The Endocrine System (Chapter 16)
... Describe the cellular structure of the thyroid gland and explain the steps involved in the synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalit ...
... Describe the cellular structure of the thyroid gland and explain the steps involved in the synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalit ...
The Plasmatic System (Part II) - The American College of Orgonomy
... , parathormonewhich then acts on bone to rele~se stored calcium ions, on the gut toenhan:ce absorption of calcium, and on the' kidney to enhance calcium reabsorption. All these actions tend to bring the concentration of the cation back to normal, If the plasma calcium ion, level, becomes elevated, a ...
... , parathormonewhich then acts on bone to rele~se stored calcium ions, on the gut toenhan:ce absorption of calcium, and on the' kidney to enhance calcium reabsorption. All these actions tend to bring the concentration of the cation back to normal, If the plasma calcium ion, level, becomes elevated, a ...
Name ____ hr ____ January 2009 Unit 6: Hormones Monday
... 4. List & describe the 3 key events that take place in signaling for any hormone. ...
... 4. List & describe the 3 key events that take place in signaling for any hormone. ...
Biochemistry, Secretion, and Transport of Hormones
... hormones because they are derived from ___________. Stimulation of the chromaffin cells causes an influx of ________ ions, which causes the vesicles to merge with the plasma membrane and release the hormone by __________. Are catecholamines water soluble or lipid soluble? ...
... hormones because they are derived from ___________. Stimulation of the chromaffin cells causes an influx of ________ ions, which causes the vesicles to merge with the plasma membrane and release the hormone by __________. Are catecholamines water soluble or lipid soluble? ...
Lecture5
... thyroxin. The control of this hormone is on the rate of body metabolism. When thyroxin is administered, the rate of oxygen consumption increases, the amount of heat produced is also increased. Several human diseases are associated with the improper functioning of the thyroid gland. Some are associat ...
... thyroxin. The control of this hormone is on the rate of body metabolism. When thyroxin is administered, the rate of oxygen consumption increases, the amount of heat produced is also increased. Several human diseases are associated with the improper functioning of the thyroid gland. Some are associat ...
Pituitary Gland Hormones
... formed from breakdown of fats and protein during times of long term stress. ...
... formed from breakdown of fats and protein during times of long term stress. ...
Chapter 16 Raging Hormones: The Endocrine System
... Topping off the kidneys: The adrenal glands Also called suprarenals, the adrenal glands lie atop each kidney. The central area of each is called the adrenal medulla, and the outer layers are called the adrenal cortex. Each glandular area secretes different hormones. The cells of the cortex produce o ...
... Topping off the kidneys: The adrenal glands Also called suprarenals, the adrenal glands lie atop each kidney. The central area of each is called the adrenal medulla, and the outer layers are called the adrenal cortex. Each glandular area secretes different hormones. The cells of the cortex produce o ...
Functions it Regulates/Affects
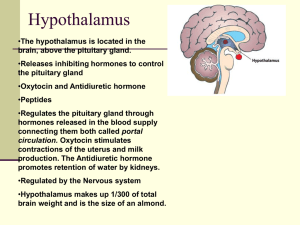
... Located: just above your spinal cord, near the center of your brain. ...
... Located: just above your spinal cord, near the center of your brain. ...
Document
... There are hormones of anterior, posterior and intermediate lobes of pituitary gland. ...
... There are hormones of anterior, posterior and intermediate lobes of pituitary gland. ...
The Endocrine System
... Thyroid hormone Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Major metabolic hormone Composed of two active iodine-containing hormones Thyroxine (T4)—secreted by thyroid follicles Triiodothyronine (T3)—conversion of T4 at target tissues Thyroid hormone disorders o Goiters Thyroid gland enlarges due to lack of i ...
... Thyroid hormone Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Major metabolic hormone Composed of two active iodine-containing hormones Thyroxine (T4)—secreted by thyroid follicles Triiodothyronine (T3)—conversion of T4 at target tissues Thyroid hormone disorders o Goiters Thyroid gland enlarges due to lack of i ...
VESTIBULAR MODULATION OF THYROID FUNCTION IN FORCED
... THYROID GLAND IT’S METABOLIC ROLES Thyroid gland is one of the largest glands (15-20 gms in adult) in endocrine system. The butter fly shaped gland located immediately below the larynx on each side anterior to trachea. It has 2 lobes connected by isthmus (figure 1). When the TSH from the hypothalamu ...
... THYROID GLAND IT’S METABOLIC ROLES Thyroid gland is one of the largest glands (15-20 gms in adult) in endocrine system. The butter fly shaped gland located immediately below the larynx on each side anterior to trachea. It has 2 lobes connected by isthmus (figure 1). When the TSH from the hypothalamu ...
Sample MCQs and EMQs
... posterior border of mylohyoid True The facial artery and vein are divided as they course through the deep part of the gland False The hypoglossal nerve is seen to loop under the ...
