(Pig) Superior Mesenteric Artery Acute Blood Flow
... catheter and maintain body temperature at 38-39°C with a radiant heat lamp and thermal blanket. Place anesthetized pig in right lateral recumbency and make a 4 cm vertical skin incision just caudal to the last rib. Extend the skin incision through the cutaneous, latissimus (Continued on next side.) ...
... catheter and maintain body temperature at 38-39°C with a radiant heat lamp and thermal blanket. Place anesthetized pig in right lateral recumbency and make a 4 cm vertical skin incision just caudal to the last rib. Extend the skin incision through the cutaneous, latissimus (Continued on next side.) ...
This week`s lab will focus on the major endocrine
... hormone can vary greatly. Some hormones have an almost instantaneous effect on that cell (such as epinephrine, aka- adrenaline) to an effect that can last days to even months (such as growth hormone). Hormonal levels are maintained by a negative feedback mechanism. As hormonal levels rise in the blo ...
... hormone can vary greatly. Some hormones have an almost instantaneous effect on that cell (such as epinephrine, aka- adrenaline) to an effect that can last days to even months (such as growth hormone). Hormonal levels are maintained by a negative feedback mechanism. As hormonal levels rise in the blo ...
2634fd6c36ebbd2
... 1-the first part of the maxillary artery (MIADA) gives origin to two major branches (the middle meningeal and inferior alveolar arteries) and a number of smaller branches (deep auricular, anterior tympanic, and accessory meningeal). 2-the second part of the maxillary artery gives origin to deep temp ...
... 1-the first part of the maxillary artery (MIADA) gives origin to two major branches (the middle meningeal and inferior alveolar arteries) and a number of smaller branches (deep auricular, anterior tympanic, and accessory meningeal). 2-the second part of the maxillary artery gives origin to deep temp ...
anatomylab4
... -investing layer of cervical deep fascia: behind the vertebrae and we call it (cervical fascia) and is divided into ( 3) layers : 1- Investing layer (outer one): that surrounds the Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid muscles. 2- prevertebral fascia: that surrounds the prevertebral muscles. 3- pretrach ...
... -investing layer of cervical deep fascia: behind the vertebrae and we call it (cervical fascia) and is divided into ( 3) layers : 1- Investing layer (outer one): that surrounds the Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid muscles. 2- prevertebral fascia: that surrounds the prevertebral muscles. 3- pretrach ...
1. Write a response to the question, “Why are we dissecting in
... 11. Locate one or more of the parotid, mandibular, and sublinqual glands. By their location and the fact that they are part of the digestive system, what must their function be? They secrete digestive enzymes to help break down food. 12. Locate the trachea and the esophagus. Describe several ways i ...
... 11. Locate one or more of the parotid, mandibular, and sublinqual glands. By their location and the fact that they are part of the digestive system, what must their function be? They secrete digestive enzymes to help break down food. 12. Locate the trachea and the esophagus. Describe several ways i ...
6.LYMPHATIC OF THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA
... Five cm. long (2 inches) Formed behind the neck of the pancreas. Formed by the union of the splenic and superior mesenteric veins, behind the neck of the pancreas. Drains blood from the gastrointestinal tract. (From the lower1/3rd of esophagus to halfway down the anal canal). It also drai ...
... Five cm. long (2 inches) Formed behind the neck of the pancreas. Formed by the union of the splenic and superior mesenteric veins, behind the neck of the pancreas. Drains blood from the gastrointestinal tract. (From the lower1/3rd of esophagus to halfway down the anal canal). It also drai ...
Document
... with endocrine system • Chemical structures similar to those of some hormones • Examples: pesticides, herbicides, etc. ...
... with endocrine system • Chemical structures similar to those of some hormones • Examples: pesticides, herbicides, etc. ...
21 Endocrine
... The Pituitary Gland • This is located in the sella tursica (totally encased in bone), which gives you a clue as to how important this gland is. • The adenohypophysis portion of the pituitary gland (anterior lobe) actually develops from an embryonic pouch that grows upward from the ectoderm of the p ...
... The Pituitary Gland • This is located in the sella tursica (totally encased in bone), which gives you a clue as to how important this gland is. • The adenohypophysis portion of the pituitary gland (anterior lobe) actually develops from an embryonic pouch that grows upward from the ectoderm of the p ...
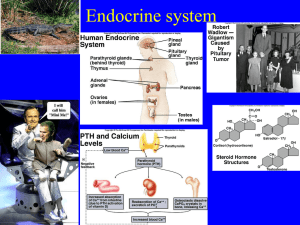
Endocrine System
... A. Considered to be part of animals communication system 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical su ...
... A. Considered to be part of animals communication system 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical su ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 47 1
... sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, and secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine in response ...
... sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, and secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine in response ...
