AMA 176 powerpoint
... tubes, release glucose and glycogen for more energy – “flight or fight” Norepinephrine constricts blood vessels to raise BP) ...
... tubes, release glucose and glycogen for more energy – “flight or fight” Norepinephrine constricts blood vessels to raise BP) ...
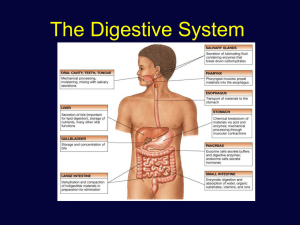
Chapter 24: The Digestive System
... 4. Describe the composition and functions of saliva, and explain how salivation is regulated. 5. Describe the mechanisms of chewing and swallowing. 6. Identify structural modifications of the wall of the stomach and small intestine that enhance the digestive process in these regions. 7. Describe the ...
... 4. Describe the composition and functions of saliva, and explain how salivation is regulated. 5. Describe the mechanisms of chewing and swallowing. 6. Identify structural modifications of the wall of the stomach and small intestine that enhance the digestive process in these regions. 7. Describe the ...
Endocrine System - University of Washington
... Located along the midline of the neck Secretes two nonsteroid hormones Triiodothyronine (T3) Thyroxine (T4) Calcitonin: calcium metabolism (osteoblast) Regulates metabolism increases protein synthesis promotes glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glucose uptake ...
... Located along the midline of the neck Secretes two nonsteroid hormones Triiodothyronine (T3) Thyroxine (T4) Calcitonin: calcium metabolism (osteoblast) Regulates metabolism increases protein synthesis promotes glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glucose uptake ...
File
... 1. atrophy = decrease size of tissue or cells 2. dystrophy = defective growth in tissue or cells 3. hypertrophy = increase greatly the size of tissue or cells H. gland = group of specialized cells that secrete material used elsewhere in the body 1. exocrine glands = secretion enters ducts that go to ...
... 1. atrophy = decrease size of tissue or cells 2. dystrophy = defective growth in tissue or cells 3. hypertrophy = increase greatly the size of tissue or cells H. gland = group of specialized cells that secrete material used elsewhere in the body 1. exocrine glands = secretion enters ducts that go to ...
Endocrine System - Westhampton Beach Elementary School
... • a hormone is a chemical produced by a gland that affects the activities of other organs or tissues ...
... • a hormone is a chemical produced by a gland that affects the activities of other organs or tissues ...
The Digestive System
... • Forces feces into rectum • Reflex involves relaxation of the internal anal sphincter and peristaltic waves through the descending colon • Can be prevented by contraction of the external anal sphincter ...
... • Forces feces into rectum • Reflex involves relaxation of the internal anal sphincter and peristaltic waves through the descending colon • Can be prevented by contraction of the external anal sphincter ...
Digestion Summary Mouth Mechanical Digestion Teeth grind, mash
... Bolus- a moist ball of partially digested food ...
... Bolus- a moist ball of partially digested food ...
Lecture 7 Animal Energy Acquisition II: Food acquisition and
... Gallbladder: stores bile. Pancreas: Important roles as both an endocrine and exocrine organ - provides a potent mixture of digestive enzymes to the small intestine which are critical for digestion of fats, carbohydrates and protein. Small Intestine: The most exciting place to be in the entire digest ...
... Gallbladder: stores bile. Pancreas: Important roles as both an endocrine and exocrine organ - provides a potent mixture of digestive enzymes to the small intestine which are critical for digestion of fats, carbohydrates and protein. Small Intestine: The most exciting place to be in the entire digest ...
human anatomy - WordPress.com
... • Sac lined with mucosa folded into rugae, inner muscularis, outer serosa • Bile arrives constantly from liver is stored and concentrated • Bile exits through cystic duct then into common bile duct emptying into duodenal ampulla (pouch) and then into duodenum through duodenal papilla ...
