Chemical Equations - Salem Community Schools
... Balancing an Equation Is the equation balanced now? Two sodium atoms are on each side. How many oxygen atoms are on each side? You should be able to find four on each side. How about hydrogen atoms? Now two are on each side. Because one carbon atom is still on each side, the entire equation is balan ...
... Balancing an Equation Is the equation balanced now? Two sodium atoms are on each side. How many oxygen atoms are on each side? You should be able to find four on each side. How about hydrogen atoms? Now two are on each side. Because one carbon atom is still on each side, the entire equation is balan ...
Introduction - Bulgarian Chemical Communications
... of the potential with the reaction coordinate as a function of the energy of the reaction and the so called “intrinsic barrier”, ΔGo‡, i.e. the energy of activation when the reaction energy ΔG, is zero (for the sake of simplicity we assume ΔG ≈ ΔH). The equation predicts reduced kinetic barriers for ...
... of the potential with the reaction coordinate as a function of the energy of the reaction and the so called “intrinsic barrier”, ΔGo‡, i.e. the energy of activation when the reaction energy ΔG, is zero (for the sake of simplicity we assume ΔG ≈ ΔH). The equation predicts reduced kinetic barriers for ...
Reactions Balancing Chemical Equations uses Law of conservation
... Sum of oxidation numbers is equal to overall charge of molecule or ion: • For a neutral compound the sum of oxidation numbers equals zero. • For a polyatomic ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. Shared electrons are assigned to the more electronegative atom of t ...
... Sum of oxidation numbers is equal to overall charge of molecule or ion: • For a neutral compound the sum of oxidation numbers equals zero. • For a polyatomic ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. Shared electrons are assigned to the more electronegative atom of t ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displacement, double replacement, or metathesis reactions. These reactions are common in nature and are responsible for the formation of coral reefs in ocean waters ...
... reactions of this type involve the exchange of ions between ionic compounds in aqueous solution and are sometimes referred to as double displacement, double replacement, or metathesis reactions. These reactions are common in nature and are responsible for the formation of coral reefs in ocean waters ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... • What kind of covalent bonds, single, double, or triple, must this ion have so that the six shared electrons are used to attach the three O atoms to the S atom? ...
... • What kind of covalent bonds, single, double, or triple, must this ion have so that the six shared electrons are used to attach the three O atoms to the S atom? ...
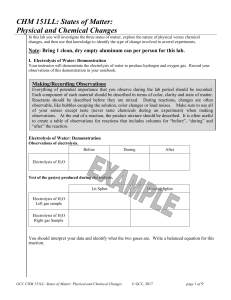
CHM 151LL: States of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
... able to classify a substance using these terms will help you identify the properties of the material. It helps to form a mental picture of a material so you can better understand how to describe it. For example, when someone says “atom”, you should visualize a single sphere. The word molecule means ...
... able to classify a substance using these terms will help you identify the properties of the material. It helps to form a mental picture of a material so you can better understand how to describe it. For example, when someone says “atom”, you should visualize a single sphere. The word molecule means ...
4_ Chemical reactions
... 4.6 Classification of Chemical Reactions There is no comprehensive classification scheme that would accommodate all known chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reacti ...
... 4.6 Classification of Chemical Reactions There is no comprehensive classification scheme that would accommodate all known chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reacti ...
Questions for Study
... standard enthalpy of formation (standard heat of formation) ( H fo ) enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a substance in its standard state from its elements in their reference forms and in their standard states (6.8) fuel* ...
... standard enthalpy of formation (standard heat of formation) ( H fo ) enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a substance in its standard state from its elements in their reference forms and in their standard states (6.8) fuel* ...
1. Write the balanced equation for the combustion of butane (C4H10
... 6. Solid copper is placed into a solution of silver nitrate. How many moles of Cu are needed to react with 3.50 moles of AgNO3? If 89.5 grams of Ag were produced, how many grams of Cu reacted? 7. Molten iron and carbon monoxide are produced in a blast furnace by the reaction of iron(III) oxide and c ...
