Experimental and Theoretical Charge Density Analysis of a
... charge density of the molecule was determined from both experimentally and theoretically derived diffraction data. The stereochemistry and electron density topology of the sulfonium group was analyzed. To understand the chemical reactivity of the molecule, the electrostatic potential difference betwee ...
... charge density of the molecule was determined from both experimentally and theoretically derived diffraction data. The stereochemistry and electron density topology of the sulfonium group was analyzed. To understand the chemical reactivity of the molecule, the electrostatic potential difference betwee ...
James Ruse with Solutions
... A soft drink may be decarbonated by heating. In observing the results, the equilibrium between gaseous and dissolved carbon dioxide can be examined. CO2 (g) ...
... A soft drink may be decarbonated by heating. In observing the results, the equilibrium between gaseous and dissolved carbon dioxide can be examined. CO2 (g) ...
Contact Angle Goniometry as a Tool for Surface Tension
... sets for four surfaces. For example, Figure 3A represents Young’s contact angle measurements on glass slides. Four liquids were used to obtain four values of γc: acetonitrile, propanol, dioxane, and acetic acid. The choice of probing liquids was dictated not only by their wetting behavior but also b ...
... sets for four surfaces. For example, Figure 3A represents Young’s contact angle measurements on glass slides. Four liquids were used to obtain four values of γc: acetonitrile, propanol, dioxane, and acetic acid. The choice of probing liquids was dictated not only by their wetting behavior but also b ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... hydrochloride with phosgene;16 however, the yield is only 36%, and hydrogen chloride must be introduced to increase the yield to 92%. The present procedure effects this reaction without additional hydrogen chloride and avoids the hazards of handling phosgene. This procedure has been successful in th ...
... hydrochloride with phosgene;16 however, the yield is only 36%, and hydrogen chloride must be introduced to increase the yield to 92%. The present procedure effects this reaction without additional hydrogen chloride and avoids the hazards of handling phosgene. This procedure has been successful in th ...
CH - YSU.edu
... 13. (5 pts) Explain using diagrams why cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane is thermodynamically more stable than trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. ...
... 13. (5 pts) Explain using diagrams why cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane is thermodynamically more stable than trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. ...
day_3_main_lecture - the Essentially Science Wiki!
... • Energy changes operate under the Law of Conservation of Energy. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. • For mass to remain constant during a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of each element must be the same before and after a chemical reaction. • Equations are bal ...
... • Energy changes operate under the Law of Conservation of Energy. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. • For mass to remain constant during a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of each element must be the same before and after a chemical reaction. • Equations are bal ...
Aromatic Chemistry - heckgrammar.co.uk
... a new position of equilibria in which the relative rates of the forward and backward reaction are once again in balance under the new set of conditions is eventually arrived at the position of equilibria is changed by: concentration (which can be easily understood using rates/collision theory) tempe ...
... a new position of equilibria in which the relative rates of the forward and backward reaction are once again in balance under the new set of conditions is eventually arrived at the position of equilibria is changed by: concentration (which can be easily understood using rates/collision theory) tempe ...
MECH 558 Combustion Class Notes - Page: notes06
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by ...
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... Explain how potential energy changes as distances between atoms change to form a covalent bond Be able to use electronegativity difference to classify the type of bond between two atoms. Understand that ionic bonding and covalent bonding are at two ends of a sliding scale of bond type Draw electron- ...
... Explain how potential energy changes as distances between atoms change to form a covalent bond Be able to use electronegativity difference to classify the type of bond between two atoms. Understand that ionic bonding and covalent bonding are at two ends of a sliding scale of bond type Draw electron- ...
Synthetic Strategy – Lecture 2 (DC, 19.1.05)
... The key idea with retrosynthetic analysis and the disconnection approach is – in an imaginary way – to sequentially break bonds (i.e. disconnect atoms) within a target structure, to reveal simpler structures. These imaginary backwards reactions are termed antithetical reactions. The resulting simple ...
... The key idea with retrosynthetic analysis and the disconnection approach is – in an imaginary way – to sequentially break bonds (i.e. disconnect atoms) within a target structure, to reveal simpler structures. These imaginary backwards reactions are termed antithetical reactions. The resulting simple ...
