Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds, existing as cyclic dimers held together by two hydrogen bonds Strong hydrogen bonding causes much higher boiling points than the corresponding alcohols ...
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds, existing as cyclic dimers held together by two hydrogen bonds Strong hydrogen bonding causes much higher boiling points than the corresponding alcohols ...
Laboratory 3
... you probably have enough evidence to select the appropriate pattern of reactivity. However, you need more information to write a chemical equation. The qualitative analysis determined what ions are present, but it did not provide any quantitative information. A chemical equation includes quantitativ ...
... you probably have enough evidence to select the appropriate pattern of reactivity. However, you need more information to write a chemical equation. The qualitative analysis determined what ions are present, but it did not provide any quantitative information. A chemical equation includes quantitativ ...
Specification – AS/A Level Chemistry A
... (ii) non-metals generally react by gaining electrons with a decrease in oxidation number to form negative ions; x ...
... (ii) non-metals generally react by gaining electrons with a decrease in oxidation number to form negative ions; x ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... 28.33°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter assembly is 4.90 kJ/°C. (a) What is the heat of combustion of sucrose, expressed in kJ/mol C12H22O11? (b) Verify the claim of sugar producers that one teaspoon of sugar (about 4.8 g) contains only 19 ...
... 28.33°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter assembly is 4.90 kJ/°C. (a) What is the heat of combustion of sucrose, expressed in kJ/mol C12H22O11? (b) Verify the claim of sugar producers that one teaspoon of sugar (about 4.8 g) contains only 19 ...
time-dependent density functional theoretical - Prof. Shih
... In recent years, the density-functional theory (DFT) has become a widely used formalism for electron structure calculations of atoms, molecules, and solids [1–5]. The DFT is based on the earlier fundamental work of Hohenberg and Kohn [6] and Kohn and Sham [7]. In the Kohn-Sham DFT formalism [7], the ...
... In recent years, the density-functional theory (DFT) has become a widely used formalism for electron structure calculations of atoms, molecules, and solids [1–5]. The DFT is based on the earlier fundamental work of Hohenberg and Kohn [6] and Kohn and Sham [7]. In the Kohn-Sham DFT formalism [7], the ...
Organic Chemistry 145 CHEM
... Electrophilic Addition Reactions 4. Addition of Water: Hydration - Addition of water to alkynes requires not only an acid catalyst but mercuric ion as well. - The mercuric ion forms a complex with the triple bond and activates it for addition. - Although the reaction is similar to that of alkenes, t ...
... Electrophilic Addition Reactions 4. Addition of Water: Hydration - Addition of water to alkynes requires not only an acid catalyst but mercuric ion as well. - The mercuric ion forms a complex with the triple bond and activates it for addition. - Although the reaction is similar to that of alkenes, t ...
ICE Tables - Chemwiki
... Know the direction of the reaction. This knowledge will affect the "change" row of the ICE table (for our example, we knew the reaction would proceed forward, as there was no initial products). Direction of reaction can be calculated using Q, the reaction quotient, which is then compared to a known ...
... Know the direction of the reaction. This knowledge will affect the "change" row of the ICE table (for our example, we knew the reaction would proceed forward, as there was no initial products). Direction of reaction can be calculated using Q, the reaction quotient, which is then compared to a known ...
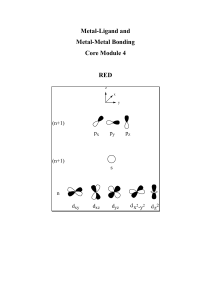
Metal-Ligand and Metal-Metal Bonding Lecture Notes
... 1. Radius (Covalent/ionic) :- Increases from right to left and down a group. 2. Electropositivity:- electropositive character increases from right to left and down a group. The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penet ...
... 1. Radius (Covalent/ionic) :- Increases from right to left and down a group. 2. Electropositivity:- electropositive character increases from right to left and down a group. The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penet ...
Fluorinated Butatrienes - diss.fu-berlin.de
... stellt sich heraus, dass das Kumulen-Isomer nicht mehr das stabilste Isomer ist. ...
... stellt sich heraus, dass das Kumulen-Isomer nicht mehr das stabilste Isomer ist. ...
More reactions of alkenes Objective
... double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compo ...
... double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compo ...
Document
... Catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction ◦ Provide a new, lower energy pathway ◦ Forward and reverse reactions pass through the same transition state ◦ Rate for forward and reverse reactions increase by the same factor ◦ Does not affect the composition of the equilibrium mixture ◦ Does not ...
... Catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction ◦ Provide a new, lower energy pathway ◦ Forward and reverse reactions pass through the same transition state ◦ Rate for forward and reverse reactions increase by the same factor ◦ Does not affect the composition of the equilibrium mixture ◦ Does not ...
Chapter 2 power point File
... A bowl of wax can be broken down over and over until it cannot be broken down anymore without loosing its properties and you would have a molecule of wax A single molecule is the smallest particle a substance can be A molecule is two or more atoms bonded together Wax is a compound made up of carbon ...
... A bowl of wax can be broken down over and over until it cannot be broken down anymore without loosing its properties and you would have a molecule of wax A single molecule is the smallest particle a substance can be A molecule is two or more atoms bonded together Wax is a compound made up of carbon ...
ppt
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
... In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Crown Ethers (Please read) ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Avg. Atomic mass of Calcium = 40.08g Avg. Atomic mass of Chlorine = 35.45g Molar Mass of calcium chloride = 40.08 g/mol Ca + (2 X 35.45) g/mol Cl 110.98 g/mol CaCl2 ...
... Avg. Atomic mass of Calcium = 40.08g Avg. Atomic mass of Chlorine = 35.45g Molar Mass of calcium chloride = 40.08 g/mol Ca + (2 X 35.45) g/mol Cl 110.98 g/mol CaCl2 ...
Chemistry - Chap 12 Homework Answers 2014
... 7. What is vapor pressure? On a microscopic basis, how does a vapor pressure develop in a closed flask containing a small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which subs ...
... 7. What is vapor pressure? On a microscopic basis, how does a vapor pressure develop in a closed flask containing a small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which subs ...
PX211-0406 The following questions were randomly selected for
... 17. When the valve between the 2.00-L bulb, in which the gas pressure is 3.00 atm, and the 3.00-L bulb, in which the gas pressure is 2.50 atm, is opened, what will be the final pressure in the two bulbs? Assume the temperature remains constant. ...
... 17. When the valve between the 2.00-L bulb, in which the gas pressure is 3.00 atm, and the 3.00-L bulb, in which the gas pressure is 2.50 atm, is opened, what will be the final pressure in the two bulbs? Assume the temperature remains constant. ...