Hormone - Denton ISD
... • Norepinephrine [a.k.a. noradrenaline] is released as a neurotransmitter by the sympathetic nerve endings AND is secreted by the adrenal gland as a hormone • As a neurotransmitter it travels a very short distance across the synaptic cleft and binds to a receptor protein to stimulate the postsynapti ...
... • Norepinephrine [a.k.a. noradrenaline] is released as a neurotransmitter by the sympathetic nerve endings AND is secreted by the adrenal gland as a hormone • As a neurotransmitter it travels a very short distance across the synaptic cleft and binds to a receptor protein to stimulate the postsynapti ...
Salivary Glands
... and fundus. Some cells are responsible for secreting acid and others secrete enzymes to break down proteins. The wall is divided into four layers as follows: ...
... and fundus. Some cells are responsible for secreting acid and others secrete enzymes to break down proteins. The wall is divided into four layers as follows: ...
Abdomen
... 58. Structure that receivers bile,concentrates it by absorbing water and salt,and stores it. 59. Structure that receivers blood from the left gonad and suprarenal ...
... 58. Structure that receivers bile,concentrates it by absorbing water and salt,and stores it. 59. Structure that receivers blood from the left gonad and suprarenal ...
Incisions made in the direction of Langer`s lines are less likely to
... It is useful to know the surface marking of the entrance of the superior vena cava into the right atrium when positioning a central venous catheter. It is represented by a transverse line 2.5 cm long that is centered on the right side over the second costochondral junction. The aorta bifurcates at t ...
... It is useful to know the surface marking of the entrance of the superior vena cava into the right atrium when positioning a central venous catheter. It is represented by a transverse line 2.5 cm long that is centered on the right side over the second costochondral junction. The aorta bifurcates at t ...
Combined_Torso_Part_2 [ screen displays inferior surface of the
... [ voice of Dr. Barbara Davis, Instructor, Biology speaking] Here, we can see the inferior surface of the liver. [ uses pointer to distinguish different sections of the liver] So to get oriented first…here’s the gallbladder; to the side of the gallbladder would be the right lobe of the liver, so the ...
... [ voice of Dr. Barbara Davis, Instructor, Biology speaking] Here, we can see the inferior surface of the liver. [ uses pointer to distinguish different sections of the liver] So to get oriented first…here’s the gallbladder; to the side of the gallbladder would be the right lobe of the liver, so the ...
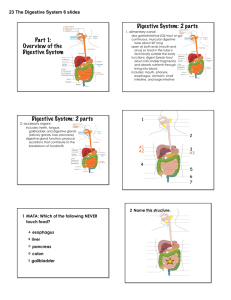
Part 1: Overview of the Digestive System Digestive System: 2 parts
... • 2 major lobes (right and left) • lies in upper right quadrant of abdominal cavity just inferior to diaphragm • digestive function - produce bile ...
... • 2 major lobes (right and left) • lies in upper right quadrant of abdominal cavity just inferior to diaphragm • digestive function - produce bile ...
Digestive System 24
... The digestive system is responsible for many body processes. Its functions begin when food is taken into the mouth, or _1_. The process called _2_ occurs as food is broken down both chemically and mechanically. For the broken-down foods to be made available to the body cells, they must be absorbed t ...
... The digestive system is responsible for many body processes. Its functions begin when food is taken into the mouth, or _1_. The process called _2_ occurs as food is broken down both chemically and mechanically. For the broken-down foods to be made available to the body cells, they must be absorbed t ...
kumc 40 abdominal aorta and ivc student
... Celiac trunk (artery): Hepatic branches: Gastroduodenal: Right gastroepiploic: Travels along greater curvature of the stomach. Superior pancreaticoduodenal: Travels along head of pancreas. Supplies duodenum and pancreas. ...
... Celiac trunk (artery): Hepatic branches: Gastroduodenal: Right gastroepiploic: Travels along greater curvature of the stomach. Superior pancreaticoduodenal: Travels along head of pancreas. Supplies duodenum and pancreas. ...
lec18
... the cells as they are made and upon binding with specific plasma proteins, they are distributed through the circulatory system. • Their target organs and functions are described in Table ...
... the cells as they are made and upon binding with specific plasma proteins, they are distributed through the circulatory system. • Their target organs and functions are described in Table ...
session 38
... move food along the tract, but also to churn, mix, and pummel the food, physically breaking it down to smaller fragments. In addition, chemical breakdown of proteins begins in the stomach. The mu- ...
... move food along the tract, but also to churn, mix, and pummel the food, physically breaking it down to smaller fragments. In addition, chemical breakdown of proteins begins in the stomach. The mu- ...
Digestive System
... Bile from the liver, gallbladder and pancreatic juices enter this section through ducts or tubes About 8 feet long (the middle section) ...
... Bile from the liver, gallbladder and pancreatic juices enter this section through ducts or tubes About 8 feet long (the middle section) ...
Chapter 23
... 1. The two adrenal (suprarenal) glands lie superior to the two kidneys. 2. Each gland is differentiated into two regions: i. large, peripherally located adrenal cortex which is subdivided into three zones: a. outer zona glomerulosa that secretes mineralocorticoids which affect mineral (especially so ...
... 1. The two adrenal (suprarenal) glands lie superior to the two kidneys. 2. Each gland is differentiated into two regions: i. large, peripherally located adrenal cortex which is subdivided into three zones: a. outer zona glomerulosa that secretes mineralocorticoids which affect mineral (especially so ...
Pituitary gland (hypophysis cerebri)
... Endocrine regulation of blood glucose -The normal blood glucose level ranges between 80-120 mg/100 ml blood. -This level is controlled by the following hormones: 1- Pancreatic h. ...
... Endocrine regulation of blood glucose -The normal blood glucose level ranges between 80-120 mg/100 ml blood. -This level is controlled by the following hormones: 1- Pancreatic h. ...
File
... The Small Intestine The small intestine receives chyme from the stomach and completes the digestion of food. Macromolecules are broken down into nutrients, which are absorbed in the small intestine and pass into the blood. Structure and Function of the Small Intestine The small intestine is composed ...
... The Small Intestine The small intestine receives chyme from the stomach and completes the digestion of food. Macromolecules are broken down into nutrients, which are absorbed in the small intestine and pass into the blood. Structure and Function of the Small Intestine The small intestine is composed ...
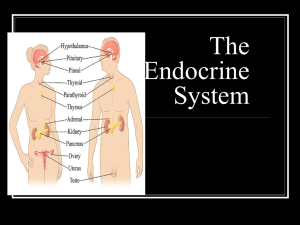
Chapter 11 Study Guide Outline: Endocrine System
... Located below the larynx on either side and in front of the trachea Synthesize two hormones _____________ (T4) & Triodothyronine (T3): regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
... Located below the larynx on either side and in front of the trachea Synthesize two hormones _____________ (T4) & Triodothyronine (T3): regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
Lecture #20 - Suraj @ LUMS
... The Thyroid Gland • The thyroid gland is located in the neck. Follicles in the thyroid secrete thyroglobulin, a storage form of thyroid hormone. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary causes conversion of thyroglobulin into thyroid hormones T4 and T3. Almost all body cells ar ...
... The Thyroid Gland • The thyroid gland is located in the neck. Follicles in the thyroid secrete thyroglobulin, a storage form of thyroid hormone. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary causes conversion of thyroglobulin into thyroid hormones T4 and T3. Almost all body cells ar ...
Animal Nutrition - EMS Secondary Department
... • Digestive enzymes – peptidases • trypsin – trypsinogen ...
... • Digestive enzymes – peptidases • trypsin – trypsinogen ...
Peritoneum and abdominal cavity
... stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. Also an injured pancreas or inflamed pancreas will cause pancreatic secretions to enter the lesser sac. This can cause a pancreatic pseudocyst. ...
... stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. Also an injured pancreas or inflamed pancreas will cause pancreatic secretions to enter the lesser sac. This can cause a pancreatic pseudocyst. ...
Unit 9 Endocrine system notes
... directly into the blood. • Affects cell activities by releasing chemical messengers ( hormones) directly into the bloodstream, the target cells are varied (may be all over body) • Hormones control generally takes from minutes to hours to occur and the changes are long lasting, usually due to changes ...
... directly into the blood. • Affects cell activities by releasing chemical messengers ( hormones) directly into the bloodstream, the target cells are varied (may be all over body) • Hormones control generally takes from minutes to hours to occur and the changes are long lasting, usually due to changes ...
File
... Cells in testes produce androgens (testosterone is most important) which are responsible for: ...
... Cells in testes produce androgens (testosterone is most important) which are responsible for: ...
Chapter 2 - SCHOOLinSITES
... b) The small intestine, after a meal, secretes hormones that suppress appetite. c) High levels of leptin, produced by fat cells, suppress appetite. d) The brain is sensitive to levels of the circulating leptin hormone. e) An activated leptin receptor triggers the hunger response. Copyright © 2008 Pe ...
... b) The small intestine, after a meal, secretes hormones that suppress appetite. c) High levels of leptin, produced by fat cells, suppress appetite. d) The brain is sensitive to levels of the circulating leptin hormone. e) An activated leptin receptor triggers the hunger response. Copyright © 2008 Pe ...
Biology: 5. The Digestive System Syllabus OB6 Identify and locate
... In the small intestine starch is broken down to maltose by amylase. Identify the enzyme, and the substrate named in this reaction. 15. [2008 OL] Name a reducing sugar. ...
... In the small intestine starch is broken down to maltose by amylase. Identify the enzyme, and the substrate named in this reaction. 15. [2008 OL] Name a reducing sugar. ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.