Test - Scioly.org
... Most of the absorption in the digestive system takes place in the stomach. False, most absorption takes place in the large intestine ...
... Most of the absorption in the digestive system takes place in the stomach. False, most absorption takes place in the large intestine ...
Methodological Instruction to Practical Lesson № 13
... 13. The chief role played by the pancreas in digestion is to: A. Secrete insulin and glucagons B. Churn the food and bring it into contact with the digestive enzymes C. Secrete enzymes that digest food in the small intestine D. Assist in the absorbtion of digested food 14. Among the structural featu ...
... 13. The chief role played by the pancreas in digestion is to: A. Secrete insulin and glucagons B. Churn the food and bring it into contact with the digestive enzymes C. Secrete enzymes that digest food in the small intestine D. Assist in the absorbtion of digested food 14. Among the structural featu ...
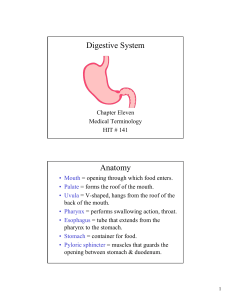
Digestive System Anatomy
... • Large intestine = 5 feet from ileum to anus. • Cecum = first part of large intestine. • Colon = second part of large intestine. • Rectum = third part of large intestine. • Anus = sphincter muscle, end of digestive tract. ...
... • Large intestine = 5 feet from ileum to anus. • Cecum = first part of large intestine. • Colon = second part of large intestine. • Rectum = third part of large intestine. • Anus = sphincter muscle, end of digestive tract. ...
Function Nervous System Endocrine System
... person without diabetes is usually about 60-110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). This is the proper level needed for normal body function. When the blood sugar level drops too low (hypoglycemia), a person's ability to reason is impaired; in extreme cases, coma may result. When the blood sugar is co ...
... person without diabetes is usually about 60-110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). This is the proper level needed for normal body function. When the blood sugar level drops too low (hypoglycemia), a person's ability to reason is impaired; in extreme cases, coma may result. When the blood sugar is co ...
Equine Science
... Esophageal – sphincter Cardiac – secretes HCl Fundic – main body of the stomach, protective lining Pyloric - sphincter Small Intestine – further digestion and nutrient absorption Extends from stomach to cecum; about 70’ long, 2” in diameter with 12 gallon capacity Distinct u-shape, folds and coils n ...
... Esophageal – sphincter Cardiac – secretes HCl Fundic – main body of the stomach, protective lining Pyloric - sphincter Small Intestine – further digestion and nutrient absorption Extends from stomach to cecum; about 70’ long, 2” in diameter with 12 gallon capacity Distinct u-shape, folds and coils n ...
Chapter 45: Chemical Signals 1 Hormone
... • Activate Vitamin D which acts with PTH on bone and intestine. Pancreas Figure 11 Both endocrine and exocrine (bicarbonate/digestive enzyme) functions • Islets of Langerhans—antagonistic hormones o alpha cells release glucagons o beta cells release insulin *insulin/glucagon are antagonistic • Insul ...
... • Activate Vitamin D which acts with PTH on bone and intestine. Pancreas Figure 11 Both endocrine and exocrine (bicarbonate/digestive enzyme) functions • Islets of Langerhans—antagonistic hormones o alpha cells release glucagons o beta cells release insulin *insulin/glucagon are antagonistic • Insul ...
hormone notes
... A. Endocrine system produces hormones that are important in maintaining homeostasis & regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). C. Unlike exocrine glands that rel ...
... A. Endocrine system produces hormones that are important in maintaining homeostasis & regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target cells). C. Unlike exocrine glands that rel ...
Chemical Signaling in Animals
... • Calcitonin increases stimulates bone formation, decreases bone destruction. • Calcitonin opposed by parathyroid hormone. • 3Parathyroid glands – located on backside of thyroid gland, secretes parathyroid hormone - regulates calcium, phosphate balance between blood, other tissue. ...
... • Calcitonin increases stimulates bone formation, decreases bone destruction. • Calcitonin opposed by parathyroid hormone. • 3Parathyroid glands – located on backside of thyroid gland, secretes parathyroid hormone - regulates calcium, phosphate balance between blood, other tissue. ...
CHAPTER 45
... • Calcitonin increases stimulates bone formation, decreases bone destruction. • Calcitonin opposed by parathyroid hormone. • 3Parathyroid glands – located on backside of thyroid gland, secretes parathyroid hormone - regulates calcium, phosphate balance between blood, other tissue. ...
... • Calcitonin increases stimulates bone formation, decreases bone destruction. • Calcitonin opposed by parathyroid hormone. • 3Parathyroid glands – located on backside of thyroid gland, secretes parathyroid hormone - regulates calcium, phosphate balance between blood, other tissue. ...
The Digestive System What are the organs of the digestive system
... Covers muscularis externa of oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, and rectum Is a dense sheath of collagen fibers Firmly attaches the digestive tract to ...
... Covers muscularis externa of oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, and rectum Is a dense sheath of collagen fibers Firmly attaches the digestive tract to ...
Anatomy of the Digestive System
... Duodenum Short superior part Duodenal papilla (minor & major) for entry of common bile duct Mucosa & submucosa thrown into folds plica circulares Microvilli ...
... Duodenum Short superior part Duodenal papilla (minor & major) for entry of common bile duct Mucosa & submucosa thrown into folds plica circulares Microvilli ...
Response
... Table 45-1d The amount of melatonin produced by the pineal gland is regulated by the amount the light/dark cycles. If melatonin production increases as the evening goes on, why would the pineal gland make more in the winter than in the summer? ...
... Table 45-1d The amount of melatonin produced by the pineal gland is regulated by the amount the light/dark cycles. If melatonin production increases as the evening goes on, why would the pineal gland make more in the winter than in the summer? ...
Class – XI Biology Chapter – 16 Human
... The other two digestive enzyme secreted by its source gland is amylase and lipases. Answer 9: The polysaccharides and disaccharides are partially digested by the amylase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice. The remaining digestion takes place by enzymes in the succus entericus. The enzyme maltase ...
... The other two digestive enzyme secreted by its source gland is amylase and lipases. Answer 9: The polysaccharides and disaccharides are partially digested by the amylase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice. The remaining digestion takes place by enzymes in the succus entericus. The enzyme maltase ...
Endocrine PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... These releasing factors stimulate specific cells in the anterior pituitary to produce and release the various tropins and other hormones of the anterior pituitary into the blood leaving the pituitary gland, to be carried to their target organs. Certain releasing factors inhibit the release of h ...
... These releasing factors stimulate specific cells in the anterior pituitary to produce and release the various tropins and other hormones of the anterior pituitary into the blood leaving the pituitary gland, to be carried to their target organs. Certain releasing factors inhibit the release of h ...
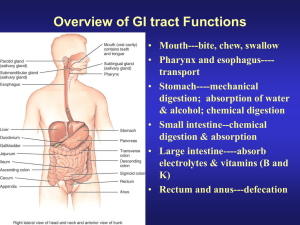
Overview of the Organs of the Digestive System
... – 20 teeth that start erupting at 6 months – 1 new pair of teeth per month • Permanent teeth – 32 teeth that erupt between 6 and 12 years of age – differing structures indicate function • incisors for biting • canines or cuspids for tearing • premolars & molars for crushing and grinding food ...
... – 20 teeth that start erupting at 6 months – 1 new pair of teeth per month • Permanent teeth – 32 teeth that erupt between 6 and 12 years of age – differing structures indicate function • incisors for biting • canines or cuspids for tearing • premolars & molars for crushing and grinding food ...
Endocrinology: Endocrine System Function Nervous vs. Endocrine
... • Both an endocrine organ and digestive organ • Endocrine cells located in Islets of Langerhans • Contain 2 cell types – α cells - secrete glucagon – β cells - secrete insulin ...
... • Both an endocrine organ and digestive organ • Endocrine cells located in Islets of Langerhans • Contain 2 cell types – α cells - secrete glucagon – β cells - secrete insulin ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • Specific actions of chemical messengers are at the level of the target cell • These two systems interact and regulate each other ...
... • Specific actions of chemical messengers are at the level of the target cell • These two systems interact and regulate each other ...
The Pituitary Gland
... – increases alertness and prepares body for physical activity • mobilize high energy fuels /// lactate, fatty acids, and glucose • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis both boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect /// because inhibits insulin secretion /// muscles use fatty acids saving glucose f ...
... – increases alertness and prepares body for physical activity • mobilize high energy fuels /// lactate, fatty acids, and glucose • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis both boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect /// because inhibits insulin secretion /// muscles use fatty acids saving glucose f ...
Stomach
... Stomach Structure • J-shaped, pouch-like organ that hangs inferior to diaphragm in upper left portion of abdominal cavity • capacity = 1L or more • empty = thick folds of mucousal and submucousal layers mark the stomach’s inner lining • full = no folds • pyloric sphincter controls gastric emptying ...
... Stomach Structure • J-shaped, pouch-like organ that hangs inferior to diaphragm in upper left portion of abdominal cavity • capacity = 1L or more • empty = thick folds of mucousal and submucousal layers mark the stomach’s inner lining • full = no folds • pyloric sphincter controls gastric emptying ...
Thyroid gland
... 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic rate ...
... 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced urine output 6. Increased metabolic rate ...
Encodocrine System Part Two
... Adrenal Glands Paired, pyramid-shaped glands atop the kidneys Essentially two glands in one Adrenal medulla Nervous tissue: part of the sympathetic nervous system NE and Epinephrine ...
... Adrenal Glands Paired, pyramid-shaped glands atop the kidneys Essentially two glands in one Adrenal medulla Nervous tissue: part of the sympathetic nervous system NE and Epinephrine ...
Histology Ass. Lec. Dentistry College Lec-7
... (taste cell) have in apices numerous microvilli that protrude through the taste pore, support cells and basal cells (stem cell). The major salivary glands salivary glands are located outside of the oral cavity and convey their secretions into the mouth via large excretory ducts. There are three majo ...
... (taste cell) have in apices numerous microvilli that protrude through the taste pore, support cells and basal cells (stem cell). The major salivary glands salivary glands are located outside of the oral cavity and convey their secretions into the mouth via large excretory ducts. There are three majo ...
DIGESTIVE TRACT
... in order of size. There are also many minor, unnamed seromucous glands within the oral cavity mucosa that add their secretion to that of the major ones to form saliva. (see the drawing to the right) ...
... in order of size. There are also many minor, unnamed seromucous glands within the oral cavity mucosa that add their secretion to that of the major ones to form saliva. (see the drawing to the right) ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.