8 I PUC – Biology Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption One Mark
... 44. What protects the gastric mucosa from the action of conc.Hcl. Ans: The mucus and bicarbonates present in the gastric juice protects the mucosal epithelium from excoriation by the HCl. 45. What is intestinal juice called as? Ans: Succus entericus 46. Mention the 2 ways by which the activities of ...
... 44. What protects the gastric mucosa from the action of conc.Hcl. Ans: The mucus and bicarbonates present in the gastric juice protects the mucosal epithelium from excoriation by the HCl. 45. What is intestinal juice called as? Ans: Succus entericus 46. Mention the 2 ways by which the activities of ...
Intestinal function in mice with small bowel growth
... growth by GLP-2 in wild-type mice results in a normal-toincreased capacity for nutrient digestion and absorption in vivo. intestinal nutrient ...
... growth by GLP-2 in wild-type mice results in a normal-toincreased capacity for nutrient digestion and absorption in vivo. intestinal nutrient ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... short. Doctors can often treat the problems by controlling the production of hormones or replacing certain hormones with ...
... short. Doctors can often treat the problems by controlling the production of hormones or replacing certain hormones with ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... release their hormones into blood or lymphatic fluid, to be distinguished from exocrine glands, which release their products directly into ducts on the epithelial surface. In the final sections of this chapter, the major endocrine organs and their hormones’ main actions and regulatory functions are ...
... release their hormones into blood or lymphatic fluid, to be distinguished from exocrine glands, which release their products directly into ducts on the epithelial surface. In the final sections of this chapter, the major endocrine organs and their hormones’ main actions and regulatory functions are ...
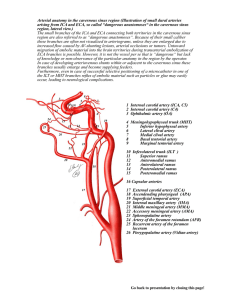
Arterial anatomy
... Arterial anatomy in the cavernous sinus region (Illustration of small dural arteries arising from ICA and ECA, so called “dangerous anastomoses“ in the cavernous sinus region, lateral view.) The small branches of the ICA and ECA connecting both territories in the cavernous sinus region are also refe ...
... Arterial anatomy in the cavernous sinus region (Illustration of small dural arteries arising from ICA and ECA, so called “dangerous anastomoses“ in the cavernous sinus region, lateral view.) The small branches of the ICA and ECA connecting both territories in the cavernous sinus region are also refe ...
Rat Anatomy Checklist
... At each end of the stomach (on the inside) is muscular valve. The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is called the cardiac sphincter. The opening between the stomach and the intestine is called the pyloric sphincter. 5. The spleen is about the same color as the liver and is attached to th ...
... At each end of the stomach (on the inside) is muscular valve. The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is called the cardiac sphincter. The opening between the stomach and the intestine is called the pyloric sphincter. 5. The spleen is about the same color as the liver and is attached to th ...
Vasculature and Lymphatics
... Three main vessels emerge from the aortic arch. The first major branch off of the aortic arch is the brachiocephalic artery. This very short artery quickly splits into two other vessels: the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. The left subclavian and left common carotid art ...
... Three main vessels emerge from the aortic arch. The first major branch off of the aortic arch is the brachiocephalic artery. This very short artery quickly splits into two other vessels: the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. The left subclavian and left common carotid art ...
Thorax
... • Slope – ant. Part 1.5 cm below than post. Part ant. Part lies at T3(U) • Obliquity approx 45 degree ...
... • Slope – ant. Part 1.5 cm below than post. Part ant. Part lies at T3(U) • Obliquity approx 45 degree ...
Introduction to the endocrine system and the hypothalamic
... rhythms, external cues can modify rhythms ...
... rhythms, external cues can modify rhythms ...
Sheet 5
... The inferoposterior compartment is further divided by the mesentery of the small intestine (which attaches the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall) into upper and lower compartments. (Slides say right and left) ...
... The inferoposterior compartment is further divided by the mesentery of the small intestine (which attaches the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall) into upper and lower compartments. (Slides say right and left) ...
Digestive Systems
... proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; absorption of the end products of digestion 1. duodenum - most digestion occurs here 2. jejunum - some digestion and some absorption occur 3. ileum - mostly absorption -Bile - made in liver, stored in gall bladder, active in the small intestine, emulsifies fat to a ...
... proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; absorption of the end products of digestion 1. duodenum - most digestion occurs here 2. jejunum - some digestion and some absorption occur 3. ileum - mostly absorption -Bile - made in liver, stored in gall bladder, active in the small intestine, emulsifies fat to a ...
14_01aLectureNotes
... Chemical breakdown of protein begins Delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine ...
... Chemical breakdown of protein begins Delivers chyme (processed food) to the small intestine ...
Histochemical and immunohistochemical study on endocrine
... two directions: internal circular and external longitudinal (Fig. 2F). This region contains myenteric plexuses arranged in sparse groups, composing the enteric nervous system and located between the muscular sub-layers. A serous layer surrounds these structures. In the non-glandular region, differen ...
... two directions: internal circular and external longitudinal (Fig. 2F). This region contains myenteric plexuses arranged in sparse groups, composing the enteric nervous system and located between the muscular sub-layers. A serous layer surrounds these structures. In the non-glandular region, differen ...
Hormonal Responses to Exercise - Yola
... • Also associated with negative side effects – Revert to normal after discontinuation ...
... • Also associated with negative side effects – Revert to normal after discontinuation ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainag ...
... Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainag ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainag ...
... Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainag ...
No Slide Title
... When the bile salts come into contact with a fat droplet their hydrophobic side faces inwards towards the fat and their hydrophilic side faces outwards into the water. This provides a coating around the droplets which keeps them in solution and prevents them from reaggregating into larger droplets. ...
... When the bile salts come into contact with a fat droplet their hydrophobic side faces inwards towards the fat and their hydrophilic side faces outwards into the water. This provides a coating around the droplets which keeps them in solution and prevents them from reaggregating into larger droplets. ...
Unit 23.3: The Digestive System
... enable peristalsis. Peristalsis is an involuntary muscle contraction that moves rapidly along an organ like a wave (see Figure below). ...
... enable peristalsis. Peristalsis is an involuntary muscle contraction that moves rapidly along an organ like a wave (see Figure below). ...
Major arteries
... 4. Reduced blood supply to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh could be due to injury of: A. Femoral artery. B. Popliteal artery. C. Dorsalis pedis artery. D. Anterior tibial artery. ...
... 4. Reduced blood supply to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh could be due to injury of: A. Femoral artery. B. Popliteal artery. C. Dorsalis pedis artery. D. Anterior tibial artery. ...
Nasogastric Intubation
... – Breaks down ingested food – Propels food through the GI tract – Absorbs nutrients across wall of lumen of GI tract – Absorbs water and salts ...
... – Breaks down ingested food – Propels food through the GI tract – Absorbs nutrients across wall of lumen of GI tract – Absorbs water and salts ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
... anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. TRH: Thyrotrophin releasing hormone (TRH): stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyrotropin (thyroid‐stimulating hormone) and stimulates the secretion of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. GnRH: Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH): ...
... anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. TRH: Thyrotrophin releasing hormone (TRH): stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyrotropin (thyroid‐stimulating hormone) and stimulates the secretion of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. GnRH: Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH): ...
Document
... Alpha or A cells secrete glucagon – raises blood sugar Beta or B cells secrete insulin – lowers blood sugar Delta or D cells secrete somatostatin – inhibits both insulin and glucagon F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide – inhibits somatostatin, gallbladder contraction, and secretion of ...
... Alpha or A cells secrete glucagon – raises blood sugar Beta or B cells secrete insulin – lowers blood sugar Delta or D cells secrete somatostatin – inhibits both insulin and glucagon F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide – inhibits somatostatin, gallbladder contraction, and secretion of ...
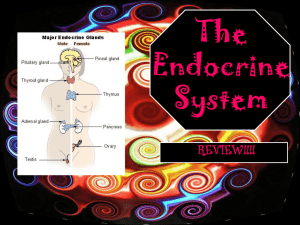
Endocrine System
... Cushing’s disease - excessive output of glucocorticoids results in “moon face” and appearance of a “buffalo hump” ...
... Cushing’s disease - excessive output of glucocorticoids results in “moon face” and appearance of a “buffalo hump” ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.