endocrine
... • Hypothalamus “releasing hormones” and “inhibiting hormones” tells of central control by brain – GHRH (growth hormone RH) and GHIH (growth hormone IH) control GH from Ant. Pituitary – PRH (prolactin RH) and PIH control PL from Ant. ...
... • Hypothalamus “releasing hormones” and “inhibiting hormones” tells of central control by brain – GHRH (growth hormone RH) and GHIH (growth hormone IH) control GH from Ant. Pituitary – PRH (prolactin RH) and PIH control PL from Ant. ...
Endocrine match worksheet
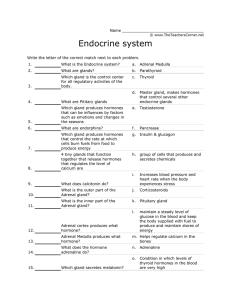
... Which gland is the control center for all regulatory activites of the body. ...
... Which gland is the control center for all regulatory activites of the body. ...
Endocrine system - aandersonbiology
... 4 tiny glands that function together that release hormones that regulates ...
... 4 tiny glands that function together that release hormones that regulates ...
Name Endocrine system Matching! Write the letter of the correct
... _____ 5. Which gland produces hormones that can be influences by factors such as emotions and changes in the seasons ...
... _____ 5. Which gland produces hormones that can be influences by factors such as emotions and changes in the seasons ...
HPA Axis Activation and Hippocampal Atrophy
... HPA axis activation begins with an increase in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) secretion by Paraventricular Nucleus (PVN) in hypothalamus and results in the release of adrenal cortex hormone, cortisol. Higher centers, such as cortex and limbic system, also involve in this reaction, especially ...
... HPA axis activation begins with an increase in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) secretion by Paraventricular Nucleus (PVN) in hypothalamus and results in the release of adrenal cortex hormone, cortisol. Higher centers, such as cortex and limbic system, also involve in this reaction, especially ...
20 Endocrine System - Orange Coast College
... most hormones are peptide hormones longer chains are called protein hormones Example: growth hormone type of lipid derived from cholesterol ...
... most hormones are peptide hormones longer chains are called protein hormones Example: growth hormone type of lipid derived from cholesterol ...
nervous system
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
presentation source
... This enzyme produces cyclic AMP (cAMP), which activates protein kinase enzymes within the cell cytoplasm. B. Other hormones may activate phospholipase C when they bind to their receptors. This leads to the release of inositol triphosphate (IP3), which stimulates the endoplasmic reticulum to release ...
... This enzyme produces cyclic AMP (cAMP), which activates protein kinase enzymes within the cell cytoplasm. B. Other hormones may activate phospholipase C when they bind to their receptors. This leads to the release of inositol triphosphate (IP3), which stimulates the endoplasmic reticulum to release ...
www.med.fsu.edu
... 1. Proteins are water soluble and therefore cannot pass through the cell membrane. Therefore nonsteroid hormones affect the activity of the cell via a secondary messenger system (see: lock and key model and cyclic ...
... 1. Proteins are water soluble and therefore cannot pass through the cell membrane. Therefore nonsteroid hormones affect the activity of the cell via a secondary messenger system (see: lock and key model and cyclic ...
58 XX Lecture Notes BLY 122 (O`Brien)
... 1. Pituitary is located at end of a stalk under the hypothalamus. Fig 47.13 2. Pituitary is the “Mastergland” gland, because it releases hormones that control other glands 3. Pituitary composed of 2 different glands: Anterior and Posterior Pituitary B. Controlling the Release of Glucocorticoids 1. E ...
... 1. Pituitary is located at end of a stalk under the hypothalamus. Fig 47.13 2. Pituitary is the “Mastergland” gland, because it releases hormones that control other glands 3. Pituitary composed of 2 different glands: Anterior and Posterior Pituitary B. Controlling the Release of Glucocorticoids 1. E ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system
... and sperm production in men. ii. LH in women stimulates ovulation. In men, LH is called interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) and this hormone influences the secretion of testosterone and other sex hormones in the testes. e. Beta Endorphins are similar to ACTH and have the same effect as morp ...
... and sperm production in men. ii. LH in women stimulates ovulation. In men, LH is called interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) and this hormone influences the secretion of testosterone and other sex hormones in the testes. e. Beta Endorphins are similar to ACTH and have the same effect as morp ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system part 2
... interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) and this hormone influences the secretion of testosterone and other sex hormones in the testes. Beta Endorphins are similar to ACTH and have the same effect as morphine and opiate drugs. Prolactin (PRL) is stimulated by prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) a ...
... interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) and this hormone influences the secretion of testosterone and other sex hormones in the testes. Beta Endorphins are similar to ACTH and have the same effect as morphine and opiate drugs. Prolactin (PRL) is stimulated by prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) a ...
