12 U Chem Review
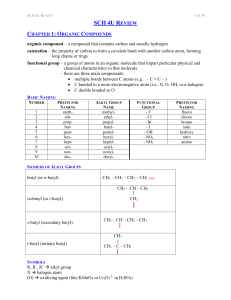
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
sch4ureview
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
... monomers; two types: addition and condensation monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made ...
carbohydrates: monosaccharides. oligo
... normal conditions does not produce coloration with Schiff’s reagent. At the same time, some reactions (formation of glycosides) can not be explained by oxo forms. Task №2. What is the essence of tautomeric transformations of monosaccharides, ...
... normal conditions does not produce coloration with Schiff’s reagent. At the same time, some reactions (formation of glycosides) can not be explained by oxo forms. Task №2. What is the essence of tautomeric transformations of monosaccharides, ...
Terpyridine-based Materials. For Catalytic, Optoelectronic and Life Science Applications Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2180128/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2180128/ ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... 30-D2.3k calculate equilibrium constants and concentrations for homogeneous systems and Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases (excluding buffers) when concentrations at equilibrium are known initial concentrations and one equilibrium concentration are known the equilibrium constant and one equilibr ...
... 30-D2.3k calculate equilibrium constants and concentrations for homogeneous systems and Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases (excluding buffers) when concentrations at equilibrium are known initial concentrations and one equilibrium concentration are known the equilibrium constant and one equilibr ...
Brazil: SAXS and High Pressure
... 1 The first prize was to reduce the words on a page by 25,000 times so that it could be read by and electron microscope. 2 “And I want to offer another prize …$1,000 to the first guy who makes an operating electric motor -- a rotating electric motor which can be controlled from the outside and, not ...
... 1 The first prize was to reduce the words on a page by 25,000 times so that it could be read by and electron microscope. 2 “And I want to offer another prize …$1,000 to the first guy who makes an operating electric motor -- a rotating electric motor which can be controlled from the outside and, not ...
1 - Academics
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
... learn how these are named. The common names of alkyl halides are derived by naming the alkyl group followed by the halide. Alkyl halides are named as halosubstituted hydrocarbons in the IUPAC system of nomenclature. Haloarenes are the common as well as IUPAC names of aryl halides. For dihalogen deri ...
... learn how these are named. The common names of alkyl halides are derived by naming the alkyl group followed by the halide. Alkyl halides are named as halosubstituted hydrocarbons in the IUPAC system of nomenclature. Haloarenes are the common as well as IUPAC names of aryl halides. For dihalogen deri ...
Chemistry SOL Review Test
... Unit 7: Chemical Equations (Ch. 11) 64) Use the activity series of metals to determine which of the following reactions will occur. If a reaction will take place, complete and balance the equation. If the reaction will not occur, write no reaction. a) 2 Al + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Al2(SO4)3 b) 6 Ag + 2 H3 ...
... Unit 7: Chemical Equations (Ch. 11) 64) Use the activity series of metals to determine which of the following reactions will occur. If a reaction will take place, complete and balance the equation. If the reaction will not occur, write no reaction. a) 2 Al + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Al2(SO4)3 b) 6 Ag + 2 H3 ...
Chemistry Unit 1
... 2. Draw diagrams to show how carbon atoms can link to one another in different ways to form a variety of compounds by considering only four carbon atoms. Discuss with your group and present it to the class. ...
... 2. Draw diagrams to show how carbon atoms can link to one another in different ways to form a variety of compounds by considering only four carbon atoms. Discuss with your group and present it to the class. ...
Supplementary Data - Royal Society of Chemistry
... However, broadening of the Soret band and a concomitant increase in molar absorptivity at max (Soret) has been observed in case of porphyrin in ionic liquid, indicates the formation of ion-pair complexes. Further, the addition of hydrogen peroxide to porphyrin in ionic liquid decreases the absorpti ...
... However, broadening of the Soret band and a concomitant increase in molar absorptivity at max (Soret) has been observed in case of porphyrin in ionic liquid, indicates the formation of ion-pair complexes. Further, the addition of hydrogen peroxide to porphyrin in ionic liquid decreases the absorpti ...
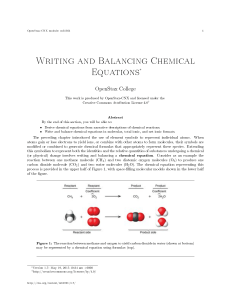
Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... This example illustrates the fundamental aspects of any chemical equation: 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the ...
... This example illustrates the fundamental aspects of any chemical equation: 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the ...
Ch. 16 Study Guide
... 12. Conversion between Kc and Kp relies on determining the change in moles of gas in a reaction. 13. Pure solids and pure liquids are not included in the equilibrium constant expression. 14. Equilibrium constants are unitless even though molarity concentrations or partial pressures are used to calcu ...
... 12. Conversion between Kc and Kp relies on determining the change in moles of gas in a reaction. 13. Pure solids and pure liquids are not included in the equilibrium constant expression. 14. Equilibrium constants are unitless even though molarity concentrations or partial pressures are used to calcu ...
Chemistry 1120, General Chemistry II, spring 2015, 4 credits
... Structures of Life, 4th Edition, Pearson ...
... Structures of Life, 4th Edition, Pearson ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... A 1.00 mol sample of CO2 is heated to 1000K with excess graphite in a container of volume 40.0 L. At this temperature, Kc is 2.11x10-2 for the reaction: C(graphite) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) a) b) ...
... A 1.00 mol sample of CO2 is heated to 1000K with excess graphite in a container of volume 40.0 L. At this temperature, Kc is 2.11x10-2 for the reaction: C(graphite) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) a) b) ...
Chemistry 209 - Experiment 3, Fall 2002
... tested as possible. Always note the color and physical form of each compound you work with in the lab. As you perform the different tests, try to observe and note any subtle differences between the behavior of different compounds. Such things as color changes, warming of the solution ("heat evolutio ...
... tested as possible. Always note the color and physical form of each compound you work with in the lab. As you perform the different tests, try to observe and note any subtle differences between the behavior of different compounds. Such things as color changes, warming of the solution ("heat evolutio ...
Reactions involving HCl and their Evaporation
... When synthesising and purifying organic molecules, such as those created by medicinal chemists during the drug discovery process, hydrochloric acid (HCl) can be a very useful reagent. Its preferential use over other mineral acids (that can produce undesirable side effects) and trifluoroacetic acid ( ...
... When synthesising and purifying organic molecules, such as those created by medicinal chemists during the drug discovery process, hydrochloric acid (HCl) can be a very useful reagent. Its preferential use over other mineral acids (that can produce undesirable side effects) and trifluoroacetic acid ( ...
Oxidation And Degradation Products Of Common Oxygen Scavengers
... attempt to explain the oxidation and degradation reactions of the more common oxygen scavengers in current use. In each case, the material will react with oxygen, and with metal oxides. The efficiency of the reaction is dependent on time, temperature, concentration and system pH. In general, as the ...
... attempt to explain the oxidation and degradation reactions of the more common oxygen scavengers in current use. In each case, the material will react with oxygen, and with metal oxides. The efficiency of the reaction is dependent on time, temperature, concentration and system pH. In general, as the ...