Chapter 15-A Functional Organization of the
... • Sympathetic neurons stimulate the release of epinephrine and smaller amounts of norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla • Epinephrine and norepinephrine prepare the body to respond to stressful conditions • Once the stressful stimuli are removed, less epinephrine is released as a result of decreas ...
... • Sympathetic neurons stimulate the release of epinephrine and smaller amounts of norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla • Epinephrine and norepinephrine prepare the body to respond to stressful conditions • Once the stressful stimuli are removed, less epinephrine is released as a result of decreas ...
Tropic Hormones
... Blood with tropic hormones enters portal vein Hypothalamic tropic hormones access anterior pituitary secretory cells through capillary beds alter release of anterior pituitary tropic hormones ...
... Blood with tropic hormones enters portal vein Hypothalamic tropic hormones access anterior pituitary secretory cells through capillary beds alter release of anterior pituitary tropic hormones ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... 29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones The hypothalamus interacts with the nervous and endocrine systems. • The hypothalamus is a gland found in the brain. – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland ...
... 29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones The hypothalamus interacts with the nervous and endocrine systems. • The hypothalamus is a gland found in the brain. – a structure of both the nervous and endocrine systems – produces releasing hormones, sent to pituitary gland ...
Introduction to Endocrinology
... – Any substance normally produced by specialized cells in some part of the body, carried by the blood stream to another part, where it effects the body as a whole – Vehicles for intracellular & extracellular communication ...
... – Any substance normally produced by specialized cells in some part of the body, carried by the blood stream to another part, where it effects the body as a whole – Vehicles for intracellular & extracellular communication ...
File
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...
... STRUCTURE OF A NEURONE Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the f ...
Unit IV: Regulation Endocrine System
... – nervous - electrical – endocrine - only chemical 2. Speed and persistence of response – nervous - reacts quickly; stops quickly – endocrine - reacts slowly ...
... – nervous - electrical – endocrine - only chemical 2. Speed and persistence of response – nervous - reacts quickly; stops quickly – endocrine - reacts slowly ...
Hormones of the Body
... This bilobed gland contains many follicles. A follicle is a group of cells encircling a lumen. The lumen contains material called colloid (a glycoprotein) within it. As hormones are produced by the cells, the hormones are either released into the colloid or directly into the blood. There are also ex ...
... This bilobed gland contains many follicles. A follicle is a group of cells encircling a lumen. The lumen contains material called colloid (a glycoprotein) within it. As hormones are produced by the cells, the hormones are either released into the colloid or directly into the blood. There are also ex ...
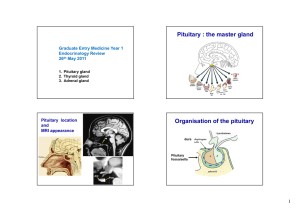
Pituitary : the master gland Organisation of the pituitary
... PRL release is increased by suckling and stress ...
... PRL release is increased by suckling and stress ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that ...
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that ...
Endocrine System Study Guide Regulation
... are considered a special type of hormone because they are made by every cell in the body, instead of specialized glands, act locally, prostaglandins are not really “hormones” as they exert their effects on nearby cells instead of being carried by the bloodstream but are considered because they have ...
... are considered a special type of hormone because they are made by every cell in the body, instead of specialized glands, act locally, prostaglandins are not really “hormones” as they exert their effects on nearby cells instead of being carried by the bloodstream but are considered because they have ...
hypothalamic-pituitary axis
... Able to stop oral hypoglycaemics Remains free of symptoms (2006) ...
... Able to stop oral hypoglycaemics Remains free of symptoms (2006) ...
ENDOCRINE: Endocrine glands Ductless Act with nervous system to
... o Is just a storage organ, not a true producing hormone gland, receives hormones from hypothalamus o Neural connection to hypothalamus o Neural hormones include oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic) o Transported to posterior, stored till neural stimulus o Portal vein carries releasing and inhibiting horm ...
... o Is just a storage organ, not a true producing hormone gland, receives hormones from hypothalamus o Neural connection to hypothalamus o Neural hormones include oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic) o Transported to posterior, stored till neural stimulus o Portal vein carries releasing and inhibiting horm ...
23-1
... Posterior Pituitary Gland (Neurohypophysis) • Does not synthesize hormones • Consists of axon terminals of hypothalamic neurons • Neurons release two neurotransmitters that enter capillaries – antidiuretic hormone – oxytocin ...
... Posterior Pituitary Gland (Neurohypophysis) • Does not synthesize hormones • Consists of axon terminals of hypothalamic neurons • Neurons release two neurotransmitters that enter capillaries – antidiuretic hormone – oxytocin ...
