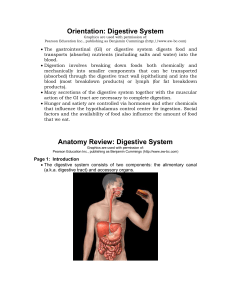
Anatomy Review: Digestive System
... The esophagus moves its contents via peristalsis (now is a good time to play the animation on page 4 of the Motility topic) Swallowing begins voluntarily but is completed by reflexive (involuntary) primary peristalsis controlled by the swallowing center in the brain stem The sequence of events in sw ...
... The esophagus moves its contents via peristalsis (now is a good time to play the animation on page 4 of the Motility topic) Swallowing begins voluntarily but is completed by reflexive (involuntary) primary peristalsis controlled by the swallowing center in the brain stem The sequence of events in sw ...
marking the start and the end of an artery 3) Branches
... 3. Patterns of Anastomoses of Arteries Some parts of the body build up arterial anastomoses to ensure constant blood supply to the specific areas or organs because these regions or organs often change their shape or are pressed & their blood flow is affected. ...
... 3. Patterns of Anastomoses of Arteries Some parts of the body build up arterial anastomoses to ensure constant blood supply to the specific areas or organs because these regions or organs often change their shape or are pressed & their blood flow is affected. ...
Receptor - WordPress.com
... from the blood Aldosterone secretion is increased by: • falling blood pressure: thus Na+ is reabsorbed, water is passively reabsorbed with it, and blood volume is maintained • rising blood levels of K+ : excess K+ is secreted from the blood, leaves the body in urine, and levels do not rise to advers ...
... from the blood Aldosterone secretion is increased by: • falling blood pressure: thus Na+ is reabsorbed, water is passively reabsorbed with it, and blood volume is maintained • rising blood levels of K+ : excess K+ is secreted from the blood, leaves the body in urine, and levels do not rise to advers ...
Radial Artery
... Dorsal venous network lies on the dorsum of the hand, in the subcutanous tissue, proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints Drains into the cephalic vein laterally, and basilic vein medially ...
... Dorsal venous network lies on the dorsum of the hand, in the subcutanous tissue, proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints Drains into the cephalic vein laterally, and basilic vein medially ...
Ruminants – Stomach
... ► Functions of microorganisms. Digest roughages to make Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA’s), make microbial protein, and make vitamins K and B-complex. ...
... ► Functions of microorganisms. Digest roughages to make Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA’s), make microbial protein, and make vitamins K and B-complex. ...
Main Function of the Digestive System
... • Liver-a large lobed glandular organ in the abdomen of vertebrates, involved in many metabolic processes. • Gallbladder-the small sac-shaped organ beneath the liver, in which bile is stored after secretion by the liver and before release into the intestine. • Small intestine-the part of the intesti ...
... • Liver-a large lobed glandular organ in the abdomen of vertebrates, involved in many metabolic processes. • Gallbladder-the small sac-shaped organ beneath the liver, in which bile is stored after secretion by the liver and before release into the intestine. • Small intestine-the part of the intesti ...
the gastrointestinal system
... products that are excreted in the bile rather than the urine, are expelled from the body. All of these functions are tightly regulated in concert with the ingestion of meals. Diseases in the digestive systems, also called gastrointestinal diseases, have become quite common in the modern day world. T ...
... products that are excreted in the bile rather than the urine, are expelled from the body. All of these functions are tightly regulated in concert with the ingestion of meals. Diseases in the digestive systems, also called gastrointestinal diseases, have become quite common in the modern day world. T ...
BIOL242Ch16EndocrineSEP2012
... Pineal gland • Secretes melatonin in inverse proportion to sunlight • Regulates circadian rhythms ...
... Pineal gland • Secretes melatonin in inverse proportion to sunlight • Regulates circadian rhythms ...
BIOL242Ch16EndocrineSEP2012
... Two types of glands in the body • Exocrine – secrete products through a duct onto epithelial surface, e.g. sweat, oil, salivary glands • Endocrine - release hormones into the blood or lymph often to travel throughout the body, e.g. pituitary, pancreas, thyroid ...
... Two types of glands in the body • Exocrine – secrete products through a duct onto epithelial surface, e.g. sweat, oil, salivary glands • Endocrine - release hormones into the blood or lymph often to travel throughout the body, e.g. pituitary, pancreas, thyroid ...
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 10: Endocrine System
... INTRODUCTION DEFINITIONS ENDO = internal CRINE = secrete a. The endocrine glands are glands of internal secretion (rather than external, as seen with the sweat glands and digestive glands). b. This internal secretion results from the fact that these glands have no ducts. Thus, they are often referr ...
