Digestion
... The cookie will then exit the system and will not even have any resemblance to that cookie. Here is where the tube ends. Ulcerative Colitis - recurring ulcers and inflammation of the large intestine, Stress Appendicitis - Inflammation of the appendix ...
... The cookie will then exit the system and will not even have any resemblance to that cookie. Here is where the tube ends. Ulcerative Colitis - recurring ulcers and inflammation of the large intestine, Stress Appendicitis - Inflammation of the appendix ...
Endocrine System
... Types of Glands • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells ot ...
... Types of Glands • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells ot ...
File - Wk 1-2
... The liver is made up of hepatocytes, which are arranged in cords forming lobules around a central vein There are radiating cords of hepatocytes and peripheral portal tracts composed of a vein, artery and one or more bile ducts The sinusoids percolate blood between cords of hepatocytes. These are sup ...
... The liver is made up of hepatocytes, which are arranged in cords forming lobules around a central vein There are radiating cords of hepatocytes and peripheral portal tracts composed of a vein, artery and one or more bile ducts The sinusoids percolate blood between cords of hepatocytes. These are sup ...
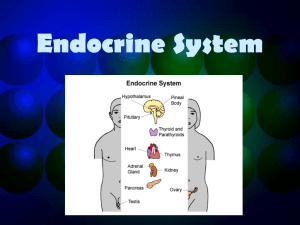
Endocrine System
... The thyroid glands and parathyroid gland are located together in the neck. The thyroid glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and calcium levels. The parathyroid gland also secretes hormones that regulate calcium levels. The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that ...
... The thyroid glands and parathyroid gland are located together in the neck. The thyroid glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and calcium levels. The parathyroid gland also secretes hormones that regulate calcium levels. The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that ...
Chapter 24
... cells that extend into lamina propria forming columns of ____________ secretory cells – gastric glands which line gastric pits Mucous neck cells- secrete mucus Parietal cells- secrete intrinsic factor & HCl Chief cells- secrete pepsinogen & gastric lipase ...
... cells that extend into lamina propria forming columns of ____________ secretory cells – gastric glands which line gastric pits Mucous neck cells- secrete mucus Parietal cells- secrete intrinsic factor & HCl Chief cells- secrete pepsinogen & gastric lipase ...
Slide 1
... the pancreatic juice and also in gastric juice which is found in the stomach. This enzyme breaks protein molecules into amino acid molecules. ...
... the pancreatic juice and also in gastric juice which is found in the stomach. This enzyme breaks protein molecules into amino acid molecules. ...
Enzymes - SchoolRack
... the pancreatic juice and also in gastric juice which is found in the stomach. This enzyme breaks protein molecules into amino acid molecules. ...
... the pancreatic juice and also in gastric juice which is found in the stomach. This enzyme breaks protein molecules into amino acid molecules. ...
H_-_Nutrition
... It has a folded inner surface to increase its surface area for absorption. It has its surface developed into millions of small finger-shaped projections called villi. It has many blood capillaries to absorb food into. The absorbed food is then carried in the blood directly to the liver. fat droplets ...
... It has a folded inner surface to increase its surface area for absorption. It has its surface developed into millions of small finger-shaped projections called villi. It has many blood capillaries to absorb food into. The absorbed food is then carried in the blood directly to the liver. fat droplets ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... hormone from the islet cells and injected it into the dogs The dogs recovered, indicating that this hormone was responsible for controlling blood sugar levels Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1923, but Best was not included ...
... hormone from the islet cells and injected it into the dogs The dogs recovered, indicating that this hormone was responsible for controlling blood sugar levels Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1923, but Best was not included ...
Digestive System Worksheet Name
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
Digestive System Notes - Full Version
... 1. Acini (acinar cells) – cluster of secretory cells around a duct that carries enzymes to small intestine; produce bicarbonate NaHCO3 (to neutralize HCL of stomach) and mucus; full of rough ER (EXOCRINE) 2. Islets of Langerhans – area of the pancreas that contains cells that secrete insulin & gluca ...