... posterior border of mylohyoid True The facial artery and vein are divided as they course through the deep part of the gland False The hypoglossal nerve is seen to loop under the ...
4. Anatomy of Phonation
... Thyroepiglottis: also known as the superior thyroarytenoid muscle. Some anatomists say this muscle is not present in all individuals. It originates higher on the internal surface of the thyroid cartilage and has a more oblique direction back down toward the muscular process of the arytenoid where it ...
... Thyroepiglottis: also known as the superior thyroarytenoid muscle. Some anatomists say this muscle is not present in all individuals. It originates higher on the internal surface of the thyroid cartilage and has a more oblique direction back down toward the muscular process of the arytenoid where it ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... neuro- 5 nerve (neurohypophysis: also called the posterior pituitary, it is an extension of the brain) oxy- 5 sharp, acid (oxytocin: a hormone that induces contractions of the uterine muscles and causes the mammary glands to eject milk during nursing) ...
... neuro- 5 nerve (neurohypophysis: also called the posterior pituitary, it is an extension of the brain) oxy- 5 sharp, acid (oxytocin: a hormone that induces contractions of the uterine muscles and causes the mammary glands to eject milk during nursing) ...
Anatomy - head and neck
... a. The surgeon would make a cut at the temporal area to the depth of deep temporal fascia, and slide along (above the fascia) to the arch b. The surgeon would make a cut at the temporal area to the depth of the temporalis muscle, and slide along the muscle to the arch c. The surgeon would make a cut ...
... a. The surgeon would make a cut at the temporal area to the depth of deep temporal fascia, and slide along (above the fascia) to the arch b. The surgeon would make a cut at the temporal area to the depth of the temporalis muscle, and slide along the muscle to the arch c. The surgeon would make a cut ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and
... lateral aspects of pharynx, larynx, oesophagus and trachea like a shield. It has been calculated that in a single minute, for each hundred grams of gland substance, about 560ml of blood circulates through the gland and is five and half times more vascular than the kidney. Apart from its significant ...
... lateral aspects of pharynx, larynx, oesophagus and trachea like a shield. It has been calculated that in a single minute, for each hundred grams of gland substance, about 560ml of blood circulates through the gland and is five and half times more vascular than the kidney. Apart from its significant ...
The Endocrine System
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands* Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Jebmh.com Original Article - journal of evidence based medicine
... lateral aspects of pharynx, larynx, oesophagus and trachea like a shield. It has been calculated that in a single minute, for each hundred grams of gland substance, about 560ml of blood circulates through the gland and is five and half times more vascular than the kidney. Apart from its significant ...
... lateral aspects of pharynx, larynx, oesophagus and trachea like a shield. It has been calculated that in a single minute, for each hundred grams of gland substance, about 560ml of blood circulates through the gland and is five and half times more vascular than the kidney. Apart from its significant ...
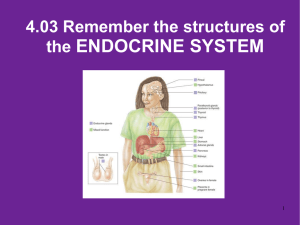
4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
... which produces progesterone in femalesTarget organs- testes, male and ovaries , females 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system ...
... which produces progesterone in femalesTarget organs- testes, male and ovaries , females 4.03 Remember the structures of the endocrine system ...
chemical coordination and integration
... It is the largest endocrine gland which is attached to trachea below larynx. It is bilobed or H-shaped. Thyroid secretes thyroxin. Iodine is required for the production of this hormone. The thyroid gland is composed of follicles and stromal tissues. Each thyroid follicle is composed of follicular ce ...
... It is the largest endocrine gland which is attached to trachea below larynx. It is bilobed or H-shaped. Thyroid secretes thyroxin. Iodine is required for the production of this hormone. The thyroid gland is composed of follicles and stromal tissues. Each thyroid follicle is composed of follicular ce ...
Thyroid Gland
... • Caused by hypothyroidism in adults • Results in physical and mental slugishness ...
... • Caused by hypothyroidism in adults • Results in physical and mental slugishness ...
16 - Brazosport College
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... pituitary (adenohypophysis) to secrete hormones. Inhibiting hormones prevent the anterior pituitary from secreting hormones. ...
... pituitary (adenohypophysis) to secrete hormones. Inhibiting hormones prevent the anterior pituitary from secreting hormones. ...
glands
... – cerebral cortex signals the salivatory nuclei in brainstem---(CN 7 & 9) – parasympathetic nn. (CN 7 & 9) ...
... – cerebral cortex signals the salivatory nuclei in brainstem---(CN 7 & 9) – parasympathetic nn. (CN 7 & 9) ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.













![[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003074182_1-7b4854fcd3d98bd44f6106e01e2c8923-300x300.png)