* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download anatomylab4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
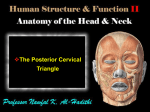
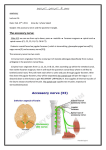
posterior triangle In this lab we will talk about posterior triangle: we said that sternocleidomastoid muscle has a key position in the neck, that divides it into : -Anterior triangle (Anteriorly) - Posterior triangle (Posteriorly) sternocleidomastoid muscle : Origin : Medial origin: Manubrium sterni. Lateral origin: med.1/3 of Clavicle. Insertion: Mastoid process Occipital bone Nerve supply: Spinal accessory nerve(cranial nerve XI) Action: Flex the neck : Bilateral : it Flexes the neck ant. unilateral : it Flexes the neck to one side, so the ear touches the shoulder. Posterior triangle: Boundaries: Anterior: sternocleidomastoid muscle Posterior: Trapezius Inferiorly: clavicle Superior: where sternocleidomastoid muscle overlaps Trapezius also it has roof, floor& contents 1.Roof: -Skin -Superficial fascia -investing layer of cervical deep fascia: behind the vertebrae and we call it (cervical fascia) and is divided into ( 3) layers : 1- Investing layer (outer one): that surrounds the Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid muscles. 2- prevertebral fascia: that surrounds the prevertebral muscles. 3- pretracheal fascia: that surrounds the thyroid gland and help it to go up and down with swallowing. 2.Floor: Muscle covered by prevertebral cervical fascia : 1-semispinalis capitis (we can see only the upper part ). 2-splenius capitis. 3-levator scapulae: attached to the scapula &elevate it. 4-scalenus medius. 5-scalenus anterior. Note: 1. between the scalenus medius and scalenus anterior we can find the brachial plexus. 2.Scalenus posterior :covered by Scalenus medius 3.Contents: 1- Muscles: inferior belly of omohyoid. 2- (3) veins. 3- (3) arteries. 4- (4) nerves. Artreies: Transveres cervical artery. Suprascapular artery . Subclavian artery (3rd part). Subclavian artery divided by Scalenus anterior into (3) parts, the 1st part gives : 1. internal thoracic artery . 2. vertebral artery. 3. thyrocervical trunk(it gives 3 branches:) - Inferior thyroid artery. - suprascapular artery. -transverse cervical artery. How to distinguish between them in the lab : Superior one: Transverse cervical artery Deepest one (horizontal to the clavicle): suprascapular artery. Veins: 1. Transverse cervical vein. 2. Suprascapular vein. 3. External jugular vein that is formed by union of posterior auricular vein and posterior division of retromandibular vein and pass external to the outer surface of sternocleidomastoid muscle to drain into subclavian vein . Nerves: 1.Accessory nerve 2.brachial plexus 3.phrenic nerve 4.cervical plexus(C2,3,4) and its branches: Greater occipital nerve. Lesser occipital nerve. Great auricular nerve. Transverse cervical. Supraclavicular nerve. Best wishes Thanks to my best friend: Sujood Hawamdeh for helping me to write this sheet Done by: Esraa Barmawe.