revised slides - luanar moodle
... • Thru this gut provides sensory info to CNS & CNS can affect GI function • Signals from outside DS relayed to DS e.g. sight of appealing food stimulates stomach secretions ...
... • Thru this gut provides sensory info to CNS & CNS can affect GI function • Signals from outside DS relayed to DS e.g. sight of appealing food stimulates stomach secretions ...
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
... Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before fertilization occurs, though the receptor(s) as yet remain unidentified. Since eggs release progesterone, sperm may use progesterone as a homing signal to swim toward eggs. ...
... Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before fertilization occurs, though the receptor(s) as yet remain unidentified. Since eggs release progesterone, sperm may use progesterone as a homing signal to swim toward eggs. ...
Unit 10: Feedback Loops
... 3. Hypothalamus secretes (TRH) Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone 4. TRH is sent to the Pituitary Gland 5. Pituitary Gland secretes (TSH) Thyroxine Secreting Hormone 6. TSH is sent to Thyroid 7. Thyroid secretes Thyroxine into blood which then spreads through body 8. Thyroxine levels increase in the body ...
... 3. Hypothalamus secretes (TRH) Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone 4. TRH is sent to the Pituitary Gland 5. Pituitary Gland secretes (TSH) Thyroxine Secreting Hormone 6. TSH is sent to Thyroid 7. Thyroid secretes Thyroxine into blood which then spreads through body 8. Thyroxine levels increase in the body ...
Anatomy – Test 2 (Part 1)
... Define the boundaries of the abdominal cavity and the skeletal components related to the abdominal wall Describe the major surface landmarks of the anterior abdominal wall Describe the lines and planes that are used to divide the abdomen into quadrants and regions Describe the attachments, o ...
... Define the boundaries of the abdominal cavity and the skeletal components related to the abdominal wall Describe the major surface landmarks of the anterior abdominal wall Describe the lines and planes that are used to divide the abdomen into quadrants and regions Describe the attachments, o ...
Anatomy – Test 2 (Part 1)
... Define the boundaries of the abdominal cavity and the skeletal components related to the abdominal wall Describe the major surface landmarks of the anterior abdominal wall Describe the lines and planes that are used to divide the abdomen into quadrants and regions Describe the attachments, o ...
... Define the boundaries of the abdominal cavity and the skeletal components related to the abdominal wall Describe the major surface landmarks of the anterior abdominal wall Describe the lines and planes that are used to divide the abdomen into quadrants and regions Describe the attachments, o ...
File
... 2) The esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, gall bladder, pancreas, and liver are all a part of which body system? A) excretory B) endocrine C) integumentary D) digestive 3) Which body system breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed into the body? A) excretory B) circulatory C ...
... 2) The esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, gall bladder, pancreas, and liver are all a part of which body system? A) excretory B) endocrine C) integumentary D) digestive 3) Which body system breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed into the body? A) excretory B) circulatory C ...
Name Chapter 18: Alterations of Hormonal Regulation I
... In the obese, insulin has a diminished ability to influence glucose uptake and metabolism (insulin resistance of target tissues). Some insulin production continues in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but the size and number of beta cells decrease. Initially insulin secretion may be high, but it decline ...
... In the obese, insulin has a diminished ability to influence glucose uptake and metabolism (insulin resistance of target tissues). Some insulin production continues in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but the size and number of beta cells decrease. Initially insulin secretion may be high, but it decline ...
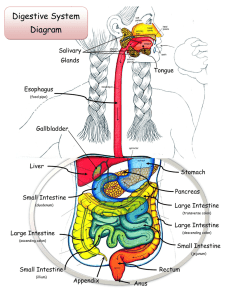
accessory digestive organs
... Involves long reflexes with CNS ~ via VAGUS nerve Smell, sight, thought of food ~ cerebral cortex Initiates secretion & motility ~ “stomach growling” Parasympathetic ~ stimulation increases activity Sympathetic ~ stimulation decreases activity Intrinsic Innervation ~ Autoregularion ~ No CNS Stimulat ...
... Involves long reflexes with CNS ~ via VAGUS nerve Smell, sight, thought of food ~ cerebral cortex Initiates secretion & motility ~ “stomach growling” Parasympathetic ~ stimulation increases activity Sympathetic ~ stimulation decreases activity Intrinsic Innervation ~ Autoregularion ~ No CNS Stimulat ...
Read pages 54 – 59 on Surface Area and Spies Leftovers then
... Surface Area and Spies Leftovers Directions: Read Spies: Leftovers then answer in COMPLETE sentences the questions below. 1. Does your body need an appendix? 2. What is the name of the undigested food that is in the colon? 3. What is the job (role) of the colon? 4. What causes us to have diarrhea? 5 ...
... Surface Area and Spies Leftovers Directions: Read Spies: Leftovers then answer in COMPLETE sentences the questions below. 1. Does your body need an appendix? 2. What is the name of the undigested food that is in the colon? 3. What is the job (role) of the colon? 4. What causes us to have diarrhea? 5 ...
3. The small intestine is the major organ of
... Where does chemical digestion of PROTEIN first take place? ...
... Where does chemical digestion of PROTEIN first take place? ...
Chapter 23: The Digestive System
... ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination of feces. Because of the external openings, you will be presented with the unique concept that food “inside” the alimentary canal (the GI tract) is actually “outside” of the body. The structural plan of the alimentary canal includes digestive organs: ...
... ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination of feces. Because of the external openings, you will be presented with the unique concept that food “inside” the alimentary canal (the GI tract) is actually “outside” of the body. The structural plan of the alimentary canal includes digestive organs: ...
Frog Dissection Organ Chart
... Movement Movement Movement; jumping Swimming Taking in food and air Grind food Grind food Internal opening of nostrils Equalizes pressure Air passage to lungs Takes swallowed food down esophagus then to stomach Catches prey Produces bile and other digestive enzymes; removes toxins from blood Stores ...
... Movement Movement Movement; jumping Swimming Taking in food and air Grind food Grind food Internal opening of nostrils Equalizes pressure Air passage to lungs Takes swallowed food down esophagus then to stomach Catches prey Produces bile and other digestive enzymes; removes toxins from blood Stores ...
Duodenum - Pure Training and Development
... • When food is partly digested, the mass is known as chyme • Chyme moves from stomach to small intestine COPYRIGHT © PURE TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT ...
... • When food is partly digested, the mass is known as chyme • Chyme moves from stomach to small intestine COPYRIGHT © PURE TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT ...
Digestion - San Elijo Elementary School
... The liver and gallbladder • Large metabolic organ that lies under the diaphragm and is made of ~100,000 lobules • Filters blood from the GI tract thus acting to remove poisons and detoxify the blood • Removes iron, vitamins A, D, E, K and B12 from the blood and stores them • Stores glucose as glycog ...
... The liver and gallbladder • Large metabolic organ that lies under the diaphragm and is made of ~100,000 lobules • Filters blood from the GI tract thus acting to remove poisons and detoxify the blood • Removes iron, vitamins A, D, E, K and B12 from the blood and stores them • Stores glucose as glycog ...
Gizmo Instructions and questions
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. Observe: Now look at the ...
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. Observe: Now look at the ...
The Endocrine System (Chapter 16)
... Describe the mechanisms by which hormones may act upon a target cell. State how hormones may alter cellular metabolism without entering the target cell. Explain how cAMP can be formed and used as a universal secondary messenger. (Review the first few pages of chapter 16). Relate this messenger syste ...
... Describe the mechanisms by which hormones may act upon a target cell. State how hormones may alter cellular metabolism without entering the target cell. Explain how cAMP can be formed and used as a universal secondary messenger. (Review the first few pages of chapter 16). Relate this messenger syste ...
Pancreas
... • Enzymes: pepsin in the stomach • Pancreatic proteases • Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and ...
... • Enzymes: pepsin in the stomach • Pancreatic proteases • Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and ...
The Endocrine System
... some areas) • Vasodilation in heart, liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Dilates air passages to lungs • Decreases digestion, increase blood glucose, and stimulate metabolism • Secretion based on neural input from hypothalamus Pancreas • Both exocrine (structurally as acini, digestive functi ...
... some areas) • Vasodilation in heart, liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Dilates air passages to lungs • Decreases digestion, increase blood glucose, and stimulate metabolism • Secretion based on neural input from hypothalamus Pancreas • Both exocrine (structurally as acini, digestive functi ...
The Endocrine System Overview of Endocrine System • Endocrine
... Secretion based on neural input from hypothalamus Pancreas • Both exocrine (structurally as acini, digestive function) and endocrine function • About 1% of cells are pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) • Four different hormone secreting cell types – Alpha (A) cells (20%) - glucagon • Increases ...
... Secretion based on neural input from hypothalamus Pancreas • Both exocrine (structurally as acini, digestive function) and endocrine function • About 1% of cells are pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) • Four different hormone secreting cell types – Alpha (A) cells (20%) - glucagon • Increases ...
Hormonal Regulation of Growth
... Glucocorticoids bind to the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor. This type of receptor gets activated upon ligand binding. After a hormone binds to the corresponding receptor, the newly formed receptor-ligand complex translocates itself into the cell nucleus, where it binds to many glucocorticoid re ...
... Glucocorticoids bind to the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor. This type of receptor gets activated upon ligand binding. After a hormone binds to the corresponding receptor, the newly formed receptor-ligand complex translocates itself into the cell nucleus, where it binds to many glucocorticoid re ...
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #1
... Part 2: Remove slide #40 from the slide box and focus using low power. At this point you should be able to see the entire ovary section. Most of the slides in our lab are an ovary from a cat or other animal which gives birth to litters of multiple offspring, so they show many different follicles dev ...
... Part 2: Remove slide #40 from the slide box and focus using low power. At this point you should be able to see the entire ovary section. Most of the slides in our lab are an ovary from a cat or other animal which gives birth to litters of multiple offspring, so they show many different follicles dev ...
File - HONORS BIOLOGY
... Absorption of water and vitamins Store and eliminate feces Mechanical and chemical digestion begins Secretes saliva Moves food to stomach by peristalsis Holds food and mixes it with acid and pepsin First section of the small intestine – large amounts of digestion Makes and stores bile Secretes large ...
... Absorption of water and vitamins Store and eliminate feces Mechanical and chemical digestion begins Secretes saliva Moves food to stomach by peristalsis Holds food and mixes it with acid and pepsin First section of the small intestine – large amounts of digestion Makes and stores bile Secretes large ...
Hormone Review Guide
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.























