Endocrine System
... controls the production and secretion of glucocorticoids (cortisol) by the cortex of the adrenal medulla ...
... controls the production and secretion of glucocorticoids (cortisol) by the cortex of the adrenal medulla ...
File - Science at St. Dominics
... Taking the hormone in tablet form once a day can solve the problem – hormone supplement Excess thyroxine can greatly increase metabolic rate. Treatment is often by removal of part of the gland. ...
... Taking the hormone in tablet form once a day can solve the problem – hormone supplement Excess thyroxine can greatly increase metabolic rate. Treatment is often by removal of part of the gland. ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... The activated receptors then alter gene expression which results in the formation of new proteins. (Fig 18.3) The new proteins alter the cells activity and result in the physiological responses of those hormones. Action of Water-Soluble Hormones Water-soluble hormones alter cell functions by activa ...
... The activated receptors then alter gene expression which results in the formation of new proteins. (Fig 18.3) The new proteins alter the cells activity and result in the physiological responses of those hormones. Action of Water-Soluble Hormones Water-soluble hormones alter cell functions by activa ...
The Human Endocrine System
... Anterior pituitary hormones that affect other glands: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Gonadotropic Hormones ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones that affect other glands: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Gonadotropic Hormones ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... • Hypothalamus produces regulatory factors that adjust activities of anterior lobe of pituitary gland, which produces 7 hormones • Most hormones control other endocrine organs, including thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and ...
... • Hypothalamus produces regulatory factors that adjust activities of anterior lobe of pituitary gland, which produces 7 hormones • Most hormones control other endocrine organs, including thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and ...
C16.1 PPT - Destiny High School
... endocrine glands – Pg. 442 Hormones – Pg. 442 thyroid gland – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 parathyroid glands – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 Pancreas – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 pituitary glands – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 adrenal glands – Pg. 444 ...
... endocrine glands – Pg. 442 Hormones – Pg. 442 thyroid gland – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 parathyroid glands – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 Pancreas – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 pituitary glands – Pg. 443 Figure 16.1 adrenal glands – Pg. 444 ...
ANATOMIA FUNCTIONALA/ FIZIOPATOLOGIA HIPOTALAMUSULUI
... generated externally and some internally. The hypothalamus is thus richly connected with many parts of the CNS, including the brainstem reticular formation and autonomic zones, the limbic forebrain (particularly the amygdala, septum, diagonal band of Broca, and the olfactory bulbs, and the cerebral ...
... generated externally and some internally. The hypothalamus is thus richly connected with many parts of the CNS, including the brainstem reticular formation and autonomic zones, the limbic forebrain (particularly the amygdala, septum, diagonal band of Broca, and the olfactory bulbs, and the cerebral ...
The Endocrine System
... Normally, any glucose that is filtered out of the blood by the kid neys is reabsorbed back into the blood. Thus, glucose is usually not present in urine. However, an individual with diabetes mel litus has glucose levels that are well above normal, a condition called hyperglycemia, and the kidneys ...
... Normally, any glucose that is filtered out of the blood by the kid neys is reabsorbed back into the blood. Thus, glucose is usually not present in urine. However, an individual with diabetes mel litus has glucose levels that are well above normal, a condition called hyperglycemia, and the kidneys ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • Largest endocrine gland with high rate of blood flow • Anterior and lateral sides of trachea • 2 large lobes connected by isthmus ...
... • Largest endocrine gland with high rate of blood flow • Anterior and lateral sides of trachea • 2 large lobes connected by isthmus ...
growth hormone (GH)
... oxytocin a hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary that is produced by the hypothalamus which stimulates contractions of the uterus during childbirth and effects the release of milk from the mammary glands. ...
... oxytocin a hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary that is produced by the hypothalamus which stimulates contractions of the uterus during childbirth and effects the release of milk from the mammary glands. ...
films/media suggestions
... Calcitonin helps regulate the levels of calcium in the blood; when too high, it lowers the calcium in the blood by helping bones absorb more calcium. B. The Parathyroids: Builders of Bone 1. The parathyroid glands are four small glands lying on the back of the thyroid. 2. Their release of parathyroi ...
... Calcitonin helps regulate the levels of calcium in the blood; when too high, it lowers the calcium in the blood by helping bones absorb more calcium. B. The Parathyroids: Builders of Bone 1. The parathyroid glands are four small glands lying on the back of the thyroid. 2. Their release of parathyroi ...
Normal pituitary Magnetic resonance scan
... • Stimulates: thyroxine synthesis thyroid growth • Regulation: – TRH: stimulates release – Inhibited by thyroid hormones (T3, T4) – feedback inhibition ...
... • Stimulates: thyroxine synthesis thyroid growth • Regulation: – TRH: stimulates release – Inhibited by thyroid hormones (T3, T4) – feedback inhibition ...
The Endocrine System
... Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, leading to chronic hypertension (high blood pressure), high body temperature and sweating, weight loss, irritability, and bulging eyes. In some cases, hyperthyroidism is treated by killing the thyroid gland with radiation. ...
... Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, leading to chronic hypertension (high blood pressure), high body temperature and sweating, weight loss, irritability, and bulging eyes. In some cases, hyperthyroidism is treated by killing the thyroid gland with radiation. ...
The Encorine System and Homeostasis
... contains axons and axon terminals of neurons whose cell bodies are located in the hypothalamus. A third region of the pituitary gland called the pars intermedia. ...
... contains axons and axon terminals of neurons whose cell bodies are located in the hypothalamus. A third region of the pituitary gland called the pars intermedia. ...
