Hormones Endocrine System Function Endocrine Systems
... • Endocrine cells located in Islets of Langerhans • Contain two cell types – α cells - secrete glucagon – β cells - secrete insulin ...
... • Endocrine cells located in Islets of Langerhans • Contain two cell types – α cells - secrete glucagon – β cells - secrete insulin ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • Controls activities that require long duration – digestion and energy metabolism – osmoregulation, water balance, ion balance and excretion – growth and development – reproduction ...
... • Controls activities that require long duration – digestion and energy metabolism – osmoregulation, water balance, ion balance and excretion – growth and development – reproduction ...
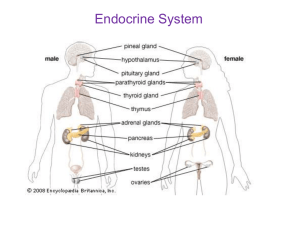
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands—secrete hormones directly into the blood – anterior pituitary – thyroid – adrenal • Exocrine glands—deliver hormones into the blood via tubes leading from the gland – sweat glands – salivary glands – mammary glands ...
... • Endocrine glands—secrete hormones directly into the blood – anterior pituitary – thyroid – adrenal • Exocrine glands—deliver hormones into the blood via tubes leading from the gland – sweat glands – salivary glands – mammary glands ...
Human Torso Model Activity
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
Endocrine System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells called target cells Protein receptors are found on the plasma membrane that respond to only a specific hormone When the binding occurs the hormone influences the cell by either turning on specific genes or using a secondary messenger to in ...
... hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells called target cells Protein receptors are found on the plasma membrane that respond to only a specific hormone When the binding occurs the hormone influences the cell by either turning on specific genes or using a secondary messenger to in ...
F13_Endocrine1
... Unlike the nervous system with which the endocrine works similarly to and in some cases with, the endocrine system sends messages to cells to perform a necessary action. Hormones are messenger molecules. The endocrines system is comprised of small organs dispersed throughout the body and secrete hor ...
... Unlike the nervous system with which the endocrine works similarly to and in some cases with, the endocrine system sends messages to cells to perform a necessary action. Hormones are messenger molecules. The endocrines system is comprised of small organs dispersed throughout the body and secrete hor ...
Endocrinology Features of Endocrine system:
... Functions as a part of sympathetic nervous system. It secretes Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) which are important for physical activity such as increase blood sugar levels, heart rate The release of these hormones is stimulated by emotions, injury, stress etc. ...
... Functions as a part of sympathetic nervous system. It secretes Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) which are important for physical activity such as increase blood sugar levels, heart rate The release of these hormones is stimulated by emotions, injury, stress etc. ...
Sectional Anatomy Terminology
... 4. While viewing the area from the anterior direction, draw an imaginary line across the area you are studying at different levels as demonstrated. The lines would represent the locations of slices acquired in the axial plane. Proceed to list the organs or structures you see in order from the right ...
... 4. While viewing the area from the anterior direction, draw an imaginary line across the area you are studying at different levels as demonstrated. The lines would represent the locations of slices acquired in the axial plane. Proceed to list the organs or structures you see in order from the right ...
Digestive System
... This is located inferior to the liver, and its function is to store and concentrate bile. Bile is a detergent/soap (not an enzyme) which emulsifies fat: It breaks down the fat into microscopic droplets which can be broken down by pancreatic enzymes. It does NOT make or secrete bile; that is done by ...
... This is located inferior to the liver, and its function is to store and concentrate bile. Bile is a detergent/soap (not an enzyme) which emulsifies fat: It breaks down the fat into microscopic droplets which can be broken down by pancreatic enzymes. It does NOT make or secrete bile; that is done by ...
Keshara Senanayake Audesirk Chapter 33
... stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary -> which is stimulated by a releasing hormone from the hypothalamus >amount of TSH release from the pituitary is regulated by negative feedback -> adequate levels of thyroxine circulating in the bloodstream inhibit the secre ...
... stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary -> which is stimulated by a releasing hormone from the hypothalamus >amount of TSH release from the pituitary is regulated by negative feedback -> adequate levels of thyroxine circulating in the bloodstream inhibit the secre ...
Arch of aorta and its relations
... The Ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk are inside the pericardium. Near the heart, the beginning of the pulmonary trunk is anterior to the ascending aorta. As it ascends, it becomes on the left side of the ascending aorta and then it terminates posterior to the aortic arch giving the right and left ...
