Chapter 13
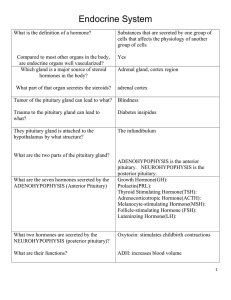
... 16. Describe the anatomical differences between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland. (p. 498) The anterior lobe is composed of layers of epithelial tissues grouped around many blood vessels. The epithelial tissues contain five types of secretory cells responsible for hormone pro ...
... 16. Describe the anatomical differences between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland. (p. 498) The anterior lobe is composed of layers of epithelial tissues grouped around many blood vessels. The epithelial tissues contain five types of secretory cells responsible for hormone pro ...
26.Surgical diseases of the thyroid gland
... wasting. Psychiatric signs may include altered sleep patterns, emotional mood swings, fatigue, excitability, and agitation. DIAGNOSIS Elevated levels of T 3 and T 4, a decreased or undetectable level of TSH are demonstrated. Thyroid antibodies are usually detected in elevated quantities. A 123 I rad ...
... wasting. Psychiatric signs may include altered sleep patterns, emotional mood swings, fatigue, excitability, and agitation. DIAGNOSIS Elevated levels of T 3 and T 4, a decreased or undetectable level of TSH are demonstrated. Thyroid antibodies are usually detected in elevated quantities. A 123 I rad ...
Full Text - Int J Endocrinol Metab
... docrine disorders, especially those dealing with thyroid gland. 9 - 15 In the present research we foun d that experimental hypothyroidism is associated with body weight loss and de creased weight and length of tibia. Mudde et al have evaluated the effects of methimazole in hypelihyroid women and co ...
... docrine disorders, especially those dealing with thyroid gland. 9 - 15 In the present research we foun d that experimental hypothyroidism is associated with body weight loss and de creased weight and length of tibia. Mudde et al have evaluated the effects of methimazole in hypelihyroid women and co ...
Comparative Vertebrate Physiology
... Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
... Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
Hashimoto Thyroiditis - Patologos de Puerto Rico
... women (mean age 59 -- men and women) • 5-7 x more common in women than men • Present with goiter • May present with hypothyroidism • Most common cause of sporadic goiter in children (rarely occurs before age 5, but 40% of adolescent goiters) ...
... women (mean age 59 -- men and women) • 5-7 x more common in women than men • Present with goiter • May present with hypothyroidism • Most common cause of sporadic goiter in children (rarely occurs before age 5, but 40% of adolescent goiters) ...
7 Endocrine Anat and Physio flashcards
... A protein made by a target cell during protein synthesis; it is inserted into the cell What does the active site on the ...
... A protein made by a target cell during protein synthesis; it is inserted into the cell What does the active site on the ...
Interpretation of thyroid function tests
... The introduction of sensitive thyrotropin assays and free thyroid hormone measurements has simplified the interpretation of thyroid function tests. However, important pitfalls and difficult cases still exist. In this review, thyroid function test results are grouped into six different patterns. We p ...
... The introduction of sensitive thyrotropin assays and free thyroid hormone measurements has simplified the interpretation of thyroid function tests. However, important pitfalls and difficult cases still exist. In this review, thyroid function test results are grouped into six different patterns. We p ...
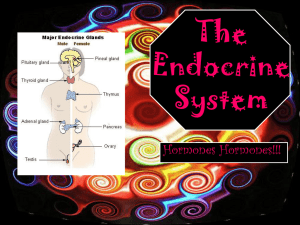
Endocrine System
... excessively tall. If it produces too little, a teen may be unusually short. Doctors can often treat the problems by controlling the production of hormones or replacing certain hormones with medication. Some endocrine problems that affect teens are… ...
... excessively tall. If it produces too little, a teen may be unusually short. Doctors can often treat the problems by controlling the production of hormones or replacing certain hormones with medication. Some endocrine problems that affect teens are… ...
Endocrine System
... Targets suprarenal (adrenal) cortex Stimulates secretion of most steroids from ...
... Targets suprarenal (adrenal) cortex Stimulates secretion of most steroids from ...
Rhythms and Blues
... 1. Alpha cells secrete glucagon, which causes glycogen stored in the liver to be converted to glucose, which then enters the bloodstream. 2. Beta cells secrete insulin, which stimulates the uptake of glucose by liver, muscle, and adipose to reduce levels in the blood, especially after a meal. 3. Del ...
... 1. Alpha cells secrete glucagon, which causes glycogen stored in the liver to be converted to glucose, which then enters the bloodstream. 2. Beta cells secrete insulin, which stimulates the uptake of glucose by liver, muscle, and adipose to reduce levels in the blood, especially after a meal. 3. Del ...
21 Endocrine 10a
... – Leads to nervousness, weight loss, sweating, and rapid heart rate • Hypothyroidism – Decreases metabolism, causes obesity ...
... – Leads to nervousness, weight loss, sweating, and rapid heart rate • Hypothyroidism – Decreases metabolism, causes obesity ...
Thyroid Hormone Excess: Graves` Disease
... The thyroid gland in Graves' disease is characterized by non-homogenous lymphocytic infiltration. Majority of the intrathyroidal lymphocytes are T lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes are much less common than Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Cytokine profile produced by intrathyroidal T lymphocytes suggested that bo ...
