Slide ()
... Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion. Myriad neural inputs influence hypothalamic secretion of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH stimulates release of thyrotropin (TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone) from the anterior pituitary; TSH stimulates the synthesis and release of the thyroid hormone ...
... Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion. Myriad neural inputs influence hypothalamic secretion of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH stimulates release of thyrotropin (TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone) from the anterior pituitary; TSH stimulates the synthesis and release of the thyroid hormone ...
Slide ()
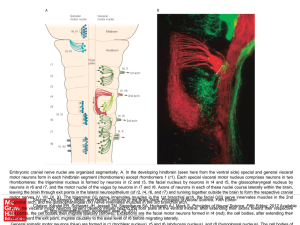
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
... • nervous and endocrine systems are similar • nervous system ...
... • nervous and endocrine systems are similar • nervous system ...
Endocrine System Introduction
... • Hormones bind only to specific sites on the plasma membrane of those Target cells: Receptors • The Target cell becomes active once the hormone is bound to its specific receptor. ...
... • Hormones bind only to specific sites on the plasma membrane of those Target cells: Receptors • The Target cell becomes active once the hormone is bound to its specific receptor. ...
Hunger
... body will increase hunger and decrease energy expenditure – Basic Metabolic Rate (BMR) – the rate your body burns calories while at rest ...
... body will increase hunger and decrease energy expenditure – Basic Metabolic Rate (BMR) – the rate your body burns calories while at rest ...
Nature of horomes
... • Chemical messenger released by one type of cells and carried in the bloodstream to act on specific target cells ...
... • Chemical messenger released by one type of cells and carried in the bloodstream to act on specific target cells ...
BehNeuro11#2 (2) - Biology Courses Server
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
hormones - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... THYROID GLAND • Thyroglobulin: converted to T3 & T4 • almost all cells are target of THs • calcitonin • metabolic rate, growth & development TRH: Thyroid-releasing hormone http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/hypopit/tsh.html ...
... THYROID GLAND • Thyroglobulin: converted to T3 & T4 • almost all cells are target of THs • calcitonin • metabolic rate, growth & development TRH: Thyroid-releasing hormone http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/hypopit/tsh.html ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... • The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Even when you are sleeping the nervous system is busy regulating your body functions. The nervous system controls your emotions, movements, thinking and behavior. ...
... • The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Even when you are sleeping the nervous system is busy regulating your body functions. The nervous system controls your emotions, movements, thinking and behavior. ...
Figure 45.4 - dannenbergapbiology
... (a) Short-term stress response and the adrenal medulla Stress Spinal cord (cross section) ...
... (a) Short-term stress response and the adrenal medulla Stress Spinal cord (cross section) ...
File
... Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cortisol, a so-called "stress hormone," is vital to survival. It helps maintain blood pressure and blood glucose levels. Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH - TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroid ...
... Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cortisol, a so-called "stress hormone," is vital to survival. It helps maintain blood pressure and blood glucose levels. Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH - TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroid ...
ch 45 clicker questions
... c) elicit the same biological response from all of their target cells. d) are carried to target cells in the blood. e) are produced by endocrine glands. ...
... c) elicit the same biological response from all of their target cells. d) are carried to target cells in the blood. e) are produced by endocrine glands. ...
Stress - Social Sciences @ Groby
... when stressors are received by the brain. A region of the hypothalamus is activated (paraventricular nucleus – PVN), and chemical messengers are produced (CRF). These are released into the bloodstream in response to the stressor. ...
... when stressors are received by the brain. A region of the hypothalamus is activated (paraventricular nucleus – PVN), and chemical messengers are produced (CRF). These are released into the bloodstream in response to the stressor. ...
Hormonal Regulation of Growth, Development, and Metabolism
... – All the energy of glucose is transferred to heat and ATP, (no storing of glucose) and ATP is consumed during activity, therefore there is no weight gain. ...
... – All the energy of glucose is transferred to heat and ATP, (no storing of glucose) and ATP is consumed during activity, therefore there is no weight gain. ...
Functions it Regulates/Affects
... gland in the strict sense because it does not make the peptide hormones it releases. Instead, it simply acts as a storage area for hormones made by ...
... gland in the strict sense because it does not make the peptide hormones it releases. Instead, it simply acts as a storage area for hormones made by ...
CNS Thalamus,Hypo,Epi
... situated rostral (superior) to brainstem, one in each cerebral hemisphere. Between them is third ventricle. They may connect with interthalamic connection (adhesion). It is an important relay and integrative station for information passing to: All areas of cerebral cortex. Basal ganglia. Hypothalamu ...
... situated rostral (superior) to brainstem, one in each cerebral hemisphere. Between them is third ventricle. They may connect with interthalamic connection (adhesion). It is an important relay and integrative station for information passing to: All areas of cerebral cortex. Basal ganglia. Hypothalamu ...
Unit IX: Animal Structure and Function, Part III
... + endocrine system: slower means of communication via hormones - hormone: chemical signal secreted into body fluids to communicate regulatory messages within the body - neurosecretory cells: nerve cells that secrete hormones • regulation of several physiological processes involves overlap + each sys ...
... + endocrine system: slower means of communication via hormones - hormone: chemical signal secreted into body fluids to communicate regulatory messages within the body - neurosecretory cells: nerve cells that secrete hormones • regulation of several physiological processes involves overlap + each sys ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do nerves play? Electrical cables made up of millions of axons connecting the CNS with body’s sensory receptors, muscles, and glands 4. What are the 3 ...
... 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do nerves play? Electrical cables made up of millions of axons connecting the CNS with body’s sensory receptors, muscles, and glands 4. What are the 3 ...
Regulatory systems
... related. Many nervous systems have neurosecretory cells that secrete hormones which act on some region of the organism. Several chemicals serve both as hormones and as signals in the nervous system. There are also several regulatory processes that overlap between the endocrine and the nervous system ...
... related. Many nervous systems have neurosecretory cells that secrete hormones which act on some region of the organism. Several chemicals serve both as hormones and as signals in the nervous system. There are also several regulatory processes that overlap between the endocrine and the nervous system ...
File
... b) decreases lipid hydrolysis (lipolysis) c) increases glucose levels d) retention of electrolytes by the kidneys e) increases osteoclast activity 8) This hormone acts on the intestines and causes increased calcium absorption: a) calcitonin b) calcitriol c) thyroxine d) pancreatic polypeptide e) co ...
... b) decreases lipid hydrolysis (lipolysis) c) increases glucose levels d) retention of electrolytes by the kidneys e) increases osteoclast activity 8) This hormone acts on the intestines and causes increased calcium absorption: a) calcitonin b) calcitriol c) thyroxine d) pancreatic polypeptide e) co ...
File
... • Water- and lipid-soluble hormones differ in their paths through a body • Water-soluble hormones are secreted by exocytosis, travel freely in the bloodstream, and bind to cellsurface receptors • Lipid-soluble hormones diffuse across cell membranes, travel in the bloodstream bound to transport prote ...
... • Water- and lipid-soluble hormones differ in their paths through a body • Water-soluble hormones are secreted by exocytosis, travel freely in the bloodstream, and bind to cellsurface receptors • Lipid-soluble hormones diffuse across cell membranes, travel in the bloodstream bound to transport prote ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.