... 1. Acini (acinar cells) – cluster of secretory cells around a duct that carries enzymes to small intestine; produce bicarbonate NaHCO3 (to neutralize HCL of stomach) and mucus; full of rough ER (EXOCRINE) 2. Islets of Langerhans – area of the pancreas that contains cells that secrete insulin & gluca ...
Fill in the blank sheet
... a. _____________: no nutritional value but needed for bodily functions b. _______________: building blocks, used for cell growth and repair (muscles, bones, skins) c. __________________: provide cells with energy (this is the glucose we use in respiration) d. _________: stores energy 3. The digestiv ...
... a. _____________: no nutritional value but needed for bodily functions b. _______________: building blocks, used for cell growth and repair (muscles, bones, skins) c. __________________: provide cells with energy (this is the glucose we use in respiration) d. _________: stores energy 3. The digestiv ...
lecture 5 git secretions gastric
... pancreatic ductules and ducts are: 1. Carbon dioxide diffuses to the interior of the cell from the blood and, under the influence of carbonic anhydrase, combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). The carbonic acid in turn dissociates into bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions. Then the bicarbon ...
... pancreatic ductules and ducts are: 1. Carbon dioxide diffuses to the interior of the cell from the blood and, under the influence of carbonic anhydrase, combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). The carbonic acid in turn dissociates into bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions. Then the bicarbon ...
File
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
Digestive_System_organs
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
... ______ 6. Literally a food chute; it has no digestive or absorptive role. ______ 7. Projections of the plasma membrane of a cell that increase the cell’s surface area. ______ 8.Produces a juice that neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes. ______ 9. Organ responsible for absorption o ...
Chapter 38: Digestive System
... B. Chemical Phase: carried out by hydrolases- enzymes which bring about hydrolysis 1. Protein + H2O ------------------------ Amino acids (soluble- can be absorbed into ...
... B. Chemical Phase: carried out by hydrolases- enzymes which bring about hydrolysis 1. Protein + H2O ------------------------ Amino acids (soluble- can be absorbed into ...
Anatomy introduction11
... • 4. Simple cuboidal—one layer of cube-shaped cells. Sites: thyroid gland (to secrete thyroid hormones); salivary glands (to secrete saliva); kidney tubules (to reabsorb useful materials back to the blood). • 5. Simple columnar—one layer of column-shaped cells. Sites: stomach lining (to secrete gast ...
... • 4. Simple cuboidal—one layer of cube-shaped cells. Sites: thyroid gland (to secrete thyroid hormones); salivary glands (to secrete saliva); kidney tubules (to reabsorb useful materials back to the blood). • 5. Simple columnar—one layer of column-shaped cells. Sites: stomach lining (to secrete gast ...
Digestive System
... Stomach: bolus of food gets churned in gastric juices, forms acid chyme, a mix of juice and food Pepsinogen: inactive form of pepsin that is first secreted, then activated by acid (HCl) Pepsin: hydrolysis of proteins into smaller polypeptides Small Intestine: 6 meters long, enzymatic digestion, most ...
... Stomach: bolus of food gets churned in gastric juices, forms acid chyme, a mix of juice and food Pepsinogen: inactive form of pepsin that is first secreted, then activated by acid (HCl) Pepsin: hydrolysis of proteins into smaller polypeptides Small Intestine: 6 meters long, enzymatic digestion, most ...
The Digestion Process
... • Digestion is the process that changes food into simpler forms that the body can absorb. • It is carried out by the Digestion System. ...
... • Digestion is the process that changes food into simpler forms that the body can absorb. • It is carried out by the Digestion System. ...
Abdominal Assessment
... Functions of The Organs Esophagus Carries liquids and saliva to the stomach ...
... Functions of The Organs Esophagus Carries liquids and saliva to the stomach ...
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM C15L2
... Although the stomach lining does not absorb many food molecules, it does absorb alcohol, water, and certain drugs. ...
... Although the stomach lining does not absorb many food molecules, it does absorb alcohol, water, and certain drugs. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.