... INTRODUCTION DEFINITIONS ENDO = internal CRINE = secrete a. The endocrine glands are glands of internal secretion (rather than external, as seen with the sweat glands and digestive glands). b. This internal secretion results from the fact that these glands have no ducts. Thus, they are often referr ...
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
... coming from the internal carotid artery, we call them superior because they go superior to the pituitary (they actually go to the hypothalamus), and in the hypothalamus they will form the first capillary network, we call it the first hypophyseal plexus, in this plexus the blood will drain from the h ...
... coming from the internal carotid artery, we call them superior because they go superior to the pituitary (they actually go to the hypothalamus), and in the hypothalamus they will form the first capillary network, we call it the first hypophyseal plexus, in this plexus the blood will drain from the h ...
The Endocrine System
... A. Corpus luteum normally secrets progesterone and estrogen B. Corpus luteum secrets progesterone and estrogen for only ~10 days, then undergo degeneration, no matter if the egg is fertilized or not. C. Corpus luteum is formed after the oocyte is ...
... A. Corpus luteum normally secrets progesterone and estrogen B. Corpus luteum secrets progesterone and estrogen for only ~10 days, then undergo degeneration, no matter if the egg is fertilized or not. C. Corpus luteum is formed after the oocyte is ...
growth hormone (GH)
... a disease caused by low level of adrenal cortex hormones resulting in the loss of sodium and low blood pressure; this disease can be fatal. adrenal glands there are two adrenal glands located one on top of each kidney. Each of these glands are divided into two endocrine glands the inner adrenal medu ...
... a disease caused by low level of adrenal cortex hormones resulting in the loss of sodium and low blood pressure; this disease can be fatal. adrenal glands there are two adrenal glands located one on top of each kidney. Each of these glands are divided into two endocrine glands the inner adrenal medu ...
Endocrine Disease in the White House
... Pineal gland • Secretes melatonin in inverse proportion to sunlight • Regulates circadian rhythms ...
... Pineal gland • Secretes melatonin in inverse proportion to sunlight • Regulates circadian rhythms ...
comp3_unit7_lecture_slides
... Location • small organ in your upper chest, under your breastbone ...
... Location • small organ in your upper chest, under your breastbone ...
variations in the arterial branching pattern of the coeliac trunk
... patterns of the CT have been described. It appears that only 87.6% of the CT exhibited the classical trifurcation, while an incomplete CT accounted for 12.2% and absence of the CT was extremely rare.[6] Anatomical variations in the branching pattern of the CT are of considerable importance in liver ...
... patterns of the CT have been described. It appears that only 87.6% of the CT exhibited the classical trifurcation, while an incomplete CT accounted for 12.2% and absence of the CT was extremely rare.[6] Anatomical variations in the branching pattern of the CT are of considerable importance in liver ...
Chapter2 Endocrine System for handouts
... Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release its hormones ...
... Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release its hormones ...
Functions
... Mucous Neck Cells: secrete a thin layer of protective mucus Parietal Cells: secrete HCL (activates pepsinogen and helps prevent bacterial infection) and intrinsic factor ...
... Mucous Neck Cells: secrete a thin layer of protective mucus Parietal Cells: secrete HCL (activates pepsinogen and helps prevent bacterial infection) and intrinsic factor ...
Endocrine PP - Laura Banks
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
... • Step 3: New hormones are released by the adrenal glands into the body AS WELL AS cutting off the hormone production in the pituitary glands • This allows the hypothalamus to start producing hormones again ...
Glands - The Anatomy of Sea Turtles by Jeanette Wyneken
... frozen, then thawed, or that have started decomposing, it may become brown. It is gelatinous in texture in fresh and fresh-frozen animals. In decomposing carcasses, it liquifies. The thyroid is involved with increasing oxygen consumption when reptiles exceed their preferred body temperatures, and it ...
... frozen, then thawed, or that have started decomposing, it may become brown. It is gelatinous in texture in fresh and fresh-frozen animals. In decomposing carcasses, it liquifies. The thyroid is involved with increasing oxygen consumption when reptiles exceed their preferred body temperatures, and it ...
Endocrine System
... – Insulin – allows glucose to cross plasma membranes into cells from beta cells – Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells – These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis ...
... – Insulin – allows glucose to cross plasma membranes into cells from beta cells – Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells – These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis ...
neuroanatomy 10 [4-20
... What artery supplies the medial sensorimotor cortex? What supplies the lateral frontal lobe? Anterior cerebral artery Middle cerebral artery ...
... What artery supplies the medial sensorimotor cortex? What supplies the lateral frontal lobe? Anterior cerebral artery Middle cerebral artery ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.