Stomach
... Figure 23.22c Structural modifications of the small intestine that increase its surface area for digestion and absorption. Absorptive cells ...
... Figure 23.22c Structural modifications of the small intestine that increase its surface area for digestion and absorption. Absorptive cells ...
Digestive System 3 - Northside Middle School
... Pancreas • Location – Mostly retroperitoneal, deep to greater curvature of stomach – Head encircled by duodenum; tail abuts spleen ...
... Pancreas • Location – Mostly retroperitoneal, deep to greater curvature of stomach – Head encircled by duodenum; tail abuts spleen ...
Assessment of the Abdomen
... Ultrasound of the Abdomen: visualize abdominal aorta, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen kidneys, ureters, and bladder CT of the Abdomen ...
... Ultrasound of the Abdomen: visualize abdominal aorta, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen kidneys, ureters, and bladder CT of the Abdomen ...
The Endocrine System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... Zona reticularis secretes gonadocorticoids which supplement sex hormones from the testes and ovaries and stimulate early development of reproductive organs. These hormones are male types (adrenal androgens), namely testosterone, but can be converted into female types, such as estrogens, by the skin, ...
... Zona reticularis secretes gonadocorticoids which supplement sex hormones from the testes and ovaries and stimulate early development of reproductive organs. These hormones are male types (adrenal androgens), namely testosterone, but can be converted into female types, such as estrogens, by the skin, ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •These hormones prepare the body to deal with short-term stress (“fight or flight”) by •Increasing heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels •Dilating small passageways of lungs ...
... •These hormones prepare the body to deal with short-term stress (“fight or flight”) by •Increasing heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels •Dilating small passageways of lungs ...
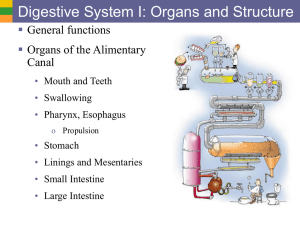
7a DigSys Ia- Organs and Structure
... Chemical breakdown of protein begins Delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine ...
... Chemical breakdown of protein begins Delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine ...
Dissector Bold terms 3
... -Greater peritoneal sac -Lesser peritoneal sac (omental bursa): posterior to stomach/lesser omentum -Inferior recess (lowest part of lesser sac) -Superior recess (highest part of lesser sac) -Omentum foramen (epiploic foramen): connects the sacs Boundaries of Omentum Foramen -Anterior-hepatic portal ...
... -Greater peritoneal sac -Lesser peritoneal sac (omental bursa): posterior to stomach/lesser omentum -Inferior recess (lowest part of lesser sac) -Superior recess (highest part of lesser sac) -Omentum foramen (epiploic foramen): connects the sacs Boundaries of Omentum Foramen -Anterior-hepatic portal ...
upper limb vessels
... Commences lower border of teres major axillary vein on medial side median nerve lateral to it proximally but then crosses in front of it to lie medial ulnar nerve is posterior to it proximally but leaves it as it slopes downward thru the medial IM septum Branches o Muscular branches o Nutr ...
... Commences lower border of teres major axillary vein on medial side median nerve lateral to it proximally but then crosses in front of it to lie medial ulnar nerve is posterior to it proximally but leaves it as it slopes downward thru the medial IM septum Branches o Muscular branches o Nutr ...
chapter 45 - Biology Junction
... responses from its target cells, while other cell types ignore that particular hormone. Concept 45.1 The endocrine system and the nervous system act individually and together in regulating an animal’s physiology Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation, the nervous system ...
... responses from its target cells, while other cell types ignore that particular hormone. Concept 45.1 The endocrine system and the nervous system act individually and together in regulating an animal’s physiology Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation, the nervous system ...
FROG DISSECTION External Anatomy
... the lymphatic system and is charge of filtering out dead blood cells and harmful bacteria. 29. The pancreas is a thin, yellowish gland that is difficult to find. It is located in the mesentery between the duodenum and the upper part of the stomach. The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes and can als ...
... the lymphatic system and is charge of filtering out dead blood cells and harmful bacteria. 29. The pancreas is a thin, yellowish gland that is difficult to find. It is located in the mesentery between the duodenum and the upper part of the stomach. The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes and can als ...
Document
... Secretes three hormones Calcitriol—Stimulates calcium and phosphate absorption in intestine Erythropoietin (EPO)—Stimulates red blood cell production by bone marrow Renin—Enzyme that leads to angiotensin II that triggers ...
... Secretes three hormones Calcitriol—Stimulates calcium and phosphate absorption in intestine Erythropoietin (EPO)—Stimulates red blood cell production by bone marrow Renin—Enzyme that leads to angiotensin II that triggers ...
