Final Exam Review Packet
... 5. - The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule of a compound. - The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a formula unit. - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quanti ...
... 5. - The molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule of a compound. - The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a formula unit. - The molecular mass is the mass of one mole of any substance. 6. The advantage of using moles is that the quanti ...
Basic Stoichometry
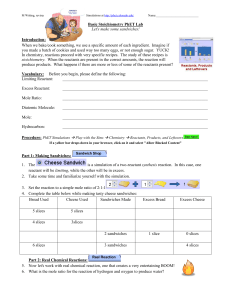
... reactant will be limiting, while the other will be in excess. 2. Take some time and familiarize yourself with the simulation. 3. Set the reaction to a simple mole ratio of 2:1:1 4. Complete the table below while making tasty cheese sandwiches: ...
... reactant will be limiting, while the other will be in excess. 2. Take some time and familiarize yourself with the simulation. 3. Set the reaction to a simple mole ratio of 2:1:1 4. Complete the table below while making tasty cheese sandwiches: ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of carbon based compounds. Bonds between carbon atoms are covalent; each carbon is capable of forming four bonds: – Four single bonds = tertrahedral geometry – Two single, one double = trigonal planar geometry – Two double = line ...
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of carbon based compounds. Bonds between carbon atoms are covalent; each carbon is capable of forming four bonds: – Four single bonds = tertrahedral geometry – Two single, one double = trigonal planar geometry – Two double = line ...
Liquid-gas phase-boundary catalytic system
... overall rate of reaction versus interaction strength of the intermediate reaction complexes with catalytic bonding site. There are many different catalytic systems. Of most basic mechanistic features are well understood. Here an attempt will be made to introduce several approach to synthesize partic ...
... overall rate of reaction versus interaction strength of the intermediate reaction complexes with catalytic bonding site. There are many different catalytic systems. Of most basic mechanistic features are well understood. Here an attempt will be made to introduce several approach to synthesize partic ...
Fulltext PDF
... Schrock carbene nucleophilic. Fischer carbenes have nearly opposite properties. The metal is electron rich, in part because of coordinate donation of an electron pair from the carbene carbon atom and CO ligands. Competition for the d-electrons of the metal takes place between bonding ligands such ...
... Schrock carbene nucleophilic. Fischer carbenes have nearly opposite properties. The metal is electron rich, in part because of coordinate donation of an electron pair from the carbene carbon atom and CO ligands. Competition for the d-electrons of the metal takes place between bonding ligands such ...
Common Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: Chemistry
... 3. List the three main parts of an atom, along with each part’s electrical charge. 4. Discuss the relative size and mass of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 5. Use the periodic table to determine the atomic number of a given element. 6. Explain what an atomic number means. 7. Define an ion and accu ...
... 3. List the three main parts of an atom, along with each part’s electrical charge. 4. Discuss the relative size and mass of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 5. Use the periodic table to determine the atomic number of a given element. 6. Explain what an atomic number means. 7. Define an ion and accu ...
Stoichiometry - Bruder Chemistry
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. Use atomic mass units. an atomic mass unit (amu) is one twelth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This gives us a basis for comparison. The decimal numbers on the table are atomic masses in amu. ...
Definition: the term “alkaloid” (alkali
... rings in a given compound. For example, hygrine has the molecular formula, C8H15NO which corresponds to 8 – 15/2 + ½ + 1 = 2 double bond equivalents. However, chemical tests reveal that hygrine contains only one carbonyl group (one double bond equivalent) and does not show other form of unsatura ...
... rings in a given compound. For example, hygrine has the molecular formula, C8H15NO which corresponds to 8 – 15/2 + ½ + 1 = 2 double bond equivalents. However, chemical tests reveal that hygrine contains only one carbonyl group (one double bond equivalent) and does not show other form of unsatura ...
CH4 Student Revision Guides pdf | GCE AS/A
... that leaves no ambiguity. Many organic compounds have been known for a long time and have trivial names that pre-date systematic nomenclature. ...
... that leaves no ambiguity. Many organic compounds have been known for a long time and have trivial names that pre-date systematic nomenclature. ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... The trigonal planar arrangement of groups around the carhonyl carbon atom means that the carbonyl carbon atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on ...
... The trigonal planar arrangement of groups around the carhonyl carbon atom means that the carbonyl carbon atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on ...
TEKS 8 - UNT College of Education
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the molecular level is the reason chemical equilibrium is frequently referred ...
... number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the molecular level is the reason chemical equilibrium is frequently referred ...
TOPIC 7. ELIMINATION REACTIONS (chapter 7 and parts of
... 1. Describe mechanisms for elimination of a leaving group and adjacent proton to form a pi-bond. 2. Discuss the effect of starting material (“substrate”), leaving group, and reaction conditions on the course and outcome of a reaction. 3. Describe syntheses of alkenes and alkynes. 4. Use combinations ...
... 1. Describe mechanisms for elimination of a leaving group and adjacent proton to form a pi-bond. 2. Discuss the effect of starting material (“substrate”), leaving group, and reaction conditions on the course and outcome of a reaction. 3. Describe syntheses of alkenes and alkynes. 4. Use combinations ...
mole concept type 1 - teko classes bhopal
... Calculation of Limiting Reagent : By calculating the required amount by the equation and comparing it with given amount. [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least p ...
... Calculation of Limiting Reagent : By calculating the required amount by the equation and comparing it with given amount. [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least p ...
Ch. 24 - Organic Compounds
... 9. The compounds shown in Figure 21-3 are isomers of each other. What is the chemical formula for these compounds? ...
... 9. The compounds shown in Figure 21-3 are isomers of each other. What is the chemical formula for these compounds? ...
Acylation of aromatic alcohols and phenols over InCl3
... Results showing the product yields in the acylation of different aromatic alcohols and phenols with different acyl chlorides over InCl3 (20%)/Mont. K-10 catalysts are presented in table 2. In all the cases, the yields are quite high, indicating high acylation activity of the catalyst, even under the ...
... Results showing the product yields in the acylation of different aromatic alcohols and phenols with different acyl chlorides over InCl3 (20%)/Mont. K-10 catalysts are presented in table 2. In all the cases, the yields are quite high, indicating high acylation activity of the catalyst, even under the ...
More Reaction Information
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
Functions of carbohydrates
... Formation of sugar sulfates • Sulfates esterified at C-2, C-4 or C-6 of aldoses • Found mostly in proteoglycans of ECM • Presence of sulfate groups mean that sugar is negatively charged at physiological pH ...
... Formation of sugar sulfates • Sulfates esterified at C-2, C-4 or C-6 of aldoses • Found mostly in proteoglycans of ECM • Presence of sulfate groups mean that sugar is negatively charged at physiological pH ...