HL Option G Organic Chemistry
... G.10.1 DESCRIBE, USING EQUATIONS, THE NITRATION, CHLORINATION, ALKYLATION AND ACYLATION OF BENZENE. G.10.2 DESCRIBE AND EXPLAIN THE MECHANISMS FOR THE NITRATION, CHLORINATION, ALKYLATION AND ACYLATION OF BENZENE. ...
... G.10.1 DESCRIBE, USING EQUATIONS, THE NITRATION, CHLORINATION, ALKYLATION AND ACYLATION OF BENZENE. G.10.2 DESCRIBE AND EXPLAIN THE MECHANISMS FOR THE NITRATION, CHLORINATION, ALKYLATION AND ACYLATION OF BENZENE. ...
Catalysis by main-group metal - Université Paris-Sud
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
1C - Edexcel
... t Try to answer everyneatly t Check your answersquestion. if you have time at the end. t ...
... t Try to answer everyneatly t Check your answersquestion. if you have time at the end. t ...
Slide 1
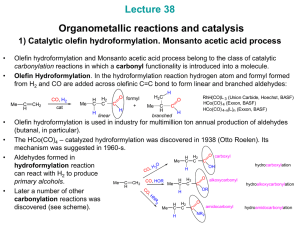
... Co – phosphine modified catalysts. Studies performed at Shell showed that addition of trialkylphosphine ligands changes dramatically the reaction rate and selectivity. When HCo(CO)3(PR3) forms, Co-CO bonds become much stronger and it becomes possible to decrease CO pressure without causing catalyst ...
... Co – phosphine modified catalysts. Studies performed at Shell showed that addition of trialkylphosphine ligands changes dramatically the reaction rate and selectivity. When HCo(CO)3(PR3) forms, Co-CO bonds become much stronger and it becomes possible to decrease CO pressure without causing catalyst ...
Towards a Theory of Organizations
... statements. It intends to give a means for describing organization in systems with a maximum of accuracy, independent of their constituting parts, be they molecules, symbols of communication, or departments of a company. These exact statements shall be applied to five examples of systems, stemming f ...
... statements. It intends to give a means for describing organization in systems with a maximum of accuracy, independent of their constituting parts, be they molecules, symbols of communication, or departments of a company. These exact statements shall be applied to five examples of systems, stemming f ...
EXAMPLE
... Ionic Bond bond formed between oppositely charged ions. This happens when the stronger atom steals 1+ electrons from the weaker atom. They both have their outer shells filled, so all is good. ...
... Ionic Bond bond formed between oppositely charged ions. This happens when the stronger atom steals 1+ electrons from the weaker atom. They both have their outer shells filled, so all is good. ...
File
... When the skeleton equation above is balanced and 27. The critical temperature of a substance is the all coefficients reduced to their lowest whole(A) temperature at which the vapor pressure of number terms, what is the coefficient for H+? the liquid is equal to the external pressure (A) 4 (C) 8 (E) ...
... When the skeleton equation above is balanced and 27. The critical temperature of a substance is the all coefficients reduced to their lowest whole(A) temperature at which the vapor pressure of number terms, what is the coefficient for H+? the liquid is equal to the external pressure (A) 4 (C) 8 (E) ...
9851a doc..9851a chapter .. Page97
... TPAP catalysed oxidations with NMO as co-oxidant Investigations were initially conducted in the ionic liquid [bmim][BF4]. This ionic liquid was chosen because it is stable to air and moisture, as well as being simple and inexpensive to prepare.20 Control reactions were performed to verify that the i ...
... TPAP catalysed oxidations with NMO as co-oxidant Investigations were initially conducted in the ionic liquid [bmim][BF4]. This ionic liquid was chosen because it is stable to air and moisture, as well as being simple and inexpensive to prepare.20 Control reactions were performed to verify that the i ...
Questionsheet 1
... The gas produced can be identified using limewater. Name the gas and the result of this test. Name of gas ............................................................................................................................................... Result of test ................................... ...
... The gas produced can be identified using limewater. Name the gas and the result of this test. Name of gas ............................................................................................................................................... Result of test ................................... ...