Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... medulla is part of the nervous system; it secretes epinephrine (commonly referred to as adrenaline) and norepinephrine (also known as noradrenalin), which are released into the blood during times of physical or emotional stress. ...
... medulla is part of the nervous system; it secretes epinephrine (commonly referred to as adrenaline) and norepinephrine (also known as noradrenalin), which are released into the blood during times of physical or emotional stress. ...
respiratory system
... At the center of a tooth is the pulp cavity, which contains the tooth’s nerve and blood supply. It is the “living” part of the tooth. The bulk of the tooth is composed of a hard, calcified CT layer called dentin. Dentin is porous and, if exposed, allows for some communication between the exterior of ...
... At the center of a tooth is the pulp cavity, which contains the tooth’s nerve and blood supply. It is the “living” part of the tooth. The bulk of the tooth is composed of a hard, calcified CT layer called dentin. Dentin is porous and, if exposed, allows for some communication between the exterior of ...
Small and Large Intestines
... different from what we've seen for monosaccharides and amino acids. The major products of lipid digestion - fatty acids and monoglycerides - enter the SI epithelium by simple diffusion across the plasma membrane ...
... different from what we've seen for monosaccharides and amino acids. The major products of lipid digestion - fatty acids and monoglycerides - enter the SI epithelium by simple diffusion across the plasma membrane ...
notes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The Pancreas releases biocarbonate (HCO3-) into the top of the small intestine that neutralizes the acid (HCl) Continues to digest food - Enzymes continue the chemical reactions on the food. Food stays in your small intestine for 4 to 8 hours The nutrients are broken down small enough to pas ...
... The Pancreas releases biocarbonate (HCO3-) into the top of the small intestine that neutralizes the acid (HCl) Continues to digest food - Enzymes continue the chemical reactions on the food. Food stays in your small intestine for 4 to 8 hours The nutrients are broken down small enough to pas ...
570525Review_Guide_chapter_15
... People without the enzyme lactase are said to be lactose intolerant. Their digestive systems cannot digest lactose. As a result, this sugar passes from the small intestine into the large intestine. A high concentration of lactose in the large intestine causes water to move from the body into the lar ...
... People without the enzyme lactase are said to be lactose intolerant. Their digestive systems cannot digest lactose. As a result, this sugar passes from the small intestine into the large intestine. A high concentration of lactose in the large intestine causes water to move from the body into the lar ...
Endocrine System
... • Lumpy organ the abdomen between the inferior border of the stomach (bottom) and the proximal (closest) portion of the small intestine. • Primarily a exocrine organ (99%) but it makes digestive enzymes • The endocrine pancreas (1%) consists of clusters known as pancreatic islets. ▫ Surrounded by ca ...
... • Lumpy organ the abdomen between the inferior border of the stomach (bottom) and the proximal (closest) portion of the small intestine. • Primarily a exocrine organ (99%) but it makes digestive enzymes • The endocrine pancreas (1%) consists of clusters known as pancreatic islets. ▫ Surrounded by ca ...
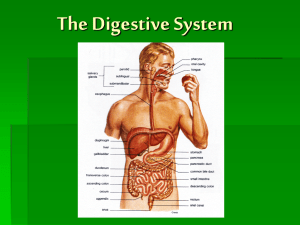
The Digestive System
... There are three pairs of salivary glands: the sublingual glands (found underneath the tongue), the submandibular glands (lie under the tongue at the back portion of the mouth and the parotid glands which are located in front of and below the ears. ...
... There are three pairs of salivary glands: the sublingual glands (found underneath the tongue), the submandibular glands (lie under the tongue at the back portion of the mouth and the parotid glands which are located in front of and below the ears. ...
endocrine1
... 2. A) Describe a situation that would lead to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system. B) How does sympathetic stimulation affect the secretion from beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans? C) Why is this beneficial for the person in terms of fuel supply? 3. After an overnight fast, a patien ...
... 2. A) Describe a situation that would lead to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system. B) How does sympathetic stimulation affect the secretion from beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans? C) Why is this beneficial for the person in terms of fuel supply? 3. After an overnight fast, a patien ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system
... 1. As an exocrine gland- releases digestive enzymes into the duct system leading to the small intestines. 2. As an endocrine gland- one to two million small islets or cells that secrete hormones. a. The Islets of Langerhans i. The types of cells that secrete hormones called alpha, beta, delta and F ...
... 1. As an exocrine gland- releases digestive enzymes into the duct system leading to the small intestines. 2. As an endocrine gland- one to two million small islets or cells that secrete hormones. a. The Islets of Langerhans i. The types of cells that secrete hormones called alpha, beta, delta and F ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system part 2
... Is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. 1. As an exocrine gland- releases digestive enzymes into the duct system leading to the small intestines. 2. As an endocrine gland- one to two million small islets or cells that secrete hormones. a. The Islets of Langerhans i. The types of cells that secre ...
... Is both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. 1. As an exocrine gland- releases digestive enzymes into the duct system leading to the small intestines. 2. As an endocrine gland- one to two million small islets or cells that secrete hormones. a. The Islets of Langerhans i. The types of cells that secre ...