9.2 Hormonal Regulation - Mrs. Franklin`s Classroom
... Thyroid Gland and Calcium The thyroid gland releases hormones (i.e. parathyroid hormone & Calcitonin) that can help control the levels of calcium that circulate in the blood. If calcium levels are too high – calcitonin is released If calcium levels are too low – parathyroid hormone is released. ...
... Thyroid Gland and Calcium The thyroid gland releases hormones (i.e. parathyroid hormone & Calcitonin) that can help control the levels of calcium that circulate in the blood. If calcium levels are too high – calcitonin is released If calcium levels are too low – parathyroid hormone is released. ...
hormones endocrine system
... Members of the same animal species sometimes communicate with pheromones, chemicals that are released into the environment ...
... Members of the same animal species sometimes communicate with pheromones, chemicals that are released into the environment ...
NEUROSCIENCE AND OBESITY
... appetite. When they become defective, however, they lead to morbid obesity. Recent research involving mice has revealed that activation of melanocortin-4 receptors in certain areas of the brain-the paraventricular hypothalamus and the amygdala-help reduce body fat by decreasing our desire to eat, ...
... appetite. When they become defective, however, they lead to morbid obesity. Recent research involving mice has revealed that activation of melanocortin-4 receptors in certain areas of the brain-the paraventricular hypothalamus and the amygdala-help reduce body fat by decreasing our desire to eat, ...
NeuroReview1
... lobes is the 3rd ventricle. Below lies the Hypothalamus, which exerts it’s effects by releasing hormones from the pituitary gland. (Pituitary actually means “snot”). ...
... lobes is the 3rd ventricle. Below lies the Hypothalamus, which exerts it’s effects by releasing hormones from the pituitary gland. (Pituitary actually means “snot”). ...
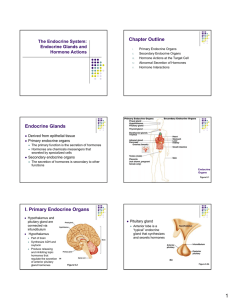
Endocrine Glands
... Hormone actions: Endocrine Paracrine Autocrine 4 structural groups: Protein/peptide = size variation secretion Steroids = cholesterol AA derivatives = tyr, tryp, glut FA derivatives = polyunsaturated ...
... Hormone actions: Endocrine Paracrine Autocrine 4 structural groups: Protein/peptide = size variation secretion Steroids = cholesterol AA derivatives = tyr, tryp, glut FA derivatives = polyunsaturated ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... responds to external stimuli through a reflex arc. A reflex arc is the pathway along the central nervous system where an impulse must travel to bring about a reflex; e.g., sneezing or coughing. Hormones work in conjunction with the nervous system, for example, in the digestive system, where insulin ...
... responds to external stimuli through a reflex arc. A reflex arc is the pathway along the central nervous system where an impulse must travel to bring about a reflex; e.g., sneezing or coughing. Hormones work in conjunction with the nervous system, for example, in the digestive system, where insulin ...
Evaporation
... of heat from the skin. During intense exercise* perspiration can occur at a rate of about 1.5 liters/hour resulting in removal of heat at a rate of ~870 Kcal/hr, or about 12 x basal heat production. ...
... of heat from the skin. During intense exercise* perspiration can occur at a rate of about 1.5 liters/hour resulting in removal of heat at a rate of ~870 Kcal/hr, or about 12 x basal heat production. ...
The Endocrine System - Appoquinimink High School
... such as fright, anger, caffeine, or low blood sugar • The cortex secretes corticosteroids such as cortisone, well-known as being anti-inflammatory, thus are prescribed for a number of conditions ...
... such as fright, anger, caffeine, or low blood sugar • The cortex secretes corticosteroids such as cortisone, well-known as being anti-inflammatory, thus are prescribed for a number of conditions ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide Outline: Endocrine System
... When hormone levels rise in the blood & it exerts its effects, negative feedback inhibits the system, decreasing hormone secretion Pituitary gland Location: at the base of the brain where a pituitary stalk attaches it to the hypothalamus Split into two lobes 1. Anterior pituitary (__________ l ...
... When hormone levels rise in the blood & it exerts its effects, negative feedback inhibits the system, decreasing hormone secretion Pituitary gland Location: at the base of the brain where a pituitary stalk attaches it to the hypothalamus Split into two lobes 1. Anterior pituitary (__________ l ...
Review for endocrine system
... 10. Water soluble hormones cannot get into the cell..how do they control intercellular processes? 11. What does target cell specificity refer to? 12. What determines the duration of a hormones effects? 13. How do hormones interact? 14. What stimulates the release of hormones? 15. What is the master ...
... 10. Water soluble hormones cannot get into the cell..how do they control intercellular processes? 11. What does target cell specificity refer to? 12. What determines the duration of a hormones effects? 13. How do hormones interact? 14. What stimulates the release of hormones? 15. What is the master ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.