* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The endocrine system
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
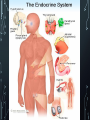
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM MR. PRALL ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Function – To secrete hormones – chemical messengers that coordinate and direct target cells and organs. • Ductless • Regulates • • • • • • • Metabolism Growth and development Tissue function Sexual function Reproduction Sleep Mood NEGATIVE FEEDBACK • Drop in hormone level triggers a chain reaction to increase secretion, for example. • 1 – Blood level of hormone drops. • 2 – Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland. • 3 – Gland stimulates more hormone. • 4 – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormone stops. Nervous Control In some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin.) *Homeostasis – Known as balance. Your body wants to stay in balance, so more, or fewer, hormones will be released to accomplish this. PITUITARY GLAND • Tiny structure the size of a “pea”, or “grape”. • Located at the base of the brain. • Connected to the hypothalamus. • Divided into anterior and posterior. • Known as the “master gland”. PITUITARY GLAND CONT. • Posterior pituitary lobe – • Vasopressin – Converts to ADH (antdiuretic hormone) in the bloodstream, acts on kidney to concentrate urine and preserve H20 in the body. • Oxytocin – Released during childbirth causing contractions of the uterus. • Anterior pituitary lobe – • • • • Somatotropin – Responsible for growth and development (Growth Hormone) Prolactin – Develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk for breast feeding. Follicle Stimulating Hormone – (FSH) Stimulates growth of Graafin follicle. Luteinizing Hormone – (LH) Stimulates ovulation and formation of corpus luteum, which produces progesterone in females. • Adrenocorticotropic Hormone – (ACTH) Stimulates the adrenal cortex. Regulates cortisol, which helps manage stress. PINEAL GLAND • Located in the center of the brain, and takes the shape of a “pine cone”. • Also referred to as the “third eye”. • Controls the body’s biological clock (sleep) by releasing a hormone called serotonin. THYROID GLAND • Butterfly-shaped mass of tissue, shaped like an H. • Located in the neck. • Main hormone, thyroxine, which is converted to triiodothyronine, which then helps with brain development, metabolism, digestive system, and muscle control • Secrets TSH, which helps control the rate of metabolism. • Produces calcitonin, which helps lower the levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood and promotes the formation of bone. PARATHYROID GLANDS • Four glands each the size of a grain of rice. • Smallest glands of the endocrine system. • Produce parathormone, which help control blood calcium levels. THYMUS • Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ. • Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart. • Begins to disappear after puberty. • Plays a key role in the development of T-lymphocytes, or T-Cells. ADRENAL GLANDS • Located on top of each kidney, and there are two parts; adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. • Adrenal cortex – Secretes hormones known as corticoids, which help with water and stress balance. • Adrenal medulla – Secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. • Adrenaline is a powerful cardiac stimulant – “fight”, or “flight” hormones that prepared the body for emergency situations. FIGHT OR FLIGHT • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtRrxNTnyh8 GONADS • Ovaries in females, testes in males. • Estrogen – Development of female reproductive organs, secondary sex characteristics. • Progesterone – Plays a part in the menstrual cycle. • Testosterone – Male reproductive organs and secondary sex characteristics. PANCREAS • Located behind the stomach. • Has an endocrine and exocrine function. • Endocrine – releases juices directly into the bloodstream. • Exocrine – releases juices into ducts. • Involved in the production of insulin. • Promotes utilization of glucose by the cells, fatty acid and amino acid transport, and facilitates protein synthesis. HOW THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM WORKS • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HXPCQBD_WGI THE END