WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... It flows to the lungs by way of the pulmonary artery and in the lungs CO2 leaves the blood and O2 enters – The blood returns via the pulmonary vein and enters the left atrium and passes through the bicuspid valve and enters the left ventricle It is then pumped out through the Aorta, which is th ...
... It flows to the lungs by way of the pulmonary artery and in the lungs CO2 leaves the blood and O2 enters – The blood returns via the pulmonary vein and enters the left atrium and passes through the bicuspid valve and enters the left ventricle It is then pumped out through the Aorta, which is th ...
Name
... level of calcium under tight control because calcium is needed inside just about every cell in the body in order to keep that cell functioning properly. Another example is the pancreas, located in the digestive system, below the stomach. The pancreas controls the level of glucose in the blood. It re ...
... level of calcium under tight control because calcium is needed inside just about every cell in the body in order to keep that cell functioning properly. Another example is the pancreas, located in the digestive system, below the stomach. The pancreas controls the level of glucose in the blood. It re ...
2 division Digestive system parts –GI
... 3 Main funct. of digestive system Digestion : mechanical & chemical Absorption: mostly SM intestine Elimination ...
... 3 Main funct. of digestive system Digestion : mechanical & chemical Absorption: mostly SM intestine Elimination ...
topic 6.1 digestion notes
... large intestine: the main function is to re-absorb water that has been used as a lubricant and solvent in the processing of the food. Waste becomes more solid as water is removed. Excess salts can be excreted into the large intestine. Symbiotic Bacteria Escherichia Coli ( E. Coli) help produce some ...
... large intestine: the main function is to re-absorb water that has been used as a lubricant and solvent in the processing of the food. Waste becomes more solid as water is removed. Excess salts can be excreted into the large intestine. Symbiotic Bacteria Escherichia Coli ( E. Coli) help produce some ...
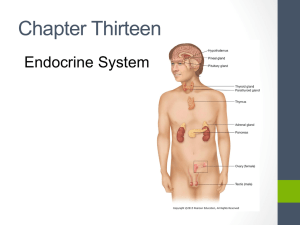
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... In both sexes, LH stimulates secretion of sex steroids from the gonads. In the testes, LH binds to cells, stimulating synthesis and secretion of testosterone. Cells in the ovary respond to LH stimulation by secretion of testosterone, which is converted into estrogen by adjacent cells. ...
... In both sexes, LH stimulates secretion of sex steroids from the gonads. In the testes, LH binds to cells, stimulating synthesis and secretion of testosterone. Cells in the ovary respond to LH stimulation by secretion of testosterone, which is converted into estrogen by adjacent cells. ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... >>> Ductless – or tubeless – organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
... >>> Ductless – or tubeless – organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
Small Intestine - Human Digestive System
... Enzymes • However, they are not fully broken down yet which causes the enzymes of the small intestine to act upon them • Enzymes include peptidase, which breaks down peptides into amino acids and the enzyme maltase acts upon maltose which produces glucose ...
... Enzymes • However, they are not fully broken down yet which causes the enzymes of the small intestine to act upon them • Enzymes include peptidase, which breaks down peptides into amino acids and the enzyme maltase acts upon maltose which produces glucose ...
The Digestive System
... the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde-----more of this enzyme found in males than females • Females have less total body fluid than same size male so end up with higher blood alcohol levels with s ...
... the intestine where absorption is more rapid • Gastric mucosal cells contain alcohol dehydrogenase that converts some alcohol to acetaldehyde-----more of this enzyme found in males than females • Females have less total body fluid than same size male so end up with higher blood alcohol levels with s ...
File
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... Chapter 18 – Study Guide ___________________________________________________________________________________ in general you should know: appearance of each gland & where in the body it is found (that includes being able to identify in a picture those structures listed as bold, italicized and underli ...
... Chapter 18 – Study Guide ___________________________________________________________________________________ in general you should know: appearance of each gland & where in the body it is found (that includes being able to identify in a picture those structures listed as bold, italicized and underli ...
chapter 18 study guide
... Chapter 18 – Study Guide ___________________________________________________________________________________ in general you should know: appearance of each gland & where in the body it is found (that includes being able to identify in a picture those structures listed as bold, italicized and underli ...
... Chapter 18 – Study Guide ___________________________________________________________________________________ in general you should know: appearance of each gland & where in the body it is found (that includes being able to identify in a picture those structures listed as bold, italicized and underli ...
Steps in Digestion
... muscles contract to move Food food along. particles 2. Digestion: 2. Digestion - Physical digestion (chemical increases surface area of breakdown) food. Nutrient - Chemical digestion uses molecules enzymes to break down complex macromolecules 3. Absorption 3. Absorption Enters - Nutrients (sugar, am ...
... muscles contract to move Food food along. particles 2. Digestion: 2. Digestion - Physical digestion (chemical increases surface area of breakdown) food. Nutrient - Chemical digestion uses molecules enzymes to break down complex macromolecules 3. Absorption 3. Absorption Enters - Nutrients (sugar, am ...
