Objectives - LSU School of Medicine
... 6. Identify the role of the CFTR in pancreatic ductular secretion, and predict the consequences of cystic fibrosis on the GI system. 7. List the major components of bile and explain how it is modified in the gall bladder. Identify the role of secretin on the hepatic production of bile. 8. Describe t ...
... 6. Identify the role of the CFTR in pancreatic ductular secretion, and predict the consequences of cystic fibrosis on the GI system. 7. List the major components of bile and explain how it is modified in the gall bladder. Identify the role of secretin on the hepatic production of bile. 8. Describe t ...
Medical Terminology
... skin, sclera,and other tissues caused by excessive bilirubin in the blood Ascites: Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen; can be a symptom of neoplasm or inflammatory disorders in the abdomen, venous hypertension caused by liver disease and heart failure ...
... skin, sclera,and other tissues caused by excessive bilirubin in the blood Ascites: Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen; can be a symptom of neoplasm or inflammatory disorders in the abdomen, venous hypertension caused by liver disease and heart failure ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
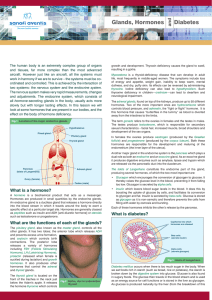
... For the test - be able to label all glands on a human diagram - go over your notes and homework - know the information covered in the following questions 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates and directs the activity of the body’s cells. Spec ...
... For the test - be able to label all glands on a human diagram - go over your notes and homework - know the information covered in the following questions 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates and directs the activity of the body’s cells. Spec ...
The Digestive System - Sinoe Medical Association
... 3. Mechanical digestion is the physical process of preparing the food for chemical digestion and involves chewing, mixing, churning, and segmentation. 4. Chemical digestion is a series of catabolic steps in which complex food molecules are broken down to their chemical building blocks by enzymes. 5. ...
... 3. Mechanical digestion is the physical process of preparing the food for chemical digestion and involves chewing, mixing, churning, and segmentation. 4. Chemical digestion is a series of catabolic steps in which complex food molecules are broken down to their chemical building blocks by enzymes. 5. ...
superior mesenteric artery compression syndrome
... or interrupted transit of contrast medium; stasis of the contrast medium at the gastrointestinal level for more than four hours; obstruction disappears when changing to left lateral decubitus or ventral position10-12. In some patients, computed tomography of abdomen is required, which can show the d ...
... or interrupted transit of contrast medium; stasis of the contrast medium at the gastrointestinal level for more than four hours; obstruction disappears when changing to left lateral decubitus or ventral position10-12. In some patients, computed tomography of abdomen is required, which can show the d ...
CHAPTER 1 3
... important functions ofvarious hormones, how hormones are classified, how steroid and nonsteroid honnones affect target cells, and how hormone secretion is controlled so that homeostasis is maintained (Learning Outcomes 2-7). Finally, you will understand stress and its effects, the general stress res ...
... important functions ofvarious hormones, how hormones are classified, how steroid and nonsteroid honnones affect target cells, and how hormone secretion is controlled so that homeostasis is maintained (Learning Outcomes 2-7). Finally, you will understand stress and its effects, the general stress res ...
Gl Glands, Hormones Diabetes
... The pituitary gland, also known as the master gland, controls all the other glands. It has two lobes; the anterior lobe which releases ADH and prevents excess urine formation, and oxytocin which controls birth contractions. The posterior lobe releases a variety of hormones ...
... The pituitary gland, also known as the master gland, controls all the other glands. It has two lobes; the anterior lobe which releases ADH and prevents excess urine formation, and oxytocin which controls birth contractions. The posterior lobe releases a variety of hormones ...
Motor function of stomach
... 3- emptying of the stomach : This promoted by intense peristaltic contraction of antum & opposed by varying degree of resistance to the passage of the chyme at the pylorus. Regulation of stomach emptying : The emptying regulated by signals from both stomach &duodenum, the duodenum provide the more ...
... 3- emptying of the stomach : This promoted by intense peristaltic contraction of antum & opposed by varying degree of resistance to the passage of the chyme at the pylorus. Regulation of stomach emptying : The emptying regulated by signals from both stomach &duodenum, the duodenum provide the more ...
Submandibular gland
... Each gland is divided into superficial and deep lobes separated by mylohyoid muscle. O 1- Superficial lobe comprises most of the gland . O 2- Deep lobe is the smaller part. O Secretions are delivered into the Wharton duct (submandibular duct ) from the anterior end of the deep lobe O ...
