic table Problems: 1. Give the number of valence electrons, physical state (metal, nonmetal, or met ...
Lab 1
... •Categorize an element as a metal , nonmetal or metalloid from its physical properties. •Given the complete symbol of an atom, determine its mass number, atomic number, and the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... •Categorize an element as a metal , nonmetal or metalloid from its physical properties. •Given the complete symbol of an atom, determine its mass number, atomic number, and the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
Empirical and Molecular Formulas and Percentage Composition
... In many ways, stoichiometry is the backbone of the most practical part of chemistry; it helps us relate actual quantities (measured by mass or volume) of reactants to products in a chemical reaction. It’s a lot like using a chocolate chip cookie recipe to produce a certain number of cookies of a giv ...
... In many ways, stoichiometry is the backbone of the most practical part of chemistry; it helps us relate actual quantities (measured by mass or volume) of reactants to products in a chemical reaction. It’s a lot like using a chocolate chip cookie recipe to produce a certain number of cookies of a giv ...
amine
... -derive from ammonia -one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by an organic group -pyramidal in structure -1° amine indicates 1 H replaced -2° amine indicates 2 H’s replaced -3° amine indicates 3 H’s replaced The N atom is more electronegative than the H so the N-H bond is polar ...
... -derive from ammonia -one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by an organic group -pyramidal in structure -1° amine indicates 1 H replaced -2° amine indicates 2 H’s replaced -3° amine indicates 3 H’s replaced The N atom is more electronegative than the H so the N-H bond is polar ...
Modeling the Rate of Heterogeneous Reactions
... surface diffusion, chemical transformations of adsorbed species, and desorption, and it is the basis for deriving the kinetics of the reaction. In the macroscopic regime, the rate of a catalytic reaction is modeled by fitting empirical equations, such as power laws, to experimental data to describe ...
... surface diffusion, chemical transformations of adsorbed species, and desorption, and it is the basis for deriving the kinetics of the reaction. In the macroscopic regime, the rate of a catalytic reaction is modeled by fitting empirical equations, such as power laws, to experimental data to describe ...