Pituitary Gland Hormones
... Target: Heart, bl. Vessels, resp. system, liver, skel. mms Action: inc. BP, bl. Sugar, heart rate, bl. fl. to brain, heart and skeletal mms (vasodialation); Vasoconstriction to the skin and GI (gut); Bronchi dialation to inc. air exchange Stimulus for Release: signals from brain to hypothalsympath ...
... Target: Heart, bl. Vessels, resp. system, liver, skel. mms Action: inc. BP, bl. Sugar, heart rate, bl. fl. to brain, heart and skeletal mms (vasodialation); Vasoconstriction to the skin and GI (gut); Bronchi dialation to inc. air exchange Stimulus for Release: signals from brain to hypothalsympath ...
Chapter 9
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
Carbohydrate Digestion and Absorption NASPGHAN Physiology
... supported by breath testing, although the sensitivity and specificity of this test is approximately 60%. In this test, malabsorption of the test sugar results in increased breath H+. ...
... supported by breath testing, although the sensitivity and specificity of this test is approximately 60%. In this test, malabsorption of the test sugar results in increased breath H+. ...
physiologicoanatomical features of the digestive system in children
... occlusion or bite. The general rule for estimating the number of temporary teeth in children who are 2 years of age or younger is: the child's age in months minus 6 months equals the number of teeth. Discoloration of tooth enamel with obvious plaque (whitish coating on the surface of the teeth) is a ...
... occlusion or bite. The general rule for estimating the number of temporary teeth in children who are 2 years of age or younger is: the child's age in months minus 6 months equals the number of teeth. Discoloration of tooth enamel with obvious plaque (whitish coating on the surface of the teeth) is a ...
Section 10.1
... down food into molecules that the body can use is called digestion. • During mechanical digestion, foods are physically broken apart into smaller pieces. • During chemical digestion, chemicals produced by your body break large molecules into smaller ones that your body can use. • Most of the chemica ...
... down food into molecules that the body can use is called digestion. • During mechanical digestion, foods are physically broken apart into smaller pieces. • During chemical digestion, chemicals produced by your body break large molecules into smaller ones that your body can use. • Most of the chemica ...
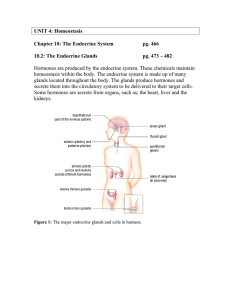
The Endocrine System
... Help resist long-term stressors Released in response to increased blood levels of ACTH Sex hormones Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex Small amounts are made throughout life Mostly androgens (male sex hormones) are made but some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... Help resist long-term stressors Released in response to increased blood levels of ACTH Sex hormones Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex Small amounts are made throughout life Mostly androgens (male sex hormones) are made but some estrogens (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
Lungs - GMCH
... deoxygenated blood to lungs Rt PA is longer Enters the root of the lung & branches in to arteries for superior middle &inferior lobe Lt PA is shorter 2 Pulmonary vein (superior & inferior) on each side PV drain in to left atria ...
... deoxygenated blood to lungs Rt PA is longer Enters the root of the lung & branches in to arteries for superior middle &inferior lobe Lt PA is shorter 2 Pulmonary vein (superior & inferior) on each side PV drain in to left atria ...
pertinent blood vessel routes
... blood from the large intestine from the splenic flexure to the rectum empties into the inferior mesenteric vein splenic vein blood from the rest of the large intestine, the small intestine, and the pancreas superior mesenteric vein the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein unite to form ...
... blood from the large intestine from the splenic flexure to the rectum empties into the inferior mesenteric vein splenic vein blood from the rest of the large intestine, the small intestine, and the pancreas superior mesenteric vein the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein unite to form ...
9/30/09 Abdomen Continued Ureters: They are muscular ducts
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
C H A P T E R 6 2
... slow, undulating changes in the resting membrane potential. Their intensity usually varies between 5 and 15 millivolts, and their frequency ranges in different parts of the human gastrointestinal tract from 3 to 12 per minute: In the body of the stomach 3/min In the duodenum 12/min In the terminal i ...
... slow, undulating changes in the resting membrane potential. Their intensity usually varies between 5 and 15 millivolts, and their frequency ranges in different parts of the human gastrointestinal tract from 3 to 12 per minute: In the body of the stomach 3/min In the duodenum 12/min In the terminal i ...
Structure of the Liver
... (duodenum) and the pancreatic duct, by the common hepatic duct. The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct enter the duodenum by a common duct called the hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater) The liver is made of several lobules. Each lobule consists of specialized epithelial cells called he ...
... (duodenum) and the pancreatic duct, by the common hepatic duct. The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct enter the duodenum by a common duct called the hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater) The liver is made of several lobules. Each lobule consists of specialized epithelial cells called he ...
The Urinary System
... The kidney is a bean shaped organ being located retroperitoneally on each side of the the vertebral column from T11- L3.The right one is at lower level than the left one due to liver. Each kidney has 2 poles, 2 margins & 2 surfaces.The medial concave margin has a vertical slit leading to a cavity kn ...
... The kidney is a bean shaped organ being located retroperitoneally on each side of the the vertebral column from T11- L3.The right one is at lower level than the left one due to liver. Each kidney has 2 poles, 2 margins & 2 surfaces.The medial concave margin has a vertical slit leading to a cavity kn ...