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
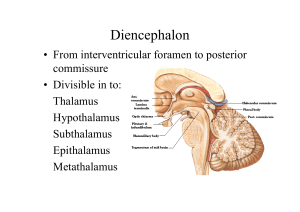
Diencephalon
... 1. From spinal cord & brainstem (via reticular formation) 2. Nucleus of tractus solitarius 3. Olfactory pathways 4. Limbic system 5. Locus coeruleus 6. From piriform cortex, orbital cortex 7. From subthalamus & zona incerta ...
... 1. From spinal cord & brainstem (via reticular formation) 2. Nucleus of tractus solitarius 3. Olfactory pathways 4. Limbic system 5. Locus coeruleus 6. From piriform cortex, orbital cortex 7. From subthalamus & zona incerta ...
Introduction 1
... having well defined effects on body functions. • Also, called ductless glands since their secretion is not conveyed along ducts but pass directly into blood and lymphatic vessels. ...
... having well defined effects on body functions. • Also, called ductless glands since their secretion is not conveyed along ducts but pass directly into blood and lymphatic vessels. ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... What are they? • Small protein-like molecules (peptides) • Used by neurons to communicate • Influence activity, act on neuronal surface receptors • NPSR- G-protein coupled receptor – Stimulates Ca++ and cAMP ...
... What are they? • Small protein-like molecules (peptides) • Used by neurons to communicate • Influence activity, act on neuronal surface receptors • NPSR- G-protein coupled receptor – Stimulates Ca++ and cAMP ...
Hormones
... and as a precursor of norepinephrine and epinephrine in the adrenal medulla. Dopamine is a potent inhibitor of PRL release by the lactotropes (and mammosomatotropes) of the anterior pituitary, and this effect is mediated by D2 receptors that are coupled to Giα inhibition of adenylate cyclase. ...
... and as a precursor of norepinephrine and epinephrine in the adrenal medulla. Dopamine is a potent inhibitor of PRL release by the lactotropes (and mammosomatotropes) of the anterior pituitary, and this effect is mediated by D2 receptors that are coupled to Giα inhibition of adenylate cyclase. ...
Dairy Cattle Breeding & Selection
... a. F.S.H. (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) to stimulate the ovary to produce an egg. b. L.H. (Luteinizing Hormone) to cause the follicle to rupture and release the egg. c. I.C.S.H. (in the male…Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone) to stimulate the interstitial cells to produce and release ...
... a. F.S.H. (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) to stimulate the ovary to produce an egg. b. L.H. (Luteinizing Hormone) to cause the follicle to rupture and release the egg. c. I.C.S.H. (in the male…Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone) to stimulate the interstitial cells to produce and release ...
O`Kane - LaGuardia Community College
... C. Inferior colliculi D. Superior colliculi 17. The diencephalon A. includes the hypothalamus, epithalamus, and thalamus. B. is superior to the brain stem. C. includes the midbrain, corpora quadrigemina, and cerebral peduncles. D. A and B are correct only. E. B and C are correct only. 18. The cell b ...
... C. Inferior colliculi D. Superior colliculi 17. The diencephalon A. includes the hypothalamus, epithalamus, and thalamus. B. is superior to the brain stem. C. includes the midbrain, corpora quadrigemina, and cerebral peduncles. D. A and B are correct only. E. B and C are correct only. 18. The cell b ...
Document
... The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to coordinate body functions and maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endo ...
... The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to coordinate body functions and maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endo ...
10 The Endocrine System
... The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to coordinate body functions and maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endo ...
... The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to coordinate body functions and maintain homeostasis. Endocrine glands release chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones affect the functioning of target organs at other locations in the body. The activity of many endo ...
2. Steroid Hormones
... Four kinds of steroid hormones differ in structure and action; they are the androgens (C19), the estrogens (C18), the progestins (C21), and the corticosteroids (C21). All are synthesized from cholesterol . ...
... Four kinds of steroid hormones differ in structure and action; they are the androgens (C19), the estrogens (C18), the progestins (C21), and the corticosteroids (C21). All are synthesized from cholesterol . ...
Endocrine System - Porterville College Home
... ______________________ can result. ________ swells the tissues behind the eyes causing the eye to bulge. IV. Parathyroid Gland _________ glands on the posterior side of the thyroid gland. Chief cells produce __________________________ Oxyphil cells _________________________________________. PTH incr ...
... ______________________ can result. ________ swells the tissues behind the eyes causing the eye to bulge. IV. Parathyroid Gland _________ glands on the posterior side of the thyroid gland. Chief cells produce __________________________ Oxyphil cells _________________________________________. PTH incr ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.