study material class X (science)
... Ans. (a) marble chips react with dilute hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride and carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + H2O +CO2 (b) Zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid to give hydrogen gas. it is a displacement reaction Zn(s)+2HCl ZnCl2(aq)+H ...
... Ans. (a) marble chips react with dilute hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride and carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + H2O +CO2 (b) Zinc granules react with dilute hydrochloric acid to give hydrogen gas. it is a displacement reaction Zn(s)+2HCl ZnCl2(aq)+H ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... reduced." There is no net change in the number of electrons in a redox reaction. Those given off in the oxidation half reaction are taken on by another species in the reduction half reaction. The two species that exchange electrons in a redox reaction are given special names. The ion or molecule th ...
... reduced." There is no net change in the number of electrons in a redox reaction. Those given off in the oxidation half reaction are taken on by another species in the reduction half reaction. The two species that exchange electrons in a redox reaction are given special names. The ion or molecule th ...
Practice Exam I FR Answers and Explanations
... Cd changes oxidation states from 0 to +2—thus, it is oxidized. Whatever species is oxidized is known as the reducing agent. (c) At a higher temperature, how would the cell potential change? Explain questions such as this with mathematical formulas if at all possible. There are two equations that all ...
... Cd changes oxidation states from 0 to +2—thus, it is oxidized. Whatever species is oxidized is known as the reducing agent. (c) At a higher temperature, how would the cell potential change? Explain questions such as this with mathematical formulas if at all possible. There are two equations that all ...
Amber Setup
... • Amber is a very sophisticated piece of scientific software and as such requires some amount of time to learn it. • Although Amber may appear very complex at first, it is reasonably straightforward once you understand the basic architecture and option choices. • The best source of help for active u ...
... • Amber is a very sophisticated piece of scientific software and as such requires some amount of time to learn it. • Although Amber may appear very complex at first, it is reasonably straightforward once you understand the basic architecture and option choices. • The best source of help for active u ...
Topic 3
... of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction. – It is based on the balanced chemical equation and on the relationship between mass and moles (molar mass is an important concept here; g mol, mol g) and mol to mol ratios. – Such calculations are fundamental to most quantitative work i ...
... of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction. – It is based on the balanced chemical equation and on the relationship between mass and moles (molar mass is an important concept here; g mol, mol g) and mol to mol ratios. – Such calculations are fundamental to most quantitative work i ...
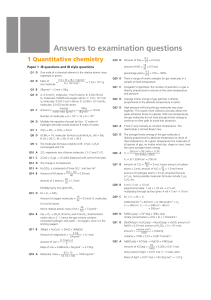
Answers to examination questions
... Q4 The ions formed across period 3 would be Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ and P3−, S2− and Cl−. There is a decrease in ionic radii from Na+ to Al3+: all the ions have the electron arrangement of 2,8 (that is they, are isoelectronic), however, there is a progressive increase in the nuclear charge due to the additi ...
... Q4 The ions formed across period 3 would be Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ and P3−, S2− and Cl−. There is a decrease in ionic radii from Na+ to Al3+: all the ions have the electron arrangement of 2,8 (that is they, are isoelectronic), however, there is a progressive increase in the nuclear charge due to the additi ...
Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
... Section 9.1: Molecular Geometry and the VSEPR Model Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule affects the physical and chemical properties of a molecule. The question is how to predict the threedimensional arrangement of at ...
... Section 9.1: Molecular Geometry and the VSEPR Model Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule affects the physical and chemical properties of a molecule. The question is how to predict the threedimensional arrangement of at ...
Chapter 20 - Cengage Learning
... Organic chemistry is devoted to the study of compounds and reactions of the element carbon. No other element forms as many different compounds as carbon. The compounds range from the simple molecule methane, which we burn as fuel, to the complex molecules that carry genetic information. This chapter ...
... Organic chemistry is devoted to the study of compounds and reactions of the element carbon. No other element forms as many different compounds as carbon. The compounds range from the simple molecule methane, which we burn as fuel, to the complex molecules that carry genetic information. This chapter ...
CHEMISTRY
... units. I use dimensional analysis to do metric-metric conversions, stressing that many different types of calculations can be done using dimensional analysis. I will also intentionally set up a problem incorrectly and show the students that the units do not cancel, demonstrating the importance of ch ...
