Larynx
... Fibres from upper section of NUCLEUS AMBIGUUS Join 9th nerve i.e. glossopharyngeal nerve and fibres from inferior portion of nucleus join ACCESORY NERVE i.e. XI nerve. 9 10 11 are intricately related nerves in medulla. Vagus has superior and inferior ganglion The vagus nerve leaves the skull base vi ...
... Fibres from upper section of NUCLEUS AMBIGUUS Join 9th nerve i.e. glossopharyngeal nerve and fibres from inferior portion of nucleus join ACCESORY NERVE i.e. XI nerve. 9 10 11 are intricately related nerves in medulla. Vagus has superior and inferior ganglion The vagus nerve leaves the skull base vi ...
BS1060
... Effects of Hormones • In all cases activation of the receptor can lead to a cascade of related and consequential molecular events inside the cell. • Events including generation of second messengers, changes in ion fluxes, activation or inhibition of protein kinases, activation or inhibition of tran ...
... Effects of Hormones • In all cases activation of the receptor can lead to a cascade of related and consequential molecular events inside the cell. • Events including generation of second messengers, changes in ion fluxes, activation or inhibition of protein kinases, activation or inhibition of tran ...
Bio 100-Ch 15
... C.lowers the blood's glucose level D.raises the blood's glucose level 61. Drinking alcohol while perspiring can quickly lead to dehydration because: A.aldosterone is lost in perspiration B.alcohol stimulates rennin secretion C.alcohol inhibits ADH secretion D.ADH is neutralized by alcohol in a chemi ...
... C.lowers the blood's glucose level D.raises the blood's glucose level 61. Drinking alcohol while perspiring can quickly lead to dehydration because: A.aldosterone is lost in perspiration B.alcohol stimulates rennin secretion C.alcohol inhibits ADH secretion D.ADH is neutralized by alcohol in a chemi ...
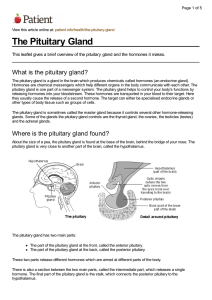
The Pituitary Gland
... Together with other hormones, prolactin stimulates the breasts to produce milk. It is also found in women who aren’t pregnant. Men also have prolactin but its function is not understood well. ...
... Together with other hormones, prolactin stimulates the breasts to produce milk. It is also found in women who aren’t pregnant. Men also have prolactin but its function is not understood well. ...
Chapter 45 Worksheet Sy Ha Hormones and the Endocrine System
... seasons. If night is longer, then melatonin is released more. ...
... seasons. If night is longer, then melatonin is released more. ...
ANP 201 Dr Smith - University of Agriculture Abeokuta
... The thyroid gland produces two different kinds of hormones. The first group are thyroxine and triiodothyronine, the second is called calcitonin. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) released form the adenohypophysis maintains the volume, weight and secretory activity of the thyroid gland. As the name i ...
... The thyroid gland produces two different kinds of hormones. The first group are thyroxine and triiodothyronine, the second is called calcitonin. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) released form the adenohypophysis maintains the volume, weight and secretory activity of the thyroid gland. As the name i ...
What is the Endocrine System
... lack of response by the target tissues. There may be decreased hormone production related to trauma, disease, infection, crowding of the hormone-producing cells by a tumor, or an inherited gene mutation that affects the quantity, quality, or structure of a hormone. Decreased production may also be d ...
... lack of response by the target tissues. There may be decreased hormone production related to trauma, disease, infection, crowding of the hormone-producing cells by a tumor, or an inherited gene mutation that affects the quantity, quality, or structure of a hormone. Decreased production may also be d ...
hormones. - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
... • Composed of a large number of follicles filled with – Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) • These hormones function to increase the metabolic rate by stimulating most of the body cells to metabolize at a faster rate • Thyroid acquires iodine to produce these compounds ...
... • Composed of a large number of follicles filled with – Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) • These hormones function to increase the metabolic rate by stimulating most of the body cells to metabolize at a faster rate • Thyroid acquires iodine to produce these compounds ...
EndocrineJS
... – Located in the brain just below the thalamus – Functions as part of both the nervous system and the endocrine system – Secretes substances that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland – Produces hormones ADH and oxytocin ...
... – Located in the brain just below the thalamus – Functions as part of both the nervous system and the endocrine system – Secretes substances that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland – Produces hormones ADH and oxytocin ...