Chapter 45 - sharpesystems2012
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
The Endocrine System
... Zona reticularis secretes gonadocorticoids which supplement sex hormones from the testes and ovaries and stimulate early development of reproductive organs. These hormones are male types (adrenal androgens), namely testosterone, but can be converted into female types, such as estrogens, by the skin, ...
... Zona reticularis secretes gonadocorticoids which supplement sex hormones from the testes and ovaries and stimulate early development of reproductive organs. These hormones are male types (adrenal androgens), namely testosterone, but can be converted into female types, such as estrogens, by the skin, ...
Anatomy - Exam 1 Lab
... ○ Cephalic vein ○ Thoracoacromial artery ○ Lateral thoracic artery ○ Right and Left Internal thoracic arteries – on inside of thoracic wall Feeds anterior intercostal arteries ○ Anterior intercostal artery and vein – same as posterior, just in the anterior area ○ Posterior intercostal artery and v ...
... ○ Cephalic vein ○ Thoracoacromial artery ○ Lateral thoracic artery ○ Right and Left Internal thoracic arteries – on inside of thoracic wall Feeds anterior intercostal arteries ○ Anterior intercostal artery and vein – same as posterior, just in the anterior area ○ Posterior intercostal artery and v ...
F3 Biology Quizzes answers for April exercise
... Ans. Their molecules are too big for it. d. State and explain one precaution for doing this experiment. Ans. Tie the knots tightly to prevent their leakage. 10. Why is digestion of food necessary? Ans. It breaks down the food until the molecules are small enough to be absorbed. 11. What is the major ...
... Ans. Their molecules are too big for it. d. State and explain one precaution for doing this experiment. Ans. Tie the knots tightly to prevent their leakage. 10. Why is digestion of food necessary? Ans. It breaks down the food until the molecules are small enough to be absorbed. 11. What is the major ...
pertinent blood vessel routes
... blood from the large intestine from the splenic flexure to the rectum empties into the inferior mesenteric vein splenic vein blood from the rest of the large intestine, the small intestine, and the pancreas superior mesenteric vein the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein unite to form ...
... blood from the large intestine from the splenic flexure to the rectum empties into the inferior mesenteric vein splenic vein blood from the rest of the large intestine, the small intestine, and the pancreas superior mesenteric vein the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein unite to form ...
Test for Skull Video 07-16-11
... B) Arthritis C) Spondylitis D) All of the above 52) The ____________ lies between the stomach, bladder and intestine, and holds other organs in place. A) Peritoneum B) Greater omentum C) Pancreas D) Mediastinum 53) Which of the following functions to remove foreign material, toxins, or pathogens fro ...
... B) Arthritis C) Spondylitis D) All of the above 52) The ____________ lies between the stomach, bladder and intestine, and holds other organs in place. A) Peritoneum B) Greater omentum C) Pancreas D) Mediastinum 53) Which of the following functions to remove foreign material, toxins, or pathogens fro ...
Chapter 31
... – The adrenal medulla produces epinephrine or adrenaline. This produces the “flight or fight” reaction. In a fraction of a second, this hormone can be secreted in response to fear, anger, pain or physical exertion. – The adrenal cortex produces a hormone that helps the body deal with long-term stres ...
... – The adrenal medulla produces epinephrine or adrenaline. This produces the “flight or fight” reaction. In a fraction of a second, this hormone can be secreted in response to fear, anger, pain or physical exertion. – The adrenal cortex produces a hormone that helps the body deal with long-term stres ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF UDDER
... process so that he receives the maximum benefit. • It is therefore essential that one understands the natural process in order to manipulate it. ...
... process so that he receives the maximum benefit. • It is therefore essential that one understands the natural process in order to manipulate it. ...
Note 10.2 - Endocrine Gland
... Hypothalamus – is the region of the brain that releases hormones to control the pituitary gland, which, in turn, controls other endocrine glands. Neurohormone – is a hormone produced by neurons, such as in the hypothalamus that controls the production of other hormones in the pituitary gland. Pituit ...
... Hypothalamus – is the region of the brain that releases hormones to control the pituitary gland, which, in turn, controls other endocrine glands. Neurohormone – is a hormone produced by neurons, such as in the hypothalamus that controls the production of other hormones in the pituitary gland. Pituit ...
A comparison of the different livestock systems
... -saliva begins the carbohydrate breakdown with salivary amylase ...
... -saliva begins the carbohydrate breakdown with salivary amylase ...
Parts and functions of the ruminant digestive system continued…
... -saliva begins the carbohydrate breakdown with salivary amylase ...
... -saliva begins the carbohydrate breakdown with salivary amylase ...
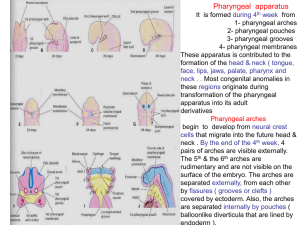
Foregut is a source for development of: Stomach, small intestine
... Additus laryngis* Esophagus Pharyngeal openings of tuba auditiva, fauces, choans 57. Choans connect pharynx with: Oral cavity Larynx Nasal cavity* Middle ear 58. Tuba auditiva connecst pharynx with: Oral cavity Larynx Nasal cavity Middle ear (tympanic cavity)* 59. Location of pharyngeal tonsil: Orop ...
... Additus laryngis* Esophagus Pharyngeal openings of tuba auditiva, fauces, choans 57. Choans connect pharynx with: Oral cavity Larynx Nasal cavity* Middle ear 58. Tuba auditiva connecst pharynx with: Oral cavity Larynx Nasal cavity Middle ear (tympanic cavity)* 59. Location of pharyngeal tonsil: Orop ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.