The endocrine system
... • Drop in hormone level triggers a chain reaction to increase secretion, for example. • 1 – Blood level of hormone drops. • 2 – Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland. • 3 – Gland stimulates more hormone. • 4 – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormone stops. Nerv ...
... • Drop in hormone level triggers a chain reaction to increase secretion, for example. • 1 – Blood level of hormone drops. • 2 – Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland. • 3 – Gland stimulates more hormone. • 4 – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormone stops. Nerv ...
Introduction to Endocrinology Body communicating system 1
... 1-Nural: act locally to central cell function, in which chemical "neurotransmitters" are released at the synaptic junction. 2-Endocrine: in which glands or specialized cells release into blood circulating chemicals "hormones" that influence the function of cells at other location in the body. 3-Neur ...
... 1-Nural: act locally to central cell function, in which chemical "neurotransmitters" are released at the synaptic junction. 2-Endocrine: in which glands or specialized cells release into blood circulating chemicals "hormones" that influence the function of cells at other location in the body. 3-Neur ...
Regulation (Endocrine)
... Diabetes -- A Disease of the Endocrine System Diabetes -- a disease that involves a decreased ability to use glucose. Some types of diabetes involve the hormone called insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas. Its function is to allow glucose to enter cell membranes. If there is no insulin the g ...
... Diabetes -- A Disease of the Endocrine System Diabetes -- a disease that involves a decreased ability to use glucose. Some types of diabetes involve the hormone called insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas. Its function is to allow glucose to enter cell membranes. If there is no insulin the g ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular activity causing a physiological response ...
... The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular activity causing a physiological response ...
The Endocrine System
... CNS controls hypothalamus, which regulates release of hormones from pituitary Hormones can act on nearby cells or be transported through blood until they reach a cell with matching receptor (target cell) Target cell carries the receptor protein which will bind to hormone, changing its shape Cellular ...
... CNS controls hypothalamus, which regulates release of hormones from pituitary Hormones can act on nearby cells or be transported through blood until they reach a cell with matching receptor (target cell) Target cell carries the receptor protein which will bind to hormone, changing its shape Cellular ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... the release of milk from the mother’s mammary glands when a baby is nursing. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Human growth hormone (hGH) stimulates body growth by promoting cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth. Disorders associated with improper levels of hGH are pituitary dwarfism, giantism, a ...
... the release of milk from the mother’s mammary glands when a baby is nursing. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Human growth hormone (hGH) stimulates body growth by promoting cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth. Disorders associated with improper levels of hGH are pituitary dwarfism, giantism, a ...
File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
... (e.g., cortisol) mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone) gonadocorticoids epinephrine and norepinephrine insulin ...
... (e.g., cortisol) mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone) gonadocorticoids epinephrine and norepinephrine insulin ...
Definition Hormone - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... cells of the body. Glands function in an orderly fashion with the nervous system, which plays an important role in the secretion of certain hormones . ...
... cells of the body. Glands function in an orderly fashion with the nervous system, which plays an important role in the secretion of certain hormones . ...
The Endocrine System
... Insulin, decreases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to form glycogen-stored energy in the muscles- from glucose. ...
... Insulin, decreases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to form glycogen-stored energy in the muscles- from glucose. ...
Lesson 2.3: Chemical Communication Preface While the nervous
... involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and regulate many of the body’s functions, including growth and development, metabolism and reproduction. Hormones are secreted by tissues in the body referred to as glands. Endocrine gla ...
... involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and regulate many of the body’s functions, including growth and development, metabolism and reproduction. Hormones are secreted by tissues in the body referred to as glands. Endocrine gla ...
File
... What Does the Endocrine System Do? • Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's speci ...
... What Does the Endocrine System Do? • Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's speci ...
Endocrine System Guide
... increased ____________________ increased ____________________ increase in the ____________________ release of ____________________ ____________________hands and palms ...
... increased ____________________ increased ____________________ increase in the ____________________ release of ____________________ ____________________hands and palms ...
How does the endocrine system help maintain
... How does the endocrine system help maintain homeostasis ? ...
... How does the endocrine system help maintain homeostasis ? ...
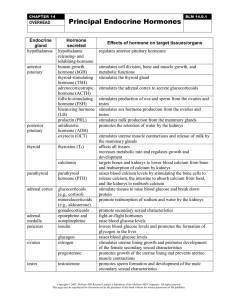
Endocrine glands and their parts 1. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 2
... or flight" reaction to stress situations by modifying metabolic rates and muscle tone. Neurohypophysis (3) That part of the pituitary gland that produces an antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Ovary (female) (20) Produce the hormones estrogen, which controls prenatal sexual differentiation, developme ...
... or flight" reaction to stress situations by modifying metabolic rates and muscle tone. Neurohypophysis (3) That part of the pituitary gland that produces an antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Ovary (female) (20) Produce the hormones estrogen, which controls prenatal sexual differentiation, developme ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... • Just like the nervous system, the endocrine controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
... • Just like the nervous system, the endocrine controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... of glands located throughout the body that secrete hormones Endocrine Glands: – Produce hormones Chemical ...
... of glands located throughout the body that secrete hormones Endocrine Glands: – Produce hormones Chemical ...
Objective: You will be able to identify all of the glands of the
... of the anterior and posterior pituitary hormones. Do Now: • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
... of the anterior and posterior pituitary hormones. Do Now: • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
Lecture 15
... Lecture 15 - The Endocrine Organs I. Endocrine Overview: Functions and Organs A. General Functions 1. hormones 2. glands 3. hormones metabolism of ...
... Lecture 15 - The Endocrine Organs I. Endocrine Overview: Functions and Organs A. General Functions 1. hormones 2. glands 3. hormones metabolism of ...
The Endocrine System
... The Hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary gland’s release of hormones, which in turn regulates other endocrine gland hormone secretion. II. The nervous system regulates some glands ...
... The Hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary gland’s release of hormones, which in turn regulates other endocrine gland hormone secretion. II. The nervous system regulates some glands ...
Chapter 18
... Female: Ovaries • Estrogen and Progesterone – Uterine and mammary gland development and function, external genitalia structure, secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle ...
... Female: Ovaries • Estrogen and Progesterone – Uterine and mammary gland development and function, external genitalia structure, secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle ...
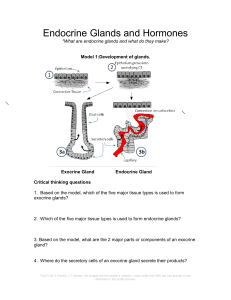
Physioactivity 1: Endocrine glands
... 1. Based on the model, which of the five major tissue types is used to form exocrine glands? ...
... 1. Based on the model, which of the five major tissue types is used to form exocrine glands? ...
The Endocrine System
... You’ve probably heard of diabetes Type 1, that happens when the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to control your blood sugar. The thymus helps your body fight off infections. It’s a key player in the production of T-cells, which identify and kill germs in your blood. ...
... You’ve probably heard of diabetes Type 1, that happens when the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to control your blood sugar. The thymus helps your body fight off infections. It’s a key player in the production of T-cells, which identify and kill germs in your blood. ...
The Endocrine System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to regulate Calcium (Ca+) and phosphate ion levels in blood ...
... butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to regulate Calcium (Ca+) and phosphate ion levels in blood ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.