* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
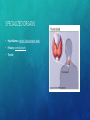
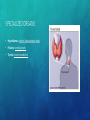
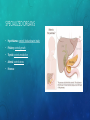
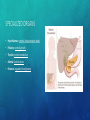
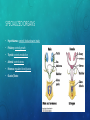
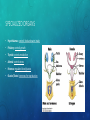
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM EQ: HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another • Common Hormones: FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another • Common Hormones: • Insulin: blood sugar FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another • Common Hormones: • Insulin: blood sugar • Oxytocin: labor (childbirth) FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another • Common Hormones: • Insulin: blood sugar • Oxytocin: labor (childbirth) • Serotonin: sleep and mood FUNCTION AND PARTS • System of glands which secrete a different type of hormone • Regulate homeostasis • Communication • Hormone: chemical message sent from one cell to another • Common Hormones: • Insulin: blood sugar • Oxytocin: labor (childbirth) • Serotonin: sleep and mood • Epinephrine: fight or flight HOW DOES THIS SYSTEM FUNCTION IN: • Nutrient Absorption: HOW DOES THIS SYSTEM FUNCTION IN: • Nutrient Absorption: insulin production to bring down sugar level, glucagon production to bring up sugar level HOW DOES THIS SYSTEM FUNCTION IN: • Nutrient Absorption: insulin production to bring down sugar level, glucagon production to bring up sugar level • Regulation: HOW DOES THIS SYSTEM FUNCTION IN: • Nutrient Absorption: insulin production to bring down sugar level, glucagon production to bring up sugar level • Regulation: production of hormones to maintain homeostasis SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: controls stress SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: controls stress • Pancreas: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: controls stress • Pancreas: regulates blood glucose SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: controls stress • Pancreas: regulates blood glucose • Ovaries/Testes: SPECIALIZED ORGANS • Hypothalamus: controls food and water intake • Pituitary: controls growth • Thyroid: controls metabolism • Adrenal: controls stress • Pancreas: regulates blood glucose • Ovaries/Testes: hormones for reproduction HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: release of adrenaline to speed up heart rate HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: release of adrenaline to speed up heart rate • Muscular and Skeletal System: HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: release of adrenaline to speed up heart rate • Muscular and Skeletal System: adrenaline will direct blood to muscle HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: release of adrenaline to speed up heart rate • Muscular and Skeletal System: adrenaline will direct blood to muscle • Digestive System: HOW DOES THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTERACT WITH… • Respiratory System: release of adrenaline to speed up breathing rate • Circulatory System: release of adrenaline to speed up heart rate • Muscular and Skeletal System: adrenaline will direct blood to muscle • Digestive System: release of insulin and glucagon to maintain blood sugar level