... 6. Solid copper is placed into a solution of silver nitrate. How many moles of Cu are needed to react with 3.50 moles of AgNO3? If 89.5 grams of Ag were produced, how many grams of Cu reacted? 7. Molten iron and carbon monoxide are produced in a blast furnace by the reaction of iron(III) oxide and c ...
Ionic Liquids Beyond Simple Solvents: Glimpses at the State of the
... by ones being derived from l-proline.[39, 40] The example shown in Scheme 3 is one in which the organocatalyst is covalently attached to an IL cation. In a recent review, Headley and Ni have called this concept ionic-liquidsupported (ILS) catalysis.[41] Apart from this organocatalytic niche, hardly ...
... by ones being derived from l-proline.[39, 40] The example shown in Scheme 3 is one in which the organocatalyst is covalently attached to an IL cation. In a recent review, Headley and Ni have called this concept ionic-liquidsupported (ILS) catalysis.[41] Apart from this organocatalytic niche, hardly ...
幻灯片 1
... According to a rule of formulated in 1875 by the Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev, base-induced elimination reactions generally give the more highly substituted (more stable) alkene product. For example: ...
... According to a rule of formulated in 1875 by the Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev, base-induced elimination reactions generally give the more highly substituted (more stable) alkene product. For example: ...
File
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
sideonnotes
... ammonia is often overused and results in toxic runoff that can result in algal blooms, it remains a very important staple for food production and can be used relatively safely. In light of the biological process that is used to form ammonia and other complex molecules from dinitrogen, we seek to und ...
... ammonia is often overused and results in toxic runoff that can result in algal blooms, it remains a very important staple for food production and can be used relatively safely. In light of the biological process that is used to form ammonia and other complex molecules from dinitrogen, we seek to und ...
Prep UK-intro.p65
... 255 recognition of: - molecular ion 256 - fragments with the help of a table 257 - typical isotope distribution ...
... 255 recognition of: - molecular ion 256 - fragments with the help of a table 257 - typical isotope distribution ...
Ground- and Excited-State Properties of DNA Base Molecules from
... optical response.12–16 In contrast to time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT), GW and BSE-based approaches yield reliable results for both localized and extended systems.17,18 Indeed, DFT calculations using a plane-wave basis set were recently performed for DNA base pairs,19 various assembl ...
... optical response.12–16 In contrast to time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT), GW and BSE-based approaches yield reliable results for both localized and extended systems.17,18 Indeed, DFT calculations using a plane-wave basis set were recently performed for DNA base pairs,19 various assembl ...
Ch13 Lecture
... Interesting Alkenes in Food and Medicine • Lycopene, the red pigment in tomatoes and watermelons, has 13 double bonds. • Lycopene is an antioxidant, a compound that ...
... Interesting Alkenes in Food and Medicine • Lycopene, the red pigment in tomatoes and watermelons, has 13 double bonds. • Lycopene is an antioxidant, a compound that ...
Complexation Reactions
... Palladium(II) tends to form complexes with coordination number 4. A compound has the composition PdCl2 · 3 NH3. (a) Write the formula for this compound that best shows the coordination structure. (b) When an aqueous solution of the compound is treated with excess AgNO3(aq), how many moles of AgCl(s) ...
... Palladium(II) tends to form complexes with coordination number 4. A compound has the composition PdCl2 · 3 NH3. (a) Write the formula for this compound that best shows the coordination structure. (b) When an aqueous solution of the compound is treated with excess AgNO3(aq), how many moles of AgCl(s) ...
THERMAL ANALYSIS
... TGA: Thermogravimetric methods are largely limited to decomposition & oxidation reaction & to such physical process like vaporization, sublimation, desorption. Qualitative analysis: Most important application of thermogravimetric methods are found in study of polymers.Thermogram provides information ...
... TGA: Thermogravimetric methods are largely limited to decomposition & oxidation reaction & to such physical process like vaporization, sublimation, desorption. Qualitative analysis: Most important application of thermogravimetric methods are found in study of polymers.Thermogram provides information ...