BMS Endocrine lecture principles Hout
... Amines and many peptides are stored in large amounts in intracellular vesicles (granules). Some peptides e.g. growth factors and cytokines are not stored but released as they are made. Steroids, prostanoids, gases are not stored to any significant extent. Large amounts of iodinated thyroglobul ...
... Amines and many peptides are stored in large amounts in intracellular vesicles (granules). Some peptides e.g. growth factors and cytokines are not stored but released as they are made. Steroids, prostanoids, gases are not stored to any significant extent. Large amounts of iodinated thyroglobul ...
Thyroid hormones
... 1. Follicular cells take up a piece of colloid (containing iodinated Tg) by phagocytosis 2. Lysosomal enzymes split off T4, T3, MIT and DIT in the process of breaking down Tg 3. T4 and T3 (biologically active thyroid hormones) diffuse across follicular cell membrane into blood, while MIT and DIT are ...
... 1. Follicular cells take up a piece of colloid (containing iodinated Tg) by phagocytosis 2. Lysosomal enzymes split off T4, T3, MIT and DIT in the process of breaking down Tg 3. T4 and T3 (biologically active thyroid hormones) diffuse across follicular cell membrane into blood, while MIT and DIT are ...
The Endocrine System
... - In childhood… lea d to cretinism (dwarfism) -in adults…lead to myxedema (poor muscle tone, low body temperature, obesity, dry skin) *HYPERTHYROIDISM….(result from tumor of thyroid gland) Lead to; -Graves disease >>increase basal metabolic rate, intolerance to heat -enlarge and protrude eye (exopht ...
... - In childhood… lea d to cretinism (dwarfism) -in adults…lead to myxedema (poor muscle tone, low body temperature, obesity, dry skin) *HYPERTHYROIDISM….(result from tumor of thyroid gland) Lead to; -Graves disease >>increase basal metabolic rate, intolerance to heat -enlarge and protrude eye (exopht ...
ch18 Endocrine System
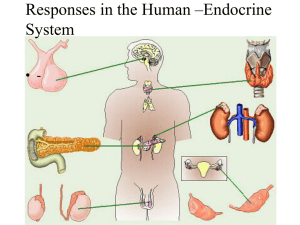
... B. Endocrine glands constitute the endocrine system and include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal organs, and pineal glands (Figure 18.1). III. HORMONE ACTIVITY A. Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. B. The Role of H ...
... B. Endocrine glands constitute the endocrine system and include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal organs, and pineal glands (Figure 18.1). III. HORMONE ACTIVITY A. Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. B. The Role of H ...
notes - Main
... B. Endocrine glands constitute the endocrine system and include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal organs, and pineal glands (Figure 18.1). III. HORMONE ACTIVITY A. Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. B. The Role of H ...
... B. Endocrine glands constitute the endocrine system and include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, kidneys, gastrointestinal organs, and pineal glands (Figure 18.1). III. HORMONE ACTIVITY A. Hormones have powerful effects when present in very low concentrations. B. The Role of H ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... and contribute to the production of peripheral t-cell population. Adrenal glands (cortex & medulla) Cortex secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine a ...
... and contribute to the production of peripheral t-cell population. Adrenal glands (cortex & medulla) Cortex secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine a ...
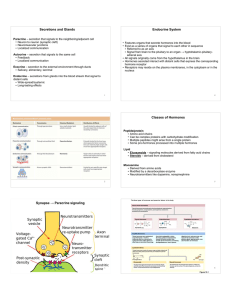
Secretions and Glands Endocrine System Classes of Hormones
... Follicular cells secrete thyroglobulin (molecule containing building block amino acid tyrosine) into colloid within follicles 1)Iodide ions from diet delivered to thyroid gland and taken up by follicular cells 2)Enzymes activate iodide and attach to tyrosine portions of thyroglobulin molecule 3)T4 ( ...
... Follicular cells secrete thyroglobulin (molecule containing building block amino acid tyrosine) into colloid within follicles 1)Iodide ions from diet delivered to thyroid gland and taken up by follicular cells 2)Enzymes activate iodide and attach to tyrosine portions of thyroglobulin molecule 3)T4 ( ...
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Endocrine glands and
... Hyperplasia of adrenal tissue due to overstimulation by the pituitary gland Tumor of the adrenal cortex Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secreting tumor outside the pituitary Overuse of corticosteroid drugs ...
... Hyperplasia of adrenal tissue due to overstimulation by the pituitary gland Tumor of the adrenal cortex Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secreting tumor outside the pituitary Overuse of corticosteroid drugs ...
• Overview of Anatomy and Physiology • Endocrine glands and
... Hyperplasia of adrenal tissue due to overstimulation by the pituitary gland Tumor of the adrenal cortex Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secreting tumor outside the pituitary Overuse of corticosteroid drugs ...
... Hyperplasia of adrenal tissue due to overstimulation by the pituitary gland Tumor of the adrenal cortex Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secreting tumor outside the pituitary Overuse of corticosteroid drugs ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
Hormonal control and the endocrine system: achieving homeostasis
... Insulin is produced by the pancreas to prevent the level of blood glucose becoming too high. To prevent the level of blood glucose falling too low, the pancreas produces glucagon. It is vital that glucose is maintained at a level that can be used by cells to produce energy. Other hormones such as ad ...
... Insulin is produced by the pancreas to prevent the level of blood glucose becoming too high. To prevent the level of blood glucose falling too low, the pancreas produces glucagon. It is vital that glucose is maintained at a level that can be used by cells to produce energy. Other hormones such as ad ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.