... • Sac lined with mucosa folded into rugae, inner muscularis, outer serosa • Bile arrives constantly from liver is stored and concentrated • Bile exits through cystic duct then into common bile duct emptying into duodenal ampulla (pouch) and then into duodenum through duodenal papilla ...
endocrinesystemshort
... The chemical product of an endocrine glands is called a hormone. Endocrine glands produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
... The chemical product of an endocrine glands is called a hormone. Endocrine glands produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
Digestive System
... VIP Intestinal Pits located above intestinal glands that are called Crypts of Leiberkuhn- secrete intestinal juice, lysozyme Brunner’s Glands- duodenum only; alkaline mucous ...
... VIP Intestinal Pits located above intestinal glands that are called Crypts of Leiberkuhn- secrete intestinal juice, lysozyme Brunner’s Glands- duodenum only; alkaline mucous ...
Document
... – Amino acids to energy producing compounds – Hydroxylation of vitamin D. Vitamin D then travels to kidney where it is hydroxylated again into its active form • Detoxification – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea • Phagocytosis – Kupffer cells phagocytize worn-out and dying red and white ...
... – Amino acids to energy producing compounds – Hydroxylation of vitamin D. Vitamin D then travels to kidney where it is hydroxylated again into its active form • Detoxification – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea • Phagocytosis – Kupffer cells phagocytize worn-out and dying red and white ...
Digestive System
... gallbladder has a duct leading to small intestine (bile duct) bile acts as an emulsifying agent, breaking large globs of fat into microscopic particles this increases the surface area available for lipases (enzymes) to act on fats ...
... gallbladder has a duct leading to small intestine (bile duct) bile acts as an emulsifying agent, breaking large globs of fat into microscopic particles this increases the surface area available for lipases (enzymes) to act on fats ...
session 42 File - E-Learning/An
... Pancreatic enzymes play the major digestive function (continued): Responsible for fat digestion (lipase) Digest nucleic acids (nucleases) Alkaline content neutralizes acidic chyme ...
... Pancreatic enzymes play the major digestive function (continued): Responsible for fat digestion (lipase) Digest nucleic acids (nucleases) Alkaline content neutralizes acidic chyme ...
Org/Dev of Living Organisms: SC.5.L.14.1
... Kidneys store unwanted fluids until they can be removed. Kidneys help to clean the oxygen that comes from the lungs. Kidneys help balance the salts and acids in the body by filtering blood. ...
... Kidneys store unwanted fluids until they can be removed. Kidneys help to clean the oxygen that comes from the lungs. Kidneys help balance the salts and acids in the body by filtering blood. ...
the endocrine system
... Think of this process like a thermostat. It is set to maintain a balance in temperature. When it goes over or under the set temperature, it cuts in or out to get the temperature back to the correct setting. This is what the Endocrine system does. An example in the body would be after eating a meal h ...
... Think of this process like a thermostat. It is set to maintain a balance in temperature. When it goes over or under the set temperature, it cuts in or out to get the temperature back to the correct setting. This is what the Endocrine system does. An example in the body would be after eating a meal h ...
Respiratory system
... Mixing food with saliva – ptyalin (amylase) Initiation of swallowing by the tongue Allowing for the sense of taste ...
... Mixing food with saliva – ptyalin (amylase) Initiation of swallowing by the tongue Allowing for the sense of taste ...
Digestion and Enzymes L4
... • Chemical digestion • Breaking down food into molecules small enough to be absorbed into cells • Enzymes are proteins that help to speed up the breaking down process ...
... • Chemical digestion • Breaking down food into molecules small enough to be absorbed into cells • Enzymes are proteins that help to speed up the breaking down process ...
The Digestive System
... • Contains numerous goblet cells • Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands • Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue – Epithelium changes at anal canal, becomes stratified squamous epithelium ...
... • Contains numerous goblet cells • Intestinal crypts – simple tubular glands • Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue – Epithelium changes at anal canal, becomes stratified squamous epithelium ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.