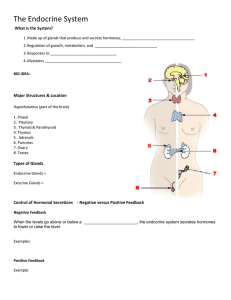
The Endocrine System (Chap 11)
... Pancreas Large gland behind stomach, maintains healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ______________________________________ ...
... Pancreas Large gland behind stomach, maintains healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ______________________________________ ...
Thyroid Gland - Fort Bend ISD
... Large gland behind stomach, maintains healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ______________________________________ Insulin – decreases blood sug ...
... Large gland behind stomach, maintains healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ______________________________________ Insulin – decreases blood sug ...
The Endocrine System
... one or two body functions – One gland sends a message to the kidneys that determines how much water is removed from the body to ...
... one or two body functions – One gland sends a message to the kidneys that determines how much water is removed from the body to ...
Name - Humble ISD
... B. Accessory Structures – structures that aid in digestion, but food does NOT enter these! 1. Liver – produces bile which is secreted into ducts which drain into the gall bladder and then into the duodenum. ...
... B. Accessory Structures – structures that aid in digestion, but food does NOT enter these! 1. Liver – produces bile which is secreted into ducts which drain into the gall bladder and then into the duodenum. ...
Functions
... found in saliva Submandibular- provides digestive enzyme (amylase) to moisten food to make it easier to swallow ...
... found in saliva Submandibular- provides digestive enzyme (amylase) to moisten food to make it easier to swallow ...
Digestive System Major Functions of the GI Tract Six Processes of
... • Intermediate products are polypeptides and peptides ...
... • Intermediate products are polypeptides and peptides ...
Digestive System
... ● comes from mucosal epithelial cells in small intestine ● increases insulin secretion in response to infusions of glucose ● affects glucose absorption and small intestine ...
... ● comes from mucosal epithelial cells in small intestine ● increases insulin secretion in response to infusions of glucose ● affects glucose absorption and small intestine ...
Digestive system and Nutrition
... enzymes, and fluids to aid in the breakdown of ingested food. But each has its own important function Liver: Makes bile, oxidizes fatty acids, Gallbladder: stores bile Pancreas:pancreatic juices, proteolytic enzymes ...
... enzymes, and fluids to aid in the breakdown of ingested food. But each has its own important function Liver: Makes bile, oxidizes fatty acids, Gallbladder: stores bile Pancreas:pancreatic juices, proteolytic enzymes ...
Gastrointestinal Physiology – Part 2
... endocrine gland cells – secrete the endocrine hormone, gastrin • Endocrine cells secrete hormones into the bloodstream – travel to a distant part of the body where they produce an effect on another cell type ...
... endocrine gland cells – secrete the endocrine hormone, gastrin • Endocrine cells secrete hormones into the bloodstream – travel to a distant part of the body where they produce an effect on another cell type ...
Gastrointestinal Physiology – Part 2
... endocrine gland cells – secrete the endocrine hormone, gastrin • Endocrine cells secrete hormones into the bloodstream – travel to a distant part of the body where they produce an effect on another cell type ...
... endocrine gland cells – secrete the endocrine hormone, gastrin • Endocrine cells secrete hormones into the bloodstream – travel to a distant part of the body where they produce an effect on another cell type ...
45-Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Introduction to Regulatory Systems • Nervous system involved with high speed responses • Endocrine system is slower and involves the production, release, and movement of chemical messages • specialized nerve cells found within the endocrine system are called neurosecretory cells • some chemicals fu ...
... Introduction to Regulatory Systems • Nervous system involved with high speed responses • Endocrine system is slower and involves the production, release, and movement of chemical messages • specialized nerve cells found within the endocrine system are called neurosecretory cells • some chemicals fu ...
Studyguide 2 of the Digestive System
... 13. The Paneth cell is within an intestinal crypt. What does an intestinal crypt do? ...
... 13. The Paneth cell is within an intestinal crypt. What does an intestinal crypt do? ...
RER
... Finds out all his excrement has been thrown out in a lab clean-up. PhD student says his career and life are ruined. Let this tragedy be a warning to us all. ...
... Finds out all his excrement has been thrown out in a lab clean-up. PhD student says his career and life are ruined. Let this tragedy be a warning to us all. ...
Endocrine system
... - located at the base of the brain, below the hypothalamus -the hypothalamus secretes releasing/inhibiting factors that affect the release of substances from the pituitary gland 2 glands: 1) anterior pituitary gland or adenohypohysis which is a separate gland 2) posterior pituatry gland or neurohypo ...
... - located at the base of the brain, below the hypothalamus -the hypothalamus secretes releasing/inhibiting factors that affect the release of substances from the pituitary gland 2 glands: 1) anterior pituitary gland or adenohypohysis which is a separate gland 2) posterior pituatry gland or neurohypo ...
Liver Microscopic Anatomy
... are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
... are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
Digestive Part C
... Lies deep to the greater curvature of the stomach The head is encircled by the duodenum and the tail abuts the spleen ...
... Lies deep to the greater curvature of the stomach The head is encircled by the duodenum and the tail abuts the spleen ...
Digestive System
... explain their function. • To understand the necessity of salivary glands and name each type. ...
... explain their function. • To understand the necessity of salivary glands and name each type. ...
Digestive System—This system consists of several organs that work
... pounds in the adult human. It consists of five lobes in the cat but only four in the human. Identify the right and left medial lobes, right and left lateral lobes, and the single caudal lobe. The liver lobules filter a tremendous blood volume from the hepatic portal system, removing some substances ...
... pounds in the adult human. It consists of five lobes in the cat but only four in the human. Identify the right and left medial lobes, right and left lateral lobes, and the single caudal lobe. The liver lobules filter a tremendous blood volume from the hepatic portal system, removing some substances ...
Anatomy and Physiology II – Spring 2015 Test 3 1. What is the
... Describe briefly THREE ways in which the endocrine and exocrine functions of the pancreas differ. (3 pts) Endocrine – ductless glands; release insulin and other hormones that travel great distance through blood Exocrine – several secretions (including trypsin and chymotrypsin) are released via ducts ...
... Describe briefly THREE ways in which the endocrine and exocrine functions of the pancreas differ. (3 pts) Endocrine – ductless glands; release insulin and other hormones that travel great distance through blood Exocrine – several secretions (including trypsin and chymotrypsin) are released via ducts ...
Endocrine System
... • Glucagon is a polypeptide made of 29 amino acids. It has the opposite effect of insulin: It raises the blood glucose levels. • Glucagon stimulates breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver. When blood glucose levels are high, large amounts of glucose are taken up by the liver and stored in form of ...
... • Glucagon is a polypeptide made of 29 amino acids. It has the opposite effect of insulin: It raises the blood glucose levels. • Glucagon stimulates breakdown of glycogen stored in the liver. When blood glucose levels are high, large amounts of glucose are taken up by the liver and stored in form of ...
B. Human digestion
... b) Incomplete digestive tract (1) A single opening serves both as a mouth and anus (2) The digestive system is called a gastrovascular cavity (3) Found in radiates, turbellarians and trematodes 2. Intracellular / extracellular digestion a) Intracellular digestion (1) Digestion occurs within a cell ( ...
... b) Incomplete digestive tract (1) A single opening serves both as a mouth and anus (2) The digestive system is called a gastrovascular cavity (3) Found in radiates, turbellarians and trematodes 2. Intracellular / extracellular digestion a) Intracellular digestion (1) Digestion occurs within a cell ( ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.