... The Ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk are inside the pericardium. Near the heart, the beginning of the pulmonary trunk is anterior to the ascending aorta. As it ascends, it becomes on the left side of the ascending aorta and then it terminates posterior to the aortic arch giving the right and left ...
GI Tract - review anatomy of upper and lower GI tract
... - review anatomy of upper and lower GI tract - define GI motility, secretion, digestion, absorption, elimination - describe the laminar histology of the GI tract: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa - identify the elements of the mucosa - describe intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of the ...
... - review anatomy of upper and lower GI tract - define GI motility, secretion, digestion, absorption, elimination - describe the laminar histology of the GI tract: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa - identify the elements of the mucosa - describe intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of the ...
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... - glucagon causes cells to release stored glucose into the blood. ...
... - glucagon causes cells to release stored glucose into the blood. ...
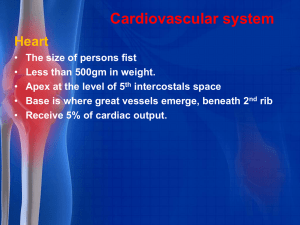
Cardiovascular system1
... motor and sensory areas of lower limbs Middle cerebral artery supply motor and sensory areas of rest of the body ...
... motor and sensory areas of lower limbs Middle cerebral artery supply motor and sensory areas of rest of the body ...
Lesson Plan: Equine Digestion Game
... hairlike projections that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients. ...
... hairlike projections that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Consists of two lobes located on the ventral surface of the trachea Produces two iodine-containing hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) The thyroid hormones Play crucial roles in stimulating metabolism and influencing development and maturation ...
... Consists of two lobes located on the ventral surface of the trachea Produces two iodine-containing hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) The thyroid hormones Play crucial roles in stimulating metabolism and influencing development and maturation ...
Class Topics
... • Largest visceral organ • divided into two lobes – each lobe contains 100,000 hepatocytes ...
... • Largest visceral organ • divided into two lobes – each lobe contains 100,000 hepatocytes ...
Slide 1
... blood glucose levels, dilates small passage ways of the lungs resulting in more oxygen and glucose in the blood and faster circulation of the blood to body organs ...
... blood glucose levels, dilates small passage ways of the lungs resulting in more oxygen and glucose in the blood and faster circulation of the blood to body organs ...
chapt11_lecture
... 1. The pancreas is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. 2. Endocrine cells are located in pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans). a. Alpha cells: glucagon b. Beta cells: insulin ...
... 1. The pancreas is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. 2. Endocrine cells are located in pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans). a. Alpha cells: glucagon b. Beta cells: insulin ...
19 Digestive System Mt SAC
... This is located inferior to the liver, and its function is to store and concentrate bile. Bile is a detergent/soap (not an enzyme) which emulsifies fat: It breaks down the fat into microscopic droplets which can be broken down by pancreatic enzymes. It does NOT make or secrete bile; that is done by ...
... This is located inferior to the liver, and its function is to store and concentrate bile. Bile is a detergent/soap (not an enzyme) which emulsifies fat: It breaks down the fat into microscopic droplets which can be broken down by pancreatic enzymes. It does NOT make or secrete bile; that is done by ...
Lumenal Disease: Response and Remission
... • HCl denatures proteins - 40, 30, and 20 structures • Converts pepsinogen to pepsin Image from: Sweety Mehta ...
... • HCl denatures proteins - 40, 30, and 20 structures • Converts pepsinogen to pepsin Image from: Sweety Mehta ...
Endocrine System Not..
... of fatty acids and glucose into blood •Anti-inflammatory effect becomes immune suppression with long-term use •SEX STEROIDS •Androgen ( including DHEA which other tissues convert to testosterone ) and estrogen ( important after menopause ) PANCREAS •EXOCRINE AND ENDOCRINE ORGAN •RETROPERITONEAL •1-2 ...
... of fatty acids and glucose into blood •Anti-inflammatory effect becomes immune suppression with long-term use •SEX STEROIDS •Androgen ( including DHEA which other tissues convert to testosterone ) and estrogen ( important after menopause ) PANCREAS •EXOCRINE AND ENDOCRINE ORGAN •RETROPERITONEAL •1-2 ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.