Digestive System
... • Chewing creates smaller pieces of food that are wet and easier to swallow. • Teeth perform mechanical digestion. Covered in enamel, the hardest material in the body which protects the interior of teeth. • Saliva that is made in the salivary glands contains enzymes that begin chemical digestion of ...
... • Chewing creates smaller pieces of food that are wet and easier to swallow. • Teeth perform mechanical digestion. Covered in enamel, the hardest material in the body which protects the interior of teeth. • Saliva that is made in the salivary glands contains enzymes that begin chemical digestion of ...
Chapter 39 - Industrial ISD
... • Jaundice is a condition in which the eyes, skin and urine become abnormally yellow as a result of increased bile pigments in the blood. • Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in ...
... • Jaundice is a condition in which the eyes, skin and urine become abnormally yellow as a result of increased bile pigments in the blood. • Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in ...
The Digestive System
... into the body ( ingested ) and broken down into minute particles which are capable of passing through the cell membrane to be used by the cell in fulfilling its function Peristalsis – the wave like movement caused by the continual contraction and relaxation of the muscular fibres in the walls of the ...
... into the body ( ingested ) and broken down into minute particles which are capable of passing through the cell membrane to be used by the cell in fulfilling its function Peristalsis – the wave like movement caused by the continual contraction and relaxation of the muscular fibres in the walls of the ...
D.2 Digestion
... mechanisms. ■ Both nerves and hormones are involved in controlling the secretions of digestive juices. ■ The sight or smell of food causes the brain to send nerve impulses via the vagus nerve from the medulla. ■ Gland cells in the stomach walls are stimulated to secrete components of gastric juices. ...
... mechanisms. ■ Both nerves and hormones are involved in controlling the secretions of digestive juices. ■ The sight or smell of food causes the brain to send nerve impulses via the vagus nerve from the medulla. ■ Gland cells in the stomach walls are stimulated to secrete components of gastric juices. ...
The Endocrine System
... question below and share your answer with me on google drive. [email protected] ...
... question below and share your answer with me on google drive. [email protected] ...
• Two hormones are produced: (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland The
... Numerous hormones are secreted by the adrenal glands o Adrenal Medulla secrete and o Adrenal Cortex secrete Pancreas The pancreas has two major types of secretory tissue This is why it is a dual functioning organ as both an gland and gland Three hormones are secreted from the islet cells (Islets of ...
... Numerous hormones are secreted by the adrenal glands o Adrenal Medulla secrete and o Adrenal Cortex secrete Pancreas The pancreas has two major types of secretory tissue This is why it is a dual functioning organ as both an gland and gland Three hormones are secreted from the islet cells (Islets of ...
Digestive System
... Esophagus: Tube made of smooth muscle that moves food from mouth to stomach. The wave-like movement of the esophagus is called peristalsis. Stomach: Organ made of smooth muscle that churns food (mechanical digestion) and secretes enzymes and acids for food digestion Liver: Organ that produces bile ( ...
... Esophagus: Tube made of smooth muscle that moves food from mouth to stomach. The wave-like movement of the esophagus is called peristalsis. Stomach: Organ made of smooth muscle that churns food (mechanical digestion) and secretes enzymes and acids for food digestion Liver: Organ that produces bile ( ...
Vocabulary
... Middle portion of the small intestine Delmar's Washing Comprehensive Medical Enzyme that aids in the digestion of fat Terminology Produces bile & enzymes to metabolize carbohydrates, fat, & protein Small and large intestine Chewing, tearing, or grinding food with teeth while mixing with saliva Back ...
... Middle portion of the small intestine Delmar's Washing Comprehensive Medical Enzyme that aids in the digestion of fat Terminology Produces bile & enzymes to metabolize carbohydrates, fat, & protein Small and large intestine Chewing, tearing, or grinding food with teeth while mixing with saliva Back ...
Digestive System Digestive Processes
... voluntary contraction of diaphragm and abdominal muscles, together with voluntary relaxation of anal sphincter, allow defecation in the absence of the voluntary actions, defecation in delayed ...
... voluntary contraction of diaphragm and abdominal muscles, together with voluntary relaxation of anal sphincter, allow defecation in the absence of the voluntary actions, defecation in delayed ...
General principles of gastrointestinal system function
... ( continues tube that extends from the mouth to the anus) Accessory digestive organs ( teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas) ...
... ( continues tube that extends from the mouth to the anus) Accessory digestive organs ( teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas) ...
File digestive system, ppt
... bilirubin, cholesterol, and other substances. It is made in the liver but is stored in the gall bladder. It does not contain enzymes but the bile salts help to emulsify fat, breaking it down from large fat globules into smaller fat droplets which help with fat digestion in small intestine. ...
... bilirubin, cholesterol, and other substances. It is made in the liver but is stored in the gall bladder. It does not contain enzymes but the bile salts help to emulsify fat, breaking it down from large fat globules into smaller fat droplets which help with fat digestion in small intestine. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.