Third Branchial Cleft Cyst Presentation in Adulthood
... showed no functional thyroid tissue in clinically palpable swelling. On axial and spiral contrast enhanced CT examination, a well-defined, nonenhancing uncomplicated cyst (typically unilocular) measuring 5x2.5x2 cm was noted in the neck, extending from the level of C3 vertebrae up to the level of th ...
... showed no functional thyroid tissue in clinically palpable swelling. On axial and spiral contrast enhanced CT examination, a well-defined, nonenhancing uncomplicated cyst (typically unilocular) measuring 5x2.5x2 cm was noted in the neck, extending from the level of C3 vertebrae up to the level of th ...
Slide 1
... pancreatic enzyme release, and gallbladder contraction, inhibit rectal gland secretion ...
... pancreatic enzyme release, and gallbladder contraction, inhibit rectal gland secretion ...
The Endocrine System
... What is the normal blood sugar range? 70-100 *SYMPTOMS: HYPERGYLCEMIA (high blood sugar), polyuria (increase urination), polydypsia (excessive thirst), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, blurred vision, possible diabetic coma ...
... What is the normal blood sugar range? 70-100 *SYMPTOMS: HYPERGYLCEMIA (high blood sugar), polyuria (increase urination), polydypsia (excessive thirst), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, blurred vision, possible diabetic coma ...
Chapter 10 - Delmar Cengage Learning
... glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
... glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... o The axon termini of the posterior pituitary release two major hormones: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH; also called vasopressin): causes reabsorption of water so that it is not lost in the urine. Oxytocin (OXT): stimulates contractions of the uterus; also involved in sexual arousal. Thyroid Glands ...
... o The axon termini of the posterior pituitary release two major hormones: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH; also called vasopressin): causes reabsorption of water so that it is not lost in the urine. Oxytocin (OXT): stimulates contractions of the uterus; also involved in sexual arousal. Thyroid Glands ...
Endocrine System Notes 1
... There are over 50 hormones in the human body, and they can be grouped together by their chemical structure. Steroids are produced from cholesterol. Peptides are chains of amino acids. Other hormones are derived from amino acids. Several glands comprise the endocrine system. The hypothalamus integrat ...
... There are over 50 hormones in the human body, and they can be grouped together by their chemical structure. Steroids are produced from cholesterol. Peptides are chains of amino acids. Other hormones are derived from amino acids. Several glands comprise the endocrine system. The hypothalamus integrat ...
Ehrlich_8e_ppt__chapter_13 Endocrine System
... •The adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (ah-DREE-noh-kor-tih-coe-TROP-ik) stimulates the growth and secretions of the adrenal cortex (adren/o means adrenal, cortic/o means cortex, trop means change, and -ic means pertaining to). •The follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the secretion of est ...
... •The adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (ah-DREE-noh-kor-tih-coe-TROP-ik) stimulates the growth and secretions of the adrenal cortex (adren/o means adrenal, cortic/o means cortex, trop means change, and -ic means pertaining to). •The follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the secretion of est ...
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
... the second plexus we call it the secondary hypophyseal plexus, and from there they will continue as the anterior hypophyseal veins that will go and drain into the anterior intercavernous sinus. This portal system is only associated with the anterior pituitary gland because there is an influence from ...
... the second plexus we call it the secondary hypophyseal plexus, and from there they will continue as the anterior hypophyseal veins that will go and drain into the anterior intercavernous sinus. This portal system is only associated with the anterior pituitary gland because there is an influence from ...
Laryngeal Cartilage`s
... Vocal Folds • 5 layers of tissue (deep= muscle) • Glottis= space between the vocal folds • Subglottal= area below the vocal folds ...
... Vocal Folds • 5 layers of tissue (deep= muscle) • Glottis= space between the vocal folds • Subglottal= area below the vocal folds ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... 2. Colloid is a viscous fluid that fills follicles and contains thyroglobulin. 3. Thyroglobulin is a glycoprotein. 4. Extrafollicular cells are located outside of follicles. 5. The follicular cells produce hormones. C. Thyroid Hormones 1. The three hormones produced by the thyroid gland are T4, T3, ...
... 2. Colloid is a viscous fluid that fills follicles and contains thyroglobulin. 3. Thyroglobulin is a glycoprotein. 4. Extrafollicular cells are located outside of follicles. 5. The follicular cells produce hormones. C. Thyroid Hormones 1. The three hormones produced by the thyroid gland are T4, T3, ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.