Chapter 4
... atom, the system treats it as if it were bonded to two such atoms In the case of isotopes, the isotope with the greater mass number has the higher priority ...
... atom, the system treats it as if it were bonded to two such atoms In the case of isotopes, the isotope with the greater mass number has the higher priority ...
Colligative Properties
... Vapor pressure depression is relatively easy to understand on the basis of a physical model. At the surface of a liquid there is a competition between the kinetic energy of the molecules (thermal energy), which is trying to push the molecules off the surface into the gas phase, and the intermolecula ...
... Vapor pressure depression is relatively easy to understand on the basis of a physical model. At the surface of a liquid there is a competition between the kinetic energy of the molecules (thermal energy), which is trying to push the molecules off the surface into the gas phase, and the intermolecula ...
File
... • It shows reactants and products. • To balance an equation means to change the numbers of each molecule involved, so that the same number of atoms of each element appear on the reactants side and on the products side. • Chemical equations balance on an atomic level, not molecular. • You cannot chan ...
... • It shows reactants and products. • To balance an equation means to change the numbers of each molecule involved, so that the same number of atoms of each element appear on the reactants side and on the products side. • Chemical equations balance on an atomic level, not molecular. • You cannot chan ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... The reaction, A + 2B 2C + D was studied using an initial concentration of B which was 1.5 more that of A. But the equilibrium concentration of A and C were found to be equal. Then the Kc for the equilibrium is : (a) 4 ...
... The reaction, A + 2B 2C + D was studied using an initial concentration of B which was 1.5 more that of A. But the equilibrium concentration of A and C were found to be equal. Then the Kc for the equilibrium is : (a) 4 ...
MC94 - Southchemistry.com
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O(g)
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
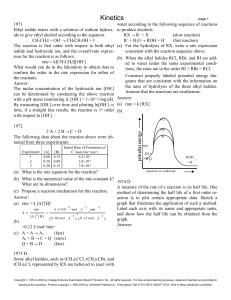
Kinetics
... (c) Catalytic nickel lowers the activation energy needed for a reaction. More often molecules have the needed energy when they collide. Reaction rate rises. (d) Greater surface area with powdered Ni. More catalytic sites means a greater rate. ...
... (c) Catalytic nickel lowers the activation energy needed for a reaction. More often molecules have the needed energy when they collide. Reaction rate rises. (d) Greater surface area with powdered Ni. More catalytic sites means a greater rate. ...
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry - Suffolk County Community College
... energy than the initial condition, the change in the internal energy will be + • If the final condition has a smaller amount of internal energy than the initial condition, the change in the internal energy will be ─ Tro: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2/e ...
... energy than the initial condition, the change in the internal energy will be + • If the final condition has a smaller amount of internal energy than the initial condition, the change in the internal energy will be ─ Tro: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2/e ...
Introduction
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
chapter 2. electrochemical methods and materials 17
... The monitoring of local electrical potential by using in-situ potential microprobes is a technique which allows to measure the spatial potential distribution. Experiments in which spatiotemporal visualisation of interfacial potential distribution along the electrified interface between solid electro ...
... The monitoring of local electrical potential by using in-situ potential microprobes is a technique which allows to measure the spatial potential distribution. Experiments in which spatiotemporal visualisation of interfacial potential distribution along the electrified interface between solid electro ...
Alcohols - Structure - University of Nebraska Omaha
... • Ethers are polar molecules. • Each C-O bond is polar covalent. • However, only weak polar forces exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid. ...
... • Ethers are polar molecules. • Each C-O bond is polar covalent. • However, only weak polar forces exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid. ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... • Lewis acids generally have an incomplete octet (e.g., BF3). Consider the reaction between NH3 and BF3. This reaction occurs because BF3 has a vacant orbital in its valence shell. It therefore acts as an electron-pair acceptor (a Lewis acid) toward NH3, which donates the electron pair. The curved a ...
... • Lewis acids generally have an incomplete octet (e.g., BF3). Consider the reaction between NH3 and BF3. This reaction occurs because BF3 has a vacant orbital in its valence shell. It therefore acts as an electron-pair acceptor (a Lewis acid) toward NH3, which donates the electron pair. The curved a ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... (C) Hund's rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 1. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 2. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 3. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no ...
... (C) Hund's rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 1. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 2. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 3. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no ...
Document
... Molecular energy levels split into many fine and hyperfine components. • 1Σ alkali dimers only display hyperfine splittings. • For nonrotating states, the zero-field splitting is due to the scalar spin-spin interaction and amounts to a few μK. • For N≠1 dimers, the zero-field splitting is dominated ...
... Molecular energy levels split into many fine and hyperfine components. • 1Σ alkali dimers only display hyperfine splittings. • For nonrotating states, the zero-field splitting is due to the scalar spin-spin interaction and amounts to a few μK. • For N≠1 dimers, the zero-field splitting is dominated ...