Activia®`s Digestive Health Tool Kit
... Digestive health issues are often both difficult to discuss and understand. Use the Digestive Health Dictionary to get to know the different elements of your system. Bacteria – microscopic organisms that have a simple, one-celled structure and live in a variety of environments, including water, soil ...
... Digestive health issues are often both difficult to discuss and understand. Use the Digestive Health Dictionary to get to know the different elements of your system. Bacteria – microscopic organisms that have a simple, one-celled structure and live in a variety of environments, including water, soil ...
Endocrine System
... Hormones are chemicals regulators Most are secreted into the blood and become circulating hormones They affect the functioning of other cells These “other cells” are called targets ...
... Hormones are chemicals regulators Most are secreted into the blood and become circulating hormones They affect the functioning of other cells These “other cells” are called targets ...
18-1
... • Chromaffin cells receive direct innervation from sympathetic nervous system – develop from same tissue as postganglionic neurons ...
... • Chromaffin cells receive direct innervation from sympathetic nervous system – develop from same tissue as postganglionic neurons ...
Lab20
... If the abdominal cavity has not been opened in studying the circulatory system, open it by making a midventral incision along the linea alba. This incision should extend from the sternum to the symphysis pubis. Be careful not to injure the underlying organs. Make two additional incisions at right an ...
... If the abdominal cavity has not been opened in studying the circulatory system, open it by making a midventral incision along the linea alba. This incision should extend from the sternum to the symphysis pubis. Be careful not to injure the underlying organs. Make two additional incisions at right an ...
Digestive System Packet
... As you swallow, two sets of muscles act together to force the food and water through the esophagus and into the stomach. One set is circular and presses inward. The other set runs up and down and also contracts inward forcing the food downward. This wave-like motion is called peristalsis. Since the ...
... As you swallow, two sets of muscles act together to force the food and water through the esophagus and into the stomach. One set is circular and presses inward. The other set runs up and down and also contracts inward forcing the food downward. This wave-like motion is called peristalsis. Since the ...
FOR THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ANSWER: A. if choices 1, 2
... 22. Which of the following statements is true in relation to the femoral triangle? A. Its medial border is the Sartorius B. The femoral nerve is its most medial structure C. Its upper border is the inguinal ligament D. The femoral canal is its most lateral structure E. The iliopsoas muscle is its an ...
... 22. Which of the following statements is true in relation to the femoral triangle? A. Its medial border is the Sartorius B. The femoral nerve is its most medial structure C. Its upper border is the inguinal ligament D. The femoral canal is its most lateral structure E. The iliopsoas muscle is its an ...
Digestive System PP
... Always NPO for tube feedings because of the reasons they are on tube feedings! HOB at least 30 degrees or higher ...
... Always NPO for tube feedings because of the reasons they are on tube feedings! HOB at least 30 degrees or higher ...
A Comparison of an Amphibious and Human Digestive System
... 1. Explain how the circulatory system works together with the digestive system? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. List the ways in which the frog’s digestive system is similar to your own. ____________________________________ ...
... 1. Explain how the circulatory system works together with the digestive system? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. List the ways in which the frog’s digestive system is similar to your own. ____________________________________ ...
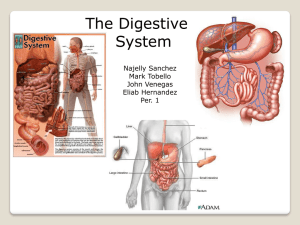
The Digestive System
... then propels the narrowed portion slowly down the length of the organ. These waves of narrowing push the food and fluid in front of them through each hollow organ. • The first major muscle movement occurs when food or liquid is swallowed. Although we are able to start swallowing by choice, once the ...
... then propels the narrowed portion slowly down the length of the organ. These waves of narrowing push the food and fluid in front of them through each hollow organ. • The first major muscle movement occurs when food or liquid is swallowed. Although we are able to start swallowing by choice, once the ...
The Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Question No. 1 of 10
... The pancreas controls sugar levels in the blood. Why is the amount of sugar in the blood so important? Too little sugar will not give cells enough energy. Too much sugar is toxic to the body. Insulin removes sugar from blood and leads to it being stored in cells. Glucagon breaks down stored sugar an ...
... The pancreas controls sugar levels in the blood. Why is the amount of sugar in the blood so important? Too little sugar will not give cells enough energy. Too much sugar is toxic to the body. Insulin removes sugar from blood and leads to it being stored in cells. Glucagon breaks down stored sugar an ...
FREE Sample Here
... The nutrients that are ready for absorption early are absorbed near the top of the gastrointestinal tract, and those that take longer to be digested are absorbed further down. Although much of the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins begins to take place in the mouth and stomach respectively, the ...
... The nutrients that are ready for absorption early are absorbed near the top of the gastrointestinal tract, and those that take longer to be digested are absorbed further down. Although much of the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins begins to take place in the mouth and stomach respectively, the ...
Digestive System - Mrs. beckham`s Science
... Chemical digestion of proteins with enzymes Homeostatic imbalance: Ulcers, erosions in stomach wall from breakdown of mucus barrier. Causes include: ...
