2-thoracic part
... directed cranial, dorsal and to wards the left. It lies against the diaphragm and liver. 2-the visceral surface: also convex, it is related to the terminal part of the large colon, pancreas, small intestine and the greater omentum. ♣ The border between two surfaces are termed the curvature. ♣ The le ...
... directed cranial, dorsal and to wards the left. It lies against the diaphragm and liver. 2-the visceral surface: also convex, it is related to the terminal part of the large colon, pancreas, small intestine and the greater omentum. ♣ The border between two surfaces are termed the curvature. ♣ The le ...
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... • They are e xocrine glands are glands that secrete their products (enzymes excluding hormones and other chemical messengers like Neurotransmitter communicates to adjacent cells, Neuropeptide - a protein sequence which acts as a hormone or neurotransmitter, Pheromone - a chemical factor that trigge ...
... • They are e xocrine glands are glands that secrete their products (enzymes excluding hormones and other chemical messengers like Neurotransmitter communicates to adjacent cells, Neuropeptide - a protein sequence which acts as a hormone or neurotransmitter, Pheromone - a chemical factor that trigge ...
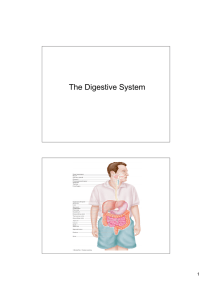
The Digestive System
... • Absorption – Absorbs almost everything presented to it – Most occurs in duodenum and jejunum – Adaptations that increase small intestine’s surface area • Inner surface has permanent circular folds • Microscopic finger-like projections called villi • Brush border (microvilli) arise from luminal sur ...
... • Absorption – Absorbs almost everything presented to it – Most occurs in duodenum and jejunum – Adaptations that increase small intestine’s surface area • Inner surface has permanent circular folds • Microscopic finger-like projections called villi • Brush border (microvilli) arise from luminal sur ...
anathomy and phisiology of digestive system
... Glands in stomach lining: stomach acid, enyzmes that digest proteins Pancreas: several enzymes that digest carbohydrates, fats and protein Liver: bile for digesting fat Small intestine: digestive juice which combines with pancreatic juice and bile – digestion of proteins and starches. ...
... Glands in stomach lining: stomach acid, enyzmes that digest proteins Pancreas: several enzymes that digest carbohydrates, fats and protein Liver: bile for digesting fat Small intestine: digestive juice which combines with pancreatic juice and bile – digestion of proteins and starches. ...
Digestive System
... C) lined with simple columnar epithelium; ciliated with goblet cells 1) possess microvilli – finger-like projection of the columnar cells D) 3 segments 1) duodenum (~5%) a) receives enzymes via the main pancreatic duct, bile via the bile duct, and chyme from the pyloric region of the stomach ...
... C) lined with simple columnar epithelium; ciliated with goblet cells 1) possess microvilli – finger-like projection of the columnar cells D) 3 segments 1) duodenum (~5%) a) receives enzymes via the main pancreatic duct, bile via the bile duct, and chyme from the pyloric region of the stomach ...
Chapter 40 Structure and Function of the Digestive System
... Food breakdown begins in the mouth with chewing and continues in the stomach, where food is churned and mixed with acid, mucus, enzymes, and other secretions. From the stomach, the fluid and partially digested food pass into the small intestine, where biochemicals and enzymes secreted by the liver, ...
... Food breakdown begins in the mouth with chewing and continues in the stomach, where food is churned and mixed with acid, mucus, enzymes, and other secretions. From the stomach, the fluid and partially digested food pass into the small intestine, where biochemicals and enzymes secreted by the liver, ...
The Digestive System
... Pancreas- produces a wide variety of enzymes to help break down food. The enzymes are secreted into the duodenum in an alkaline fluid, which neutralizes the acidic chyme coming in from the stomach. The pancreas also produces the hormones insulin and glucagon. ...
... Pancreas- produces a wide variety of enzymes to help break down food. The enzymes are secreted into the duodenum in an alkaline fluid, which neutralizes the acidic chyme coming in from the stomach. The pancreas also produces the hormones insulin and glucagon. ...
textbook resource
... The columnar epithelial lining of the stomach has millions of gastric pits, which lead into gastric glands. The gastric glands produce gastric juice. Gastric juice contains an enzyme called pepsin, which digests protein, plus hydrochloric acid (HCl) and mucus. HCl causes the stomach to have a high a ...
... The columnar epithelial lining of the stomach has millions of gastric pits, which lead into gastric glands. The gastric glands produce gastric juice. Gastric juice contains an enzyme called pepsin, which digests protein, plus hydrochloric acid (HCl) and mucus. HCl causes the stomach to have a high a ...
013368718X_CH30_465-482.indd
... Absorption and Elimination Most nutrients from food are absorbed by the small intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and prepares waste for elimination from the body. The small intestine has fingerlike projections (villi) that are covered with microvilli, which absorb nutrients. Most nutrients ...
... Absorption and Elimination Most nutrients from food are absorbed by the small intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and prepares waste for elimination from the body. The small intestine has fingerlike projections (villi) that are covered with microvilli, which absorb nutrients. Most nutrients ...
