Inorganic and organic chemistry 2
... The substance that could carry out a reduction of vanadium must be on the right-hand side of the half-equations, so it cannot be iodine. Sulfur dioxide being oxidised to sulfate(VI) ions has a potential of −0.17 V. Adding this to each of the potentials for the vanadium half-equations gives +0.83 V ( ...
... The substance that could carry out a reduction of vanadium must be on the right-hand side of the half-equations, so it cannot be iodine. Sulfur dioxide being oxidised to sulfate(VI) ions has a potential of −0.17 V. Adding this to each of the potentials for the vanadium half-equations gives +0.83 V ( ...
Lecture 1 Atomic Structure
... to develop an equation. This equation is the foundation stone of the quantum mechanics. It offers a mathematical approach to understanding the wave nature of matter. The quantum mechanical treatment of an electron is highly mathematical as the Schrodinger equation is a very complex equation. Hydroge ...
... to develop an equation. This equation is the foundation stone of the quantum mechanics. It offers a mathematical approach to understanding the wave nature of matter. The quantum mechanical treatment of an electron is highly mathematical as the Schrodinger equation is a very complex equation. Hydroge ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Front Nucleation in a Bistable
... fronts reaches far enough into the unreactive part of the surface totrigger the formation of secondaryreaction fronts, hut intensity profiles of the PEEM images do not show such an effect. Theexplanation that appears to bemost likelycomesupasone follows the further development of the front behavior ...
... fronts reaches far enough into the unreactive part of the surface totrigger the formation of secondaryreaction fronts, hut intensity profiles of the PEEM images do not show such an effect. Theexplanation that appears to bemost likelycomesupasone follows the further development of the front behavior ...
Chemistry - Northeastern Illinois University
... The chemistry of complex molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates is studied from the point of view of their physical properties and their reaction, synthesis and structure-function relationships. Lecture 3 hours. Prerequisite: CHEM-232 minimum grade of C. CHEM-349. Organic Synthe ...
... The chemistry of complex molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates is studied from the point of view of their physical properties and their reaction, synthesis and structure-function relationships. Lecture 3 hours. Prerequisite: CHEM-232 minimum grade of C. CHEM-349. Organic Synthe ...
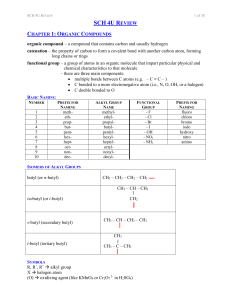
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
Chapter 7 lecture notes: Solutions
... solute particles be able to interact with the solvent molecules through noncovalent interactions. ...
... solute particles be able to interact with the solvent molecules through noncovalent interactions. ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... Solute is the substance being dissolved. Solvent is the substance doing the dissolving. When an ionic solid is dissolved in a liquid like water, the negative pole of the water molecule is attracted to the cations of the ionic solid whereas the positive pole of the water molecule is attracted to the ...
... Solute is the substance being dissolved. Solvent is the substance doing the dissolving. When an ionic solid is dissolved in a liquid like water, the negative pole of the water molecule is attracted to the cations of the ionic solid whereas the positive pole of the water molecule is attracted to the ...
Chapter One Chemistry
... isproperty made atoms that of two is combine has a or characteristic mass more toand form substances— takes larger of aup pure particles space. substance called elements, molecules—groups compounds, that describes or its both—that ofability two or tomore are change together atoms into held in Chemis ...
... isproperty made atoms that of two is combine has a or characteristic mass more toand form substances— takes larger of aup pure particles space. substance called elements, molecules—groups compounds, that describes or its both—that ofability two or tomore are change together atoms into held in Chemis ...
Uranyl Ion Complexes with Ammoniobenzoates as
... pairs of atoms U1, U2 and U3, U4. Two hydroxide ions (O11, O12) provide additional bridging. Curiously, instead of another chelating HL3 ligand, two water molecules complete the coordination sphere of U4. U2 and U3 are also bound to one water molecule each, all uranium atoms being thus in pentagonal ...
... pairs of atoms U1, U2 and U3, U4. Two hydroxide ions (O11, O12) provide additional bridging. Curiously, instead of another chelating HL3 ligand, two water molecules complete the coordination sphere of U4. U2 and U3 are also bound to one water molecule each, all uranium atoms being thus in pentagonal ...
Fall 2012
... 67. (11 pts) When 35.00 mL of 0.100 M HBr is added to 0. 275 g of strontium hydroxide in a calorimeter, 195.3 J of energy are released. What is the ΔH for this reaction? The balanced reaction is: Sr(OH)2 + 2 HBr ! SrBr2 + 2 H2O 68. (11 pts) One type of weather balloon has a volume limit of 2.00 x 10 ...
... 67. (11 pts) When 35.00 mL of 0.100 M HBr is added to 0. 275 g of strontium hydroxide in a calorimeter, 195.3 J of energy are released. What is the ΔH for this reaction? The balanced reaction is: Sr(OH)2 + 2 HBr ! SrBr2 + 2 H2O 68. (11 pts) One type of weather balloon has a volume limit of 2.00 x 10 ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... 6. (2.5) True or False? A molecule with a non-superimposable mirror image must be chiral. 7. (2.5) True or False? A hydrogen attached to a carbon of a triple bond can be abstracted using a base, the conjugate acid of which is stronger than the alkyne. ...
... 6. (2.5) True or False? A molecule with a non-superimposable mirror image must be chiral. 7. (2.5) True or False? A hydrogen attached to a carbon of a triple bond can be abstracted using a base, the conjugate acid of which is stronger than the alkyne. ...
Electronic excitation gives informative fragmentation of polypeptide
... CAD of the same species, requires explanation. Of course, the fragmenting species in both techniques are different: they are radical ions in the first case and even-electron species in the latter case. However, stable polypeptide radical cations tend to produce less backbone fragmentation than do th ...
... CAD of the same species, requires explanation. Of course, the fragmenting species in both techniques are different: they are radical ions in the first case and even-electron species in the latter case. However, stable polypeptide radical cations tend to produce less backbone fragmentation than do th ...
Chemistry 12 - Correspondence Studies
... Thermochemistry is the study of the change in thermal energy (energy due to the motion of particles). It takes place during physical and chemical changes. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Work is defined as a force exerted over a distance. There are two types of energy, kinetic and poten ...
... Thermochemistry is the study of the change in thermal energy (energy due to the motion of particles). It takes place during physical and chemical changes. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Work is defined as a force exerted over a distance. There are two types of energy, kinetic and poten ...
Slide 1
... charged ions, called anions when atoms lose electrons, they become positively charged ions, called cations ions behave much differently than the neutral atom e.g., The metal sodium, made of neutral Na atoms, is highly reactive and quite unstable. However, the sodium cations, Na+, found in table sa ...
... charged ions, called anions when atoms lose electrons, they become positively charged ions, called cations ions behave much differently than the neutral atom e.g., The metal sodium, made of neutral Na atoms, is highly reactive and quite unstable. However, the sodium cations, Na+, found in table sa ...