Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous
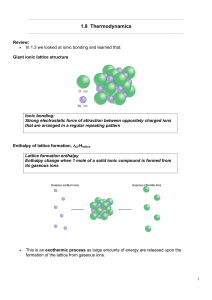
... When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When stro ...
... When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When stro ...
Document
... • Cr6+ oxidations are characterized by a color change, as the red-orange Cr6+ reagent is reduced to green Cr3+. • Some devices used to measure blood alcohol content make use of this color change—Oxidation of CH3CH2OH, the 1° alcohol in alcoholic beverages, with orange K2Cr2O7 forms CH3COOH and green ...
... • Cr6+ oxidations are characterized by a color change, as the red-orange Cr6+ reagent is reduced to green Cr3+. • Some devices used to measure blood alcohol content make use of this color change—Oxidation of CH3CH2OH, the 1° alcohol in alcoholic beverages, with orange K2Cr2O7 forms CH3COOH and green ...
1 Mole
... Label the reactants and the products in the reaction above Are the reactants and products covalent or ionic? How many oxygen atoms are in the compound Pb(NO3)3? ...
... Label the reactants and the products in the reaction above Are the reactants and products covalent or ionic? How many oxygen atoms are in the compound Pb(NO3)3? ...
Energy
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsys = - qsur. If we know the energy of combustion for a compound, in units of kJ/g, then we can say q = m Ucom m = mass of compound burned Ucom = energy of combustion (in kJ/g) Note th ...
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsys = - qsur. If we know the energy of combustion for a compound, in units of kJ/g, then we can say q = m Ucom m = mass of compound burned Ucom = energy of combustion (in kJ/g) Note th ...
NMR and Parity Violation Anomalous Temperature Dependence in
... contribution to the spin-spin coupling between electrons S1DS2 in the triplet state of chiral molecules has been considered; a ratio of about 10-12- 10-13 eV with respect to the spin-orbit coupling has been estimated [ 18 ]. The simple physical description of and J clearly shows that their values ...
... contribution to the spin-spin coupling between electrons S1DS2 in the triplet state of chiral molecules has been considered; a ratio of about 10-12- 10-13 eV with respect to the spin-orbit coupling has been estimated [ 18 ]. The simple physical description of and J clearly shows that their values ...
Research on Hydrogenation of FAME to Fatty Alcohols
... velocity. Besides, the date in Table 4 and Figure 5 shows that the conversion rate of fatty acid methyl ester was above 99% with the condition of less than 4.0h-1 space velocity. While in terms of purpose products, it was more than 90%, and increased slightly with space velocity increased. Compared ...
... velocity. Besides, the date in Table 4 and Figure 5 shows that the conversion rate of fatty acid methyl ester was above 99% with the condition of less than 4.0h-1 space velocity. While in terms of purpose products, it was more than 90%, and increased slightly with space velocity increased. Compared ...
Nordonia Hills City Schools Honors Chemistry Course of Study
... Compare and contrast contributors to early atomic theory: Greeks, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, and Bohr) Describe concepts involved in Dalton's postulates (i.e. constant composition) as well as shortcomings of same postulates. Perform different experiments using indirect methods Calculate ...
... Compare and contrast contributors to early atomic theory: Greeks, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, and Bohr) Describe concepts involved in Dalton's postulates (i.e. constant composition) as well as shortcomings of same postulates. Perform different experiments using indirect methods Calculate ...
Organic Chemistry Introduction
... Compounds With 4n Electrons Are Not Aromatic (May be Anti-aromatic) • Planar, cyclic molecules with 4 n electrons are much less stable than expected (anti-aromatic) ...
... Compounds With 4n Electrons Are Not Aromatic (May be Anti-aromatic) • Planar, cyclic molecules with 4 n electrons are much less stable than expected (anti-aromatic) ...
Equilibrium STUDY GUIDE by Keshara Senanayake ---
... Q is less than Keq (Q < Keq), the denominator of the reaction quotient expression is too large and the numerator is too small. This means that at the time of measurement there is too much of the reactants and too little of the products. The reaction will consume reactants and form the products to re ...
... Q is less than Keq (Q < Keq), the denominator of the reaction quotient expression is too large and the numerator is too small. This means that at the time of measurement there is too much of the reactants and too little of the products. The reaction will consume reactants and form the products to re ...
Unit 2.6 Completed - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Like water, ethanol is an excellent solvent able to dissolve a variety of substances. Ethanol is widely used as the solvent for many ink based pens and is, therefore, the ideal chemical to be used when attempting to remove ink stains. In industrial and consumer products, ethanol is the second most i ...
... Like water, ethanol is an excellent solvent able to dissolve a variety of substances. Ethanol is widely used as the solvent for many ink based pens and is, therefore, the ideal chemical to be used when attempting to remove ink stains. In industrial and consumer products, ethanol is the second most i ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... The notes have been prepared in order to give students (and teachers) some indication of the sort of things that the National Examiner expects high school students to know - and what topics might appear on future exams. Unless otherwise stated, the National High School Chemistry Examination is based ...
... The notes have been prepared in order to give students (and teachers) some indication of the sort of things that the National Examiner expects high school students to know - and what topics might appear on future exams. Unless otherwise stated, the National High School Chemistry Examination is based ...
Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II
... With α-methylstyrene (6, R = Ph), the yield of the diacetylation with acetic anhydride and perchloric or sulfoacetic acid affording 2,6-dimethyl-4phenylpyrylium salts is lowered because of polymerization side-products.58 Whereas the resulting phenyl group in position 4 (γ) is deactivated towards ele ...
... With α-methylstyrene (6, R = Ph), the yield of the diacetylation with acetic anhydride and perchloric or sulfoacetic acid affording 2,6-dimethyl-4phenylpyrylium salts is lowered because of polymerization side-products.58 Whereas the resulting phenyl group in position 4 (γ) is deactivated towards ele ...
In the bachelor thesis of Esther Schippers, research is
... 1. The peptides are set onto scaffolds via CLIPS-chemistry. To be able to do a CLIPS-reaction, a part of the molecule should exist of a phenyl ring with two bromomethyl groups, at which the peptide can bind. 2. Many peptide reactions are done in aqueous solutions. The scaffolds should therefore also ...
... 1. The peptides are set onto scaffolds via CLIPS-chemistry. To be able to do a CLIPS-reaction, a part of the molecule should exist of a phenyl ring with two bromomethyl groups, at which the peptide can bind. 2. Many peptide reactions are done in aqueous solutions. The scaffolds should therefore also ...
ORGANOHALIDES + Nucleophilic Reactions (SN1
... • THE LEAVING GROUP should be stable on its own as a free anion • Comparing halides, we go down the column ...
... • THE LEAVING GROUP should be stable on its own as a free anion • Comparing halides, we go down the column ...
Pirogov National Medical Univercity of Vinnitsa
... At work with harmful and toxic substances (cyanide, salts of barium, mercury, lead, arsenic, mercury metal, sulfide, etc.) is necessary to ensure that hazardous or toxic substances are not included in the body through the gastrointestinal tract. In the bond with the food consumed in the laboratory i ...
... At work with harmful and toxic substances (cyanide, salts of barium, mercury, lead, arsenic, mercury metal, sulfide, etc.) is necessary to ensure that hazardous or toxic substances are not included in the body through the gastrointestinal tract. In the bond with the food consumed in the laboratory i ...
Document
... (b) Electrical - in certain materials, you can remove electrons from one area and send them to another. The area losing the electrons becomes more and ...
... (b) Electrical - in certain materials, you can remove electrons from one area and send them to another. The area losing the electrons becomes more and ...