Endocrine System Study Guide Anatomy
... Released hormones provide for immediate body response Thyroid Hormones – function is to stimulate cellular metabolism ...
... Released hormones provide for immediate body response Thyroid Hormones – function is to stimulate cellular metabolism ...
Anatomy: Small intestine
... 1. Pyloric sphincter controls amount of food entering from stomach 2. Pancreas produces enzymes that are secreted to small intestines through pancreatic duct 3. Bile formed in liver is secreted through bile duct 4. Pancreatic & bile ducts join to form hepatopancreatic ampulla 5. Together enzymes, bi ...
... 1. Pyloric sphincter controls amount of food entering from stomach 2. Pancreas produces enzymes that are secreted to small intestines through pancreatic duct 3. Bile formed in liver is secreted through bile duct 4. Pancreatic & bile ducts join to form hepatopancreatic ampulla 5. Together enzymes, bi ...
products
... (d) Parietal cells that produce HCL which kills microorganism that enter the digestive system. This also converts inactive pepsinogen to active pepsin (e) Chief cells: produces pepsinogen a protease enzyme ...
... (d) Parietal cells that produce HCL which kills microorganism that enter the digestive system. This also converts inactive pepsinogen to active pepsin (e) Chief cells: produces pepsinogen a protease enzyme ...
Gastric secretions
... Normal hard, dark Soft, pale (over 50% bacteria, reingested) Further fermentation produces lactate ...
... Normal hard, dark Soft, pale (over 50% bacteria, reingested) Further fermentation produces lactate ...
Human Digestion
... • Food never actually enters body tissues until it is broken down • The food has to be small enough to diffuse through the cell membrane • Remember the State Diffusion lab? ...
... • Food never actually enters body tissues until it is broken down • The food has to be small enough to diffuse through the cell membrane • Remember the State Diffusion lab? ...
Chapter 12 - Biology12-Lum
... – Descending colon – part of colon that goes down – Cecum – attached to ascending colon. Goes nowhere – Appendix – attached to cecum. Can get infected. – Rectum – where all the feces is stored. End of colon. – Anus – the muscular opening to expel feces. ...
... – Descending colon – part of colon that goes down – Cecum – attached to ascending colon. Goes nowhere – Appendix – attached to cecum. Can get infected. – Rectum – where all the feces is stored. End of colon. – Anus – the muscular opening to expel feces. ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy
... and causes the mammary glands to eject milk. Its production is an example of positive feedback. What is oxytocin? ...
... and causes the mammary glands to eject milk. Its production is an example of positive feedback. What is oxytocin? ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... and causes the mammary glands to eject milk. Its production is an example of positive feedback. What is oxytocin? ...
... and causes the mammary glands to eject milk. Its production is an example of positive feedback. What is oxytocin? ...
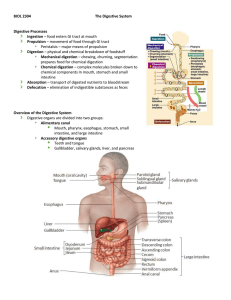
Digestive System
... 8. What substance in the mouth contains enzymes that begin chemical digestion? saliva 9. What is digestion? process in which your body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules 10. What organ produces bile? liver 11. What organ stores bile? gallbladder ...
... 8. What substance in the mouth contains enzymes that begin chemical digestion? saliva 9. What is digestion? process in which your body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules 10. What organ produces bile? liver 11. What organ stores bile? gallbladder ...
Digestion and Excretory Test-2012-anskey
... 15. Explain how food can be passed through your esophagus even if you are standing on your head. Peristalsis-wavelike contracts force food down ...
... 15. Explain how food can be passed through your esophagus even if you are standing on your head. Peristalsis-wavelike contracts force food down ...
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Unit
... • Gallbladder is a saclike organ that lies on inferior surface of the liver • Function of gallbladder is to store & concentrate bile between meals • Gallbladder holds about 90 mL of bile ...
... • Gallbladder is a saclike organ that lies on inferior surface of the liver • Function of gallbladder is to store & concentrate bile between meals • Gallbladder holds about 90 mL of bile ...
Digestive System
... • Liver grows rapidly & fills most of abdominal cavity – Initially right & left lobe are = size • Right lobe becomes larger & subdivides into caudate & quadrant lobes – At 9th week 10% of fetal body weight – At full term 5% of fetal body weight ...
... • Liver grows rapidly & fills most of abdominal cavity – Initially right & left lobe are = size • Right lobe becomes larger & subdivides into caudate & quadrant lobes – At 9th week 10% of fetal body weight – At full term 5% of fetal body weight ...
Digestive System Notes Mouth / Oral Cavity: Pharynx: Epiglottis
... 5. Produces bile (stored in gall bladder) that emulsifies fats by breaking fats into smaller pieces which increases the surface area of fats for digestion by lipase. 6. Produces blood plasma proteins. For example, blood clotting proteins (fibrinogen and prothrombin) and another protein called albumi ...
... 5. Produces bile (stored in gall bladder) that emulsifies fats by breaking fats into smaller pieces which increases the surface area of fats for digestion by lipase. 6. Produces blood plasma proteins. For example, blood clotting proteins (fibrinogen and prothrombin) and another protein called albumi ...
LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTER 25
... d. blood supply from both hepatic portal and hepatic artery 5. bile produced and flows into canaliculi 5. bile flow a. bile canaliculi into b. right & left hepatic ducts c. common hepatic duct d. joins with cystic duct from gall bladder e. to become the common bile duct f. empties into duodenum at p ...
... d. blood supply from both hepatic portal and hepatic artery 5. bile produced and flows into canaliculi 5. bile flow a. bile canaliculi into b. right & left hepatic ducts c. common hepatic duct d. joins with cystic duct from gall bladder e. to become the common bile duct f. empties into duodenum at p ...
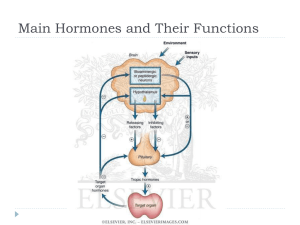
Main Hormones and Their functions
... stimulates liver to secrete growth factors protein synthesis, cell division/growth, breakdown fats ...
... stimulates liver to secrete growth factors protein synthesis, cell division/growth, breakdown fats ...
Name Anatomy 3 Review OLLCHS
... effects of insulin and glucagon on the amount of (A) fats digested into glycerol (B) amino acids absorbed by villi (C) oxygen transported to the lungs (D) glucose in the blood ____23. The secretion of chemicals that stimulate responses in specific body tissues is a function of (A) the nervous system ...
... effects of insulin and glucagon on the amount of (A) fats digested into glycerol (B) amino acids absorbed by villi (C) oxygen transported to the lungs (D) glucose in the blood ____23. The secretion of chemicals that stimulate responses in specific body tissues is a function of (A) the nervous system ...
right & left hepatic ducts - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... – receives stomach contents, pancreatic juice & bile – neutralizes stomach acids, emulsifies fats, pepsin inactivated by pH increase, pancreatic enzymes ...
... – receives stomach contents, pancreatic juice & bile – neutralizes stomach acids, emulsifies fats, pepsin inactivated by pH increase, pancreatic enzymes ...
Normal Anatomy and Imaging Stations
... Pancreas - ventral anlage The ventral portion of the pancreas (V) contains relatively less fat than the larger dorsal portion (D) and therefore appears darker on EUS. This appearance is seen in up to 75% of normal people and should not be mistaken for a mass. It is seen upon withdrawing the probe ...
... Pancreas - ventral anlage The ventral portion of the pancreas (V) contains relatively less fat than the larger dorsal portion (D) and therefore appears darker on EUS. This appearance is seen in up to 75% of normal people and should not be mistaken for a mass. It is seen upon withdrawing the probe ...
Human Physiology
... Composition and Function of Gastric Juice Each day stomach secreted about 2 liters gastric juice. The pH is about 2.0 and specific gravity is Parietal cell secretes HCl that partially denatures the protein. Chief cells secreted • Protein digestive enzyme: Pepsinogen (inactive form) Pepsin (active f ...
... Composition and Function of Gastric Juice Each day stomach secreted about 2 liters gastric juice. The pH is about 2.0 and specific gravity is Parietal cell secretes HCl that partially denatures the protein. Chief cells secreted • Protein digestive enzyme: Pepsinogen (inactive form) Pepsin (active f ...
Ch 29 Digestive System
... optimum pH is 2 and temperature 37ºC. Salivary amylase activity stops when it is denatured by hydrochloric acid. Mucus lines the inner surface of the stomach protecting it from its acid and digestive enzymes. Mucus is secreted by goblet cells. Small Intestine – duodenum and ileum Bile passes to the ...
... optimum pH is 2 and temperature 37ºC. Salivary amylase activity stops when it is denatured by hydrochloric acid. Mucus lines the inner surface of the stomach protecting it from its acid and digestive enzymes. Mucus is secreted by goblet cells. Small Intestine – duodenum and ileum Bile passes to the ...
Digestive
... Contains numerous mucus-secreting goblet cells Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue Epithelium changes at anal canal, becomes stratified squamous epithelium ...
... Contains numerous mucus-secreting goblet cells Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue Epithelium changes at anal canal, becomes stratified squamous epithelium ...
File
... glycogen to glucose, blood flow to strategic organs, breathing rate and cellular respiration rate. It also allows for dilation of pupils, decrease in blood flow to intestines and skin (same as sympathetic ...
... glycogen to glucose, blood flow to strategic organs, breathing rate and cellular respiration rate. It also allows for dilation of pupils, decrease in blood flow to intestines and skin (same as sympathetic ...
GI-Pt2Yola
... • Elongated gland located near the first part of the duodenum. • Exocrine and endocrine gland. – Exocrine cells secrete pancreatic enzymes needed for digestion and transfer them through a duct into the small intestine. – Endocrine cells produce and secrete insulin and glucagon directly into the bloo ...
... • Elongated gland located near the first part of the duodenum. • Exocrine and endocrine gland. – Exocrine cells secrete pancreatic enzymes needed for digestion and transfer them through a duct into the small intestine. – Endocrine cells produce and secrete insulin and glucagon directly into the bloo ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.