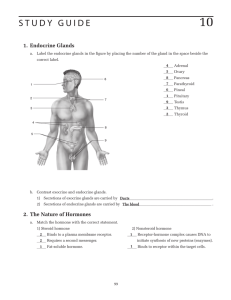
S T U D Y G U I D E
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
Liver and Gall Bladder
... 3. Hepatic acinus. This is the most accepted structural and functional unit of the liver. The cells are divided into three zones. Zone 1 cells are first to receive oxygenated blood. Zone 3 cells are the last to regenerate, and showing effects of toxins. Zone 2 cells have characteristics that interm ...
... 3. Hepatic acinus. This is the most accepted structural and functional unit of the liver. The cells are divided into three zones. Zone 1 cells are first to receive oxygenated blood. Zone 3 cells are the last to regenerate, and showing effects of toxins. Zone 2 cells have characteristics that interm ...
Equine Nutrition #2 - Canadian Pony Club
... important digestive structures near the front, the horse has its most important digestive structures, those associated with fermentation, situated near the rear of the animal This allows the horse to not only run, but run far and fast ...
... important digestive structures near the front, the horse has its most important digestive structures, those associated with fermentation, situated near the rear of the animal This allows the horse to not only run, but run far and fast ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Secretion of digestive enzymes allows chemical digestion Absorption—movement of nutrients through the GI mucosa into the internal ...
... Secretion of digestive enzymes allows chemical digestion Absorption—movement of nutrients through the GI mucosa into the internal ...
38–2 The Process of Digestion
... Chemical Digestion The lining of the stomach contains millions of microscopic gastric glands that release a number of substances into the stomach. Some of these glands produce mucus, a fluid that lubricates and protects the stomach wall. Other glands produce hydrochloric acid, which makes the content ...
... Chemical Digestion The lining of the stomach contains millions of microscopic gastric glands that release a number of substances into the stomach. Some of these glands produce mucus, a fluid that lubricates and protects the stomach wall. Other glands produce hydrochloric acid, which makes the content ...
chapter 23-the digestive system
... 1. Omenta extend from these curvatures to attach the stomach to other structures in the abdominal cavity. 2. The Lesser Omentum-extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and becomes continuous with the visceral peritoneum that covers the stomach. 3. The Greater Omentum-extends f ...
... 1. Omenta extend from these curvatures to attach the stomach to other structures in the abdominal cavity. 2. The Lesser Omentum-extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and becomes continuous with the visceral peritoneum that covers the stomach. 3. The Greater Omentum-extends f ...
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... travel to the posterior pituitary gland for release. The hypothalamus has another function; it produces releasing and inhibiting hormones, which control the release of the anterior pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus also plays a part in maintaining body temperature, hunger, and thirst. Anatomy and ...
... travel to the posterior pituitary gland for release. The hypothalamus has another function; it produces releasing and inhibiting hormones, which control the release of the anterior pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus also plays a part in maintaining body temperature, hunger, and thirst. Anatomy and ...
Esophagus and stomach
... • 1.Paraesophageal hiatal hernia:the cardia remains in its normal position, however, a pouch of peritoneum, often containing part of the fundus, extends through the esophageal hiatus • 2.Sliding hiatal hernia:the abdominal part of the esophagus, the cardia, and parts of the fundus of the stomach sli ...
... • 1.Paraesophageal hiatal hernia:the cardia remains in its normal position, however, a pouch of peritoneum, often containing part of the fundus, extends through the esophageal hiatus • 2.Sliding hiatal hernia:the abdominal part of the esophagus, the cardia, and parts of the fundus of the stomach sli ...
Chapter 16 Section 2 The Digestive System
... and chemicals that help break down food as it passes through the digestive tract. ...
... and chemicals that help break down food as it passes through the digestive tract. ...
19_QuizShowQuestions
... hypothalamic control of the adenohypophysis is/are true? a. The secondary capillary plexus in the floor of the tuberal area receives blood from the superior hypophyseal artery. b. The vessels between the hypothalamus and the adenohypophysis are called the hypophyseal portal system. c. After leaving ...
... hypothalamic control of the adenohypophysis is/are true? a. The secondary capillary plexus in the floor of the tuberal area receives blood from the superior hypophyseal artery. b. The vessels between the hypothalamus and the adenohypophysis are called the hypophyseal portal system. c. After leaving ...
Document
... how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
... how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of
... Name the organism digestive organ where each of the following chiefly occurs. Some answers may be repeated more than once. 1. This organ produces gastric juice in humans. 2. HCl is produced in this human alimentary canal organ. 3. This is where bile is temporarily stored in many humans. 4. This org ...
... Name the organism digestive organ where each of the following chiefly occurs. Some answers may be repeated more than once. 1. This organ produces gastric juice in humans. 2. HCl is produced in this human alimentary canal organ. 3. This is where bile is temporarily stored in many humans. 4. This org ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.