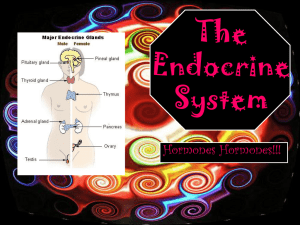
Glands - cloudfront.net
... of calcium in the blood within a narrow range. It stimulates bone cells to dissolve calcium in bone matrix and release it into the blood. • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other ...
... of calcium in the blood within a narrow range. It stimulates bone cells to dissolve calcium in bone matrix and release it into the blood. • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other ...
Ventral Cavity
... The diaphragm is a curved sheet forming the posterior wall of the thoracic cavity and completely separating it from the abdominal cavity. The center of the anterior face of the diaphragm is seen to consist of connective tissue forming a circular tendon, the central tendon. The rest of the diaphragm ...
... The diaphragm is a curved sheet forming the posterior wall of the thoracic cavity and completely separating it from the abdominal cavity. The center of the anterior face of the diaphragm is seen to consist of connective tissue forming a circular tendon, the central tendon. The rest of the diaphragm ...
File - Mr. Ashe`s Science Site
... Absorption and Elimination Most nutrients from food are absorbed by the small intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and prepares waste for elimination from the body. The small intestine has fingerlike projections (villi) that are covered with microvilli, which absorb nutrients. Most nutrients ...
... Absorption and Elimination Most nutrients from food are absorbed by the small intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and prepares waste for elimination from the body. The small intestine has fingerlike projections (villi) that are covered with microvilli, which absorb nutrients. Most nutrients ...
File
... its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's specific receptors and these hormone-receptor combinations transmit chemical instructions to the inner workings of the cell. • When hormone levels reach a certain normal amount, the ...
... its message. These cells are called target cells. • When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's specific receptors and these hormone-receptor combinations transmit chemical instructions to the inner workings of the cell. • When hormone levels reach a certain normal amount, the ...
chapt11answers
... What is the difference between an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland? Endocrine glands secrete hormones which circulate in the blood, while exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts leading to a body surface hormone: What types of chemicals can hormones be? Steroids, amines, peptides, protein ...
... What is the difference between an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland? Endocrine glands secrete hormones which circulate in the blood, while exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts leading to a body surface hormone: What types of chemicals can hormones be? Steroids, amines, peptides, protein ...
Sarah Harney_AHS Digestion 2
... • Protein digestion is continued in small intestine by pancreatic enzymes • Proenzymes (zymogens) secreted by the pancreas are converted to active forms following activation of trypsin by a brush border enzyme, enterokinase ...
... • Protein digestion is continued in small intestine by pancreatic enzymes • Proenzymes (zymogens) secreted by the pancreas are converted to active forms following activation of trypsin by a brush border enzyme, enterokinase ...
Power Point
... Condensation is a chemical process by which 2 molecules are joined together to make a larger, more complex, molecule, with the loss of water. It is the basis for the synthesis of all the important biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) from their simpler sub-units ...
... Condensation is a chemical process by which 2 molecules are joined together to make a larger, more complex, molecule, with the loss of water. It is the basis for the synthesis of all the important biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) from their simpler sub-units ...
Endocrine System Powerpoint
... communication and control of the body • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Other glands that secrete substan ...
... communication and control of the body • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Other glands that secrete substan ...
C16.1 PPT - Destiny High School
... The Adrenal Glands The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that inhibit the amount of sodium excreted in urine and maintain blood volume and blood pressure aid in the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates ...
... The Adrenal Glands The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that inhibit the amount of sodium excreted in urine and maintain blood volume and blood pressure aid in the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates ...
Endocrine System
... the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and several other processes. Pituitary Glands: Attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk. The posterior (back) lobe stores hor ...
... the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and several other processes. Pituitary Glands: Attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk. The posterior (back) lobe stores hor ...
Lingual artery
... It loops upward and then passes deep to the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle to enter the submandibular region. The loop of the artery is crossed superficially by the hypoglossal nerve. The lingual artery supplies structures of the floor of the mouth and the posterior and inferior surface o ...
... It loops upward and then passes deep to the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle to enter the submandibular region. The loop of the artery is crossed superficially by the hypoglossal nerve. The lingual artery supplies structures of the floor of the mouth and the posterior and inferior surface o ...
Chapter26
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary causes the adrenal cortex to secrete ...
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary causes the adrenal cortex to secrete ...
Chapter 13: The Endocrine System
... Long slender organ that lies transversely across the upper abdomen from the curve of the duodenum to the spleen Exocrine and endocrine gland o Exocrine function concerned with digestion of food o Endocrine function secretes insulin and glucagon Hormone-secreting cell called the islets of L ...
... Long slender organ that lies transversely across the upper abdomen from the curve of the duodenum to the spleen Exocrine and endocrine gland o Exocrine function concerned with digestion of food o Endocrine function secretes insulin and glucagon Hormone-secreting cell called the islets of L ...
Chapter 22 - Las Positas College
... I. The stomach churns food into chyme; it extends from the esophagus to the duodenum; microscopically, the muscularis externa shows special features. (pp. 660–665, Figs. 22.18–22.19) J. The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal; its subdivisions are the duodenum, the jejunum, a ...
... I. The stomach churns food into chyme; it extends from the esophagus to the duodenum; microscopically, the muscularis externa shows special features. (pp. 660–665, Figs. 22.18–22.19) J. The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal; its subdivisions are the duodenum, the jejunum, a ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.