Unit 2: The Human Brain and Body
... stimulation going to other parts of the brain. Hypothalamus- (under the thalamus). Involved in many aspects of behavior and ...
... stimulation going to other parts of the brain. Hypothalamus- (under the thalamus). Involved in many aspects of behavior and ...
The Endocrine Syetem
... Mineralocorticoids increase blood sodium, decrease blood potassium sex hormones - small amount secreted, female converted to estrigens ...
... Mineralocorticoids increase blood sodium, decrease blood potassium sex hormones - small amount secreted, female converted to estrigens ...
The Endocrine System - St. Ambrose School
... The Endocrine System is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not resp ...
... The Endocrine System is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not resp ...
Document
... into cellular spaces, then into blood Hormones in blood find a specific receptor (target organ cell) Example, thyroid gland ...
... into cellular spaces, then into blood Hormones in blood find a specific receptor (target organ cell) Example, thyroid gland ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... The anterior pituitary secretes (1) adrenocoticotropic hormone [ACTH] to stimulate the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones, (2 and 3) gonadotropins (FSH and LH) to stimulate the gonads in males and females both for regulation of reproductive system activities through h ...
... The anterior pituitary secretes (1) adrenocoticotropic hormone [ACTH] to stimulate the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones, (2 and 3) gonadotropins (FSH and LH) to stimulate the gonads in males and females both for regulation of reproductive system activities through h ...
A1982PA24800001
... secretion. After our stuçJies in parkinsonian patients, I enthusiastically recruited all of the endocrine fellows at Duke to come to Lebovitz’s home on Sunday mornings to take the drug. L-dopa is a powerful emetic and my bloodletting was frequently interrupted by the rush of my friends to the bathro ...
... secretion. After our stuçJies in parkinsonian patients, I enthusiastically recruited all of the endocrine fellows at Duke to come to Lebovitz’s home on Sunday mornings to take the drug. L-dopa is a powerful emetic and my bloodletting was frequently interrupted by the rush of my friends to the bathro ...
3 Test – Sp 09 – 8:00 1. When substances move from the peritubular
... 16. Hormones are released by this gland when someone is in stressful situations. It causes more oxygen to be sent to energy demanding cells. a. posterior lobe of the pituitary ...
... 16. Hormones are released by this gland when someone is in stressful situations. It causes more oxygen to be sent to energy demanding cells. a. posterior lobe of the pituitary ...
Endocrine System Glands - Fall River Public Schools
... remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat – Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose back into the blood • Also releases fatty acids from stored fats ...
... remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat – Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose back into the blood • Also releases fatty acids from stored fats ...
Endocrine System - El Camino College
... Mechanism of Hormonal Action – Peptide/Protein (hydrophilic) hormones bind with a membrane receptor stimulate a membrane enzyme Mechanism of Hormonal Action – Steroid/Thyroid (hydrophobic) hormones diffuse into the cells bind to a receptor protein mostly inside nucleus. Endocrine Gland Stimulus: 3-k ...
... Mechanism of Hormonal Action – Peptide/Protein (hydrophilic) hormones bind with a membrane receptor stimulate a membrane enzyme Mechanism of Hormonal Action – Steroid/Thyroid (hydrophobic) hormones diffuse into the cells bind to a receptor protein mostly inside nucleus. Endocrine Gland Stimulus: 3-k ...
Pituitary Gland
... Positive feedback in ovulation; LH & estradiol increase until egg released Negative feedback for the thyroid; T3 & T4 suppress TSH ...
... Positive feedback in ovulation; LH & estradiol increase until egg released Negative feedback for the thyroid; T3 & T4 suppress TSH ...
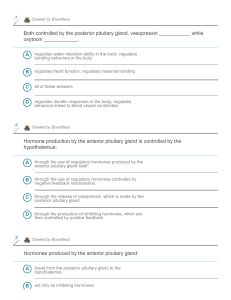
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... are both produced by alpha cells. ...
... are both produced by alpha cells. ...
Hypothalamus and Visceral Function
... Axons of these neurons converge toward the pituitary stalk ii. Abut the primary plexus of the portal system of the median eminence iii. Synthesize and secrete hypophysiotropic factors Hypophyseal portal system Primary plexus a. Drains interstitial space of the median eminence Hypophyseal portal vein ...
... Axons of these neurons converge toward the pituitary stalk ii. Abut the primary plexus of the portal system of the median eminence iii. Synthesize and secrete hypophysiotropic factors Hypophyseal portal system Primary plexus a. Drains interstitial space of the median eminence Hypophyseal portal vein ...
16 - Brazosport College
... Hormonal Stimulus Hormone release caused by another hormone (a tropic hormone). Hypothalamus ...
... Hormonal Stimulus Hormone release caused by another hormone (a tropic hormone). Hypothalamus ...
Name______________________________________ Due Date
... Compare and contrast Endocrine glands and Exocrine glands Compare and contrast Endocrine system and Nervous system Know the Endocrine glands location on a diagram of the Human Body (Diagram in notes) Describe the terms Receptor and Target cell and how they apply to the endocrine system Describe the ...
... Compare and contrast Endocrine glands and Exocrine glands Compare and contrast Endocrine system and Nervous system Know the Endocrine glands location on a diagram of the Human Body (Diagram in notes) Describe the terms Receptor and Target cell and how they apply to the endocrine system Describe the ...
The endocrine system (overview) The endocrine system (overview)
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
Document
... by one cell that affects a specific target cell with appropriate cell surface receptors. Chemistry of Hormones C. Action of Hormones D. Prostaglandins ...
... by one cell that affects a specific target cell with appropriate cell surface receptors. Chemistry of Hormones C. Action of Hormones D. Prostaglandins ...
UNIT 3 BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... • Sensory neuron and motor neuron communicate through interneuron • Pain Reflux—actually act before we feel the pain ...
... • Sensory neuron and motor neuron communicate through interneuron • Pain Reflux—actually act before we feel the pain ...
SChapter9
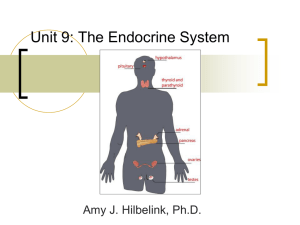
... Major Endocrine Organs- include pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus glands, pancreas and gonads. -Hypothalamus is also considered an endocrine organ, produces several hormones -Pituitary Gland- hangs from a stalk from the inferior surface of the hypothalamus, has two functio ...
... Major Endocrine Organs- include pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, and thymus glands, pancreas and gonads. -Hypothalamus is also considered an endocrine organ, produces several hormones -Pituitary Gland- hangs from a stalk from the inferior surface of the hypothalamus, has two functio ...
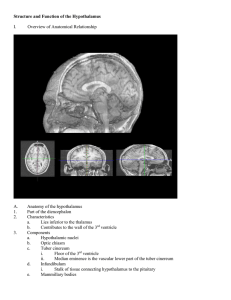
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.