... units. I use dimensional analysis to do metric-metric conversions, stressing that many different types of calculations can be done using dimensional analysis. I will also intentionally set up a problem incorrectly and show the students that the units do not cancel, demonstrating the importance of ch ...
Lecture1
... -nanoparticles (appliations in electronic, magnetic, or optical devices or in sensors) d) Main use in organic synthesis and (homogeneous) catalysis. Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistr ...
... -nanoparticles (appliations in electronic, magnetic, or optical devices or in sensors) d) Main use in organic synthesis and (homogeneous) catalysis. Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistr ...
INTRODUCING ACYL CHLORIDES (acid
... acyl chlorides menu (link below). If you are interested in exploring the general mechanism for these reactions, you will find it by following this link to another part of the site dealing with nucleophilic additionelimination reactions. If you want mechanisms for specific reactions you could explore ...
... acyl chlorides menu (link below). If you are interested in exploring the general mechanism for these reactions, you will find it by following this link to another part of the site dealing with nucleophilic additionelimination reactions. If you want mechanisms for specific reactions you could explore ...
CO 2 - TrimbleChemistry
... • A compound is represented by using the symbols for the elements of which it is composed • Subscripts are used to indicate how many atoms of a particular element exist in the compound • If there is only one atom of a particular element, the one is assumed ...
... • A compound is represented by using the symbols for the elements of which it is composed • Subscripts are used to indicate how many atoms of a particular element exist in the compound • If there is only one atom of a particular element, the one is assumed ...
Atomic Structure
... For the energy levels in an atom, which one of the following statement is incorrect? (a) There are seven principle electron energy levels (b) The second principal energy level can have four sub-energy levels and contain a Maximum of eight electrons (c) The M energy level can have a maximum of 32 ele ...
... For the energy levels in an atom, which one of the following statement is incorrect? (a) There are seven principle electron energy levels (b) The second principal energy level can have four sub-energy levels and contain a Maximum of eight electrons (c) The M energy level can have a maximum of 32 ele ...
EEW508 II. Structure of Surfaces
... Ionic bonds: Na+ (cation) - Cl-(anion) These oppositely charged cations and anions are attracted to one another because of their opposite charges. That attraction is called an ionic bond. ...
... Ionic bonds: Na+ (cation) - Cl-(anion) These oppositely charged cations and anions are attracted to one another because of their opposite charges. That attraction is called an ionic bond. ...
Molecular electrostatic potentials and Mulliken charge populations of DNA mini-sequences ´ R. Santamaria
... thymine which produces a hydrogen bridge with N1 of adenine. Equivalent results about the lost of binding sites are observed for complex GC, where the formation of hydrogen bridges N3–H14 and O8–H12 essentially eliminates two potential wells initially attached to atoms N3 and O8 of cytosine. On the ...
... thymine which produces a hydrogen bridge with N1 of adenine. Equivalent results about the lost of binding sites are observed for complex GC, where the formation of hydrogen bridges N3–H14 and O8–H12 essentially eliminates two potential wells initially attached to atoms N3 and O8 of cytosine. On the ...
Subject Materials for Chemistry
... 27. How is steel manufactured by Bessemer process? Ans: For fig ref.page number 22 fig.number2.6. Steel is manufactured from pig iron in a Bessemer converter, which is a pear shaped furnace lined inside with silicon. Molten pig iron is taken in Bessemer converter is heated with a hot blast of air. O ...
... 27. How is steel manufactured by Bessemer process? Ans: For fig ref.page number 22 fig.number2.6. Steel is manufactured from pig iron in a Bessemer converter, which is a pear shaped furnace lined inside with silicon. Molten pig iron is taken in Bessemer converter is heated with a hot blast of air. O ...
H o - CashmereChemistry
... 1. Write the data in the form of equations 2. Rewrite the equations to give the desired species on the correct side of the equation. If the reaction must be reversed (perhaps because we require a species to be a reactant and not a product) then the sign of the H must also be ...
... 1. Write the data in the form of equations 2. Rewrite the equations to give the desired species on the correct side of the equation. If the reaction must be reversed (perhaps because we require a species to be a reactant and not a product) then the sign of the H must also be ...