... Each gland is divided into superficial and deep lobes separated by mylohyoid muscle. O 1- Superficial lobe comprises most of the gland . O 2- Deep lobe is the smaller part. O Secretions are delivered into the Wharton duct (submandibular duct ) from the anterior end of the deep lobe O ...
SMA and IMA
... nodes will apply pressure to surrounding tissue; since veins are thin walled they are more likely than arteries to be compressed. Also, hepatic dysfunction can lead to novel and abnormal venous return ...
... nodes will apply pressure to surrounding tissue; since veins are thin walled they are more likely than arteries to be compressed. Also, hepatic dysfunction can lead to novel and abnormal venous return ...
45 Campbell 9th Endocrine
... excessive pathway activity • Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response • For example, in mammals- the neurohormone oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of more oxytocin ...
... excessive pathway activity • Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response • For example, in mammals- the neurohormone oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of more oxytocin ...
Abdomen Review Sheet
... incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity ⇒ fluid will collect here, frequent site of infection Route for spread of infection between pelvis ...
... incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity ⇒ fluid will collect here, frequent site of infection Route for spread of infection between pelvis ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
... • Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – Reproduction – Growth and development – Mobilization of body defenses – Maintenance of much of homeostasis – Regulation of metabolism ...
Chapter 15
... 2. Pancreatic enzymes include pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, and two nucleases. 3. Protein-digesting enzymes are released in an inactive form and are activated upon reaching the small intestine. ...
... 2. Pancreatic enzymes include pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, and two nucleases. 3. Protein-digesting enzymes are released in an inactive form and are activated upon reaching the small intestine. ...
Development of the Mesodermal Organs in Vertebrates
... Blood vessels form from aggregations of mesenchyme cells, called angioblasts. The angioblasts form a thin epithelium surrounding a cavity (which is the future lumen of the blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much ...
... Blood vessels form from aggregations of mesenchyme cells, called angioblasts. The angioblasts form a thin epithelium surrounding a cavity (which is the future lumen of the blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much ...
The Mouth and Esophagus
... choose certain types of food in preference to others. Interestingly, taste preference often changes in conjunction with body needs. Similarly, animals often develop food aversions, particularly if they become ill soon after eating a certain food, even though that food was not the cause of the illnes ...
... choose certain types of food in preference to others. Interestingly, taste preference often changes in conjunction with body needs. Similarly, animals often develop food aversions, particularly if they become ill soon after eating a certain food, even though that food was not the cause of the illnes ...
Ch. 41 - Ltcconline.net
... other enzymes produced by the duodenal cells. 9. Fat digestion does not begin until duodenum. a. hydrolysis of fat is a special problem because fat is insoluble in water. b. first, bile salts from gall bladder coat each droplet and keep them separate - emulsification c. when there are many small dro ...
... other enzymes produced by the duodenal cells. 9. Fat digestion does not begin until duodenum. a. hydrolysis of fat is a special problem because fat is insoluble in water. b. first, bile salts from gall bladder coat each droplet and keep them separate - emulsification c. when there are many small dro ...
HORMON
... First, it must be able to distinguish the hormone from all the other chemicals present in the circulation and bind it. The hormone binding sites on receptors have evolved to have unique configurations that are complementary to the hormones they bind. Generally, hormone-receptor interactions are nonc ...
... First, it must be able to distinguish the hormone from all the other chemicals present in the circulation and bind it. The hormone binding sites on receptors have evolved to have unique configurations that are complementary to the hormones they bind. Generally, hormone-receptor interactions are nonc ...
Lecture 34. Digestion in the stomach
... Stomach phase is depends on the quantity of food, which are present in stomach. It has vago-vagal reflexes (by mean of central nerves system) and local – peripheral reflexes, which are closed in stomach walls. Duration of these phase is longer and quantity of juice is much. It has humoral mechanisms ...
... Stomach phase is depends on the quantity of food, which are present in stomach. It has vago-vagal reflexes (by mean of central nerves system) and local – peripheral reflexes, which are closed in stomach walls. Duration of these phase is longer and quantity of juice is much. It has humoral mechanisms ...
Product Features Natural Full Spectrum Digestive Aid KEY
... chewable enzymes is a unique formula of supplementary enzymes that help your body’s gastrointestinal tract efficiently digest all types of food.* Digestive enzymes1, together with stomach acid, break down your food to allow transformation of nutrients by gastrointestinal bacteria and absorption of n ...
... chewable enzymes is a unique formula of supplementary enzymes that help your body’s gastrointestinal tract efficiently digest all types of food.* Digestive enzymes1, together with stomach acid, break down your food to allow transformation of nutrients by gastrointestinal bacteria and absorption of n ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.