Endocrine System - ocw@unimas
... • Endocrine system is made up of ductless glands, which secretes chemical signal (hormone) into circula
... • Endocrine system is made up of ductless glands, which secretes chemical signal (hormone) into circula
Chapter 17 - Dr. Wilson`s Site
... • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect because inhibits insulin secretion – muscles use fatty acids saving glucose for brain ...
... • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect because inhibits insulin secretion – muscles use fatty acids saving glucose for brain ...
Vessels of Lower Abdomen, Thigh, and Leg
... Only those veins that do not parallel their respective arteries are described. The Inferior Mesenteric Vein arises from the lower portion of the large intestine and proceeds superiorly. The Superior Mesenteric Vein collects blood from the stomach, small intestine, and most of large intestine returni ...
... Only those veins that do not parallel their respective arteries are described. The Inferior Mesenteric Vein arises from the lower portion of the large intestine and proceeds superiorly. The Superior Mesenteric Vein collects blood from the stomach, small intestine, and most of large intestine returni ...
Endocrine System
... – Diurnal (or circadian), i.e. “day-night”. characterised by repetitive oscillations in hormone levels that are very regular and have a frequency of one cycle every 24 hours. Eg. Cortisol secretion. – Other rhythm. Monthly menstrual period. ...
... – Diurnal (or circadian), i.e. “day-night”. characterised by repetitive oscillations in hormone levels that are very regular and have a frequency of one cycle every 24 hours. Eg. Cortisol secretion. – Other rhythm. Monthly menstrual period. ...
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... Name the sphincter muscles that open to the outside and explain how their action is controlled. ...
... Name the sphincter muscles that open to the outside and explain how their action is controlled. ...
Digestive Information
... Name the sphincter muscles that open to the outside and explain how their action is controlled. ...
... Name the sphincter muscles that open to the outside and explain how their action is controlled. ...
The Digestive System
... GERD: Gastric esophageal reflux disorder; the upward movement of stomach acids and contents into the esophagus. It is commonly called heart burn. Hemorrhoids: Varicose veins occurring at the anus and in the rectum. Hernia: The protrusion of an organ or part, such as the intestine through a weak plac ...
... GERD: Gastric esophageal reflux disorder; the upward movement of stomach acids and contents into the esophagus. It is commonly called heart burn. Hemorrhoids: Varicose veins occurring at the anus and in the rectum. Hernia: The protrusion of an organ or part, such as the intestine through a weak plac ...
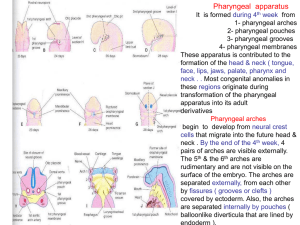
02-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... degenerates .By the 6th week the epithelium of each dorsal bulbar part begins to differentiate into an inferior parathyroid gland . The epithelium of the elongate ventral parts proliferates& obliterating their cavities to form the thymus gland. These bilateral primordia come together in the median p ...
... degenerates .By the 6th week the epithelium of each dorsal bulbar part begins to differentiate into an inferior parathyroid gland . The epithelium of the elongate ventral parts proliferates& obliterating their cavities to form the thymus gland. These bilateral primordia come together in the median p ...
Penile Anatomy
... o laterally to the pubic rami and fascia lata of the thighs o posteriorly to the urogenital diaphragm and perineal membrane. Blood Supply (Cormack and Lamberty) Superficial Supply The arterial supply of the superficial fascia and skin of the shaft of the penis to the corona comes from the superfic ...
... o laterally to the pubic rami and fascia lata of the thighs o posteriorly to the urogenital diaphragm and perineal membrane. Blood Supply (Cormack and Lamberty) Superficial Supply The arterial supply of the superficial fascia and skin of the shaft of the penis to the corona comes from the superfic ...
hormones - Spring Branch ISD
... reducing the initial stimulus, thus preventing excessive pathway activity • Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response • For example, in mammals oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of more oxytocin ...
... reducing the initial stimulus, thus preventing excessive pathway activity • Positive feedback reinforces a stimulus to produce an even greater response • For example, in mammals oxytocin causes the release of milk, causing greater suckling by offspring, which stimulates the release of more oxytocin ...
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE OUTLINE COMPARISON of CONTROL by
... overproduction or underproduction of a particular hormone; when these regulating mechanisms do not operate properly, disorders result. B. Hormone secretion is controlled by stimuli that are: 1. signals from the nervous system 2. chemical changes in the blood 3. other hormones. 4. Most often, negativ ...
... overproduction or underproduction of a particular hormone; when these regulating mechanisms do not operate properly, disorders result. B. Hormone secretion is controlled by stimuli that are: 1. signals from the nervous system 2. chemical changes in the blood 3. other hormones. 4. Most often, negativ ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.