May 2005: Guide to the Horse's Gut
... Travels from right flank to liver to left flank back to liver back to right flank Anchored on right by short mesentery, free on left Ferementation and fiber digestion ...
... Travels from right flank to liver to left flank back to liver back to right flank Anchored on right by short mesentery, free on left Ferementation and fiber digestion ...
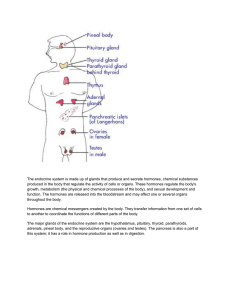
The Endocrine System
... hormones require more regulation because they cannot easily pass through the cellular membranes to affect cells •Protein hormones must interact with cells via receptors on the surface of the cell ...
... hormones require more regulation because they cannot easily pass through the cellular membranes to affect cells •Protein hormones must interact with cells via receptors on the surface of the cell ...
Endocrine System
... Each adrenal gland is actually two endocrine organs. The outer portion is called the adrenal cortex. The inner portion is called the adrenal medulla. The hormones of the adrenal cortex are essential for life. The types of hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla are not. The adrenal cortex produces ...
... Each adrenal gland is actually two endocrine organs. The outer portion is called the adrenal cortex. The inner portion is called the adrenal medulla. The hormones of the adrenal cortex are essential for life. The types of hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla are not. The adrenal cortex produces ...
Digestive System Review
... The mucosal epithelial cells are mitotically active, thus the epithelium is replaced approximately every three to six days. The function of the double-layered muscularis mucosa is to aid in digestion and absorption by moving the mucosal villi in the small intestine. Blood and lymph vessels as well a ...
... The mucosal epithelial cells are mitotically active, thus the epithelium is replaced approximately every three to six days. The function of the double-layered muscularis mucosa is to aid in digestion and absorption by moving the mucosal villi in the small intestine. Blood and lymph vessels as well a ...
Animal Structure and Function
... Amino Acids Essential Fatty Acids Essential Vitamins Essential Minerals ...
... Amino Acids Essential Fatty Acids Essential Vitamins Essential Minerals ...
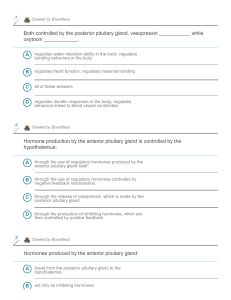
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
Short Version - Digestive system
... Only digestive function is to produce bile for export to the duodenum ◦ Bile is used to emulsify fats – distribute fat into solution to be accessible to digestive enzymes ...
... Only digestive function is to produce bile for export to the duodenum ◦ Bile is used to emulsify fats – distribute fat into solution to be accessible to digestive enzymes ...
Chapter 13 Notes - Biology at the Rural
... high, result may be osteoporosis (brittle bones due to bone density loss) Calcitonin- hormone release is stimulated by high blood calcium ion levels and it causes bone tissue to take up calcium ions and deposit it in bone tissue as well increasing the calcium ion secretion in the kidneys . Pancreas ...
... high, result may be osteoporosis (brittle bones due to bone density loss) Calcitonin- hormone release is stimulated by high blood calcium ion levels and it causes bone tissue to take up calcium ions and deposit it in bone tissue as well increasing the calcium ion secretion in the kidneys . Pancreas ...
The Human Digestive System
... 65. Where is bile stored after it has been made in the liver? 66. Give one role that the bile salts play in the digestive process. 67. Give two further functions of the liver, other than the manufacture of bile. 68. Name one good source of protein in the human diet 69. What is meant by the term dige ...
... 65. Where is bile stored after it has been made in the liver? 66. Give one role that the bile salts play in the digestive process. 67. Give two further functions of the liver, other than the manufacture of bile. 68. Name one good source of protein in the human diet 69. What is meant by the term dige ...
Document
... After digestion starch brake down in to small glucose molecules and fructose molecules. The fructose get absorb by the intestinal villi through the process of facilitated diffusion. Glucose and galactose molecules absorb by villi through the carrier translocase present on the plasma membrane o ...
... After digestion starch brake down in to small glucose molecules and fructose molecules. The fructose get absorb by the intestinal villi through the process of facilitated diffusion. Glucose and galactose molecules absorb by villi through the carrier translocase present on the plasma membrane o ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... • Causes cells to release stored glucose into the blood • Increases blood [Glucose] ...
... • Causes cells to release stored glucose into the blood • Increases blood [Glucose] ...
Enzyme Basics
... (enzymes, water, and electrolytes) are released every day in addition to such hormones as glucagon and insulin to control glucose metabolism. Pancreatic amylases break down about 300 grams of carbohydrates every day; lipases break down about 175 grams of fat per hour; and proteases (chymotrypsin, ...
... (enzymes, water, and electrolytes) are released every day in addition to such hormones as glucagon and insulin to control glucose metabolism. Pancreatic amylases break down about 300 grams of carbohydrates every day; lipases break down about 175 grams of fat per hour; and proteases (chymotrypsin, ...
Chapter 18
... (“good,” normal secretion) Dietary intake of iodine may be inadequate thyroid hormone in blood stimulates TSH enlarge ...
... (“good,” normal secretion) Dietary intake of iodine may be inadequate thyroid hormone in blood stimulates TSH enlarge ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.