... The thyroid gland in Graves' disease is characterized by non-homogenous lymphocytic infiltration. Majority of the intrathyroidal lymphocytes are T lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes are much less common than Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Cytokine profile produced by intrathyroidal T lymphocytes suggested that bo ...
Atypical clinical manifestations of multiple endocrine neoplasia type
... agnose MEN1 there is a need to show hyperpla‑ sia in at least 2 of the 3 main glands (parathyroid, pituitary, pancreas or duodenum).5 ...
... agnose MEN1 there is a need to show hyperpla‑ sia in at least 2 of the 3 main glands (parathyroid, pituitary, pancreas or duodenum).5 ...
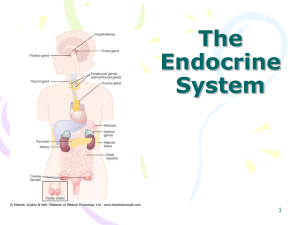
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... travel to the posterior pituitary gland for release. The hypothalamus has another function; it produces releasing and inhibiting hormones, which control the release of the anterior pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus also plays a part in maintaining body temperature, hunger, and thirst. Anatomy and ...
... travel to the posterior pituitary gland for release. The hypothalamus has another function; it produces releasing and inhibiting hormones, which control the release of the anterior pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus also plays a part in maintaining body temperature, hunger, and thirst. Anatomy and ...
Research Article Correlation between Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
... Thyroid hormones are recognized as catabolic hormones and they regulate various processes of metabolism [1]. The relationship between thyroid hormones and lipid metabolism is clearly displayed in patients suffering from thyroid dysfunctions. Overt hypothyroid patients show elevated total cholesterol ...
... Thyroid hormones are recognized as catabolic hormones and they regulate various processes of metabolism [1]. The relationship between thyroid hormones and lipid metabolism is clearly displayed in patients suffering from thyroid dysfunctions. Overt hypothyroid patients show elevated total cholesterol ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... Rapid sexual development in a prepubertal boy is indicative of hypersecretion of sex steroids. The two most likely tissues are the testes and adrenal glands. Because the testes are of normal size, it is possible that removal of an adrenal tumor could cure the boy. ...
... Rapid sexual development in a prepubertal boy is indicative of hypersecretion of sex steroids. The two most likely tissues are the testes and adrenal glands. Because the testes are of normal size, it is possible that removal of an adrenal tumor could cure the boy. ...
thyroid uptake enzyme
... The thyroid gland secretes two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine is the most commonly measured hormone for the diagnosis of thyroid function. Thyroxine has its primary influence in protein synthesis and oxygen consumption in virtually all tissues but it is al important fo ...
... The thyroid gland secretes two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine is the most commonly measured hormone for the diagnosis of thyroid function. Thyroxine has its primary influence in protein synthesis and oxygen consumption in virtually all tissues but it is al important fo ...
autotransplantation in lingual ectopia of the thyroid gland
... 'thyroglossal cyst' is solid and represents the only thyroid tissue which the patient possesses. Such cases are analogous to lingual ectopia, the difference lying in the point at which migration is arrested. If this designation is accepted, the term 'aberrant thyroid' could be reserved for those cas ...
... 'thyroglossal cyst' is solid and represents the only thyroid tissue which the patient possesses. Such cases are analogous to lingual ectopia, the difference lying in the point at which migration is arrested. If this designation is accepted, the term 'aberrant thyroid' could be reserved for those cas ...
thyroid testing - Endocrine Sciences
... estimated 25% of patients with DCT.19 In those patients, there is a risk of interference with Tg measurement using immunometric (IMA) methods that can lead to false-negative (inappropriately low or undetectable) ...
... estimated 25% of patients with DCT.19 In those patients, there is a risk of interference with Tg measurement using immunometric (IMA) methods that can lead to false-negative (inappropriately low or undetectable) ...
Vocabulary for Test: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Medulla - the part of the brain below the cerebellum and continuous with the spinal cord; controls involuntary activities Meninges - 3 membranes forming a protective sheath around brain and spinal cord Menstrual Cycle - 28 day hormone controlled cycle in which a human egg develops, is released from ...
... Medulla - the part of the brain below the cerebellum and continuous with the spinal cord; controls involuntary activities Meninges - 3 membranes forming a protective sheath around brain and spinal cord Menstrual Cycle - 28 day hormone controlled cycle in which a human egg develops, is released from ...
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type II B with Simultaneous Papillary
... Microcarcinoma of Thyroid Gland – A Case Report. Urol Nephrol Open Access J 2(5): 00054. DOI: 10.15406/unoaj.2015.02.00054 ...
... Microcarcinoma of Thyroid Gland – A Case Report. Urol Nephrol Open Access J 2(5): 00054. DOI: 10.15406/unoaj.2015.02.00054 ...
Night-Lighting
... the endocrine (hormonal) system. Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete its hormones; and these, in turn, stimulate the thyroid gland, the adrenals and the ovaries to secrete yet other hormones. The reproductive system is also thought to contain melat ...
... the endocrine (hormonal) system. Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete its hormones; and these, in turn, stimulate the thyroid gland, the adrenals and the ovaries to secrete yet other hormones. The reproductive system is also thought to contain melat ...
THYROID PROBLEMS
... immunes system mistakenly recognizes thyroid gland cells and its enzymes as nonself or invaders and attacks them. After destruction by immune system, not enough thyroid cells and its enzymes left that leads to hypothyroidism. It can begin suddenly or can follow a slow long-term course. Most common f ...
... immunes system mistakenly recognizes