... Chemical digestion of proteins with enzymes Homeostatic imbalance: Ulcers, erosions in stomach wall from breakdown of mucus barrier. Causes include: ...
05 Introduction to Splanchnology. General anatomy of the dig
... Foreign bodies are therefore more likely to lodge in this bronchus or one of its branches ...
... Foreign bodies are therefore more likely to lodge in this bronchus or one of its branches ...
Digestion/Excretion PowerPoint
... stomach contents are “thrown up” o There is a “ring” muscle that is found at the opening of the stomach called the SPHINCTER. It controls the passage of food into the stomach. There is also a sphincter muscle found along the rectum; you can guess what this is for. http://www.medicalook.com/systems_i ...
... stomach contents are “thrown up” o There is a “ring” muscle that is found at the opening of the stomach called the SPHINCTER. It controls the passage of food into the stomach. There is also a sphincter muscle found along the rectum; you can guess what this is for. http://www.medicalook.com/systems_i ...
Key Vocabulary
... cartilagenous structure that connects nasal and oral cavities to lungs conduct blood from aorta to arterioles conduct blood from arteries to capillaries conduct blood from capillaries to veins conduct blood from venules to vena cava conduct oxygenated blood to tissues, deoxygenated blood away contin ...
... cartilagenous structure that connects nasal and oral cavities to lungs conduct blood from aorta to arterioles conduct blood from arteries to capillaries conduct blood from capillaries to veins conduct blood from venules to vena cava conduct oxygenated blood to tissues, deoxygenated blood away contin ...
Chapter 45
... What are the 3 general types of signaling pathways? How can 1 ligand cause different effects? What are some common endocrine glands? How does the hypothalamus control the anterior & posterior pituitary differently? How is the thyroid regulated? How is homeostasis of blood calcium achieved? How is ho ...
... What are the 3 general types of signaling pathways? How can 1 ligand cause different effects? What are some common endocrine glands? How does the hypothalamus control the anterior & posterior pituitary differently? How is the thyroid regulated? How is homeostasis of blood calcium achieved? How is ho ...
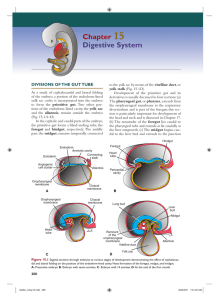
Chapter 15 Digestive System
... is initiated by a concentration gradient of retinoic acid (RA) from the pharynx, that is exposed to little or no RA, to the colon, that sees the highest concentration of RA. This RA gradient causes transcription factors to be expressed in different regions of the gut tube. Thus, SOX2 “specifies” the ...
... is initiated by a concentration gradient of retinoic acid (RA) from the pharynx, that is exposed to little or no RA, to the colon, that sees the highest concentration of RA. This RA gradient causes transcription factors to be expressed in different regions of the gut tube. Thus, SOX2 “specifies” the ...
Anatomy 2006
... 2. The path of the ureter runs over the bifurcation of the common iliac artery? a. True b. False 3. Which of the following is true? a. A “saddle” joint is bi-axial b. A “ball” joint is multi-axial c. A “hinge” joint is mono-axial d. A + B e. B + C f. A + C g. All of the above ...
... 2. The path of the ureter runs over the bifurcation of the common iliac artery? a. True b. False 3. Which of the following is true? a. A “saddle” joint is bi-axial b. A “ball” joint is multi-axial c. A “hinge” joint is mono-axial d. A + B e. B + C f. A + C g. All of the above ...
Chapter 25 and 26 Test Review
... Describe the anatomical landmarks of the stomach, small intestine and large intestine. Describe the specialization of the stomach’s walls. (be specific - talk about each layer) Describe the function of parietal and chief cells. What controls their secretion? What is the function of the mesentery? De ...
... Describe the anatomical landmarks of the stomach, small intestine and large intestine. Describe the specialization of the stomach’s walls. (be specific - talk about each layer) Describe the function of parietal and chief cells. What controls their secretion? What is the function of the mesentery? De ...
Digestive System Presentation
... What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal (also called the digestive tract) is the long tube of organs — including the esophagus, the stomach, and the intestines — that runs from the mouth to the anus. An adult's digestive tract is about 30 feet long. ...
... What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal (also called the digestive tract) is the long tube of organs — including the esophagus, the stomach, and the intestines — that runs from the mouth to the anus. An adult's digestive tract is about 30 feet long. ...
Digestive System Packet
... • Produces pancreatic juice, which has many digestive enzymes that get sent to the small intestine Liver • Large organ that makes bile • Important in removing toxins and processing digested food Bile Facts! • Bile acts as a detergent, and emulsifies (breaks down into small pieces) the fat in food so ...
... • Produces pancreatic juice, which has many digestive enzymes that get sent to the small intestine Liver • Large organ that makes bile • Important in removing toxins and processing digested food Bile Facts! • Bile acts as a detergent, and emulsifies (breaks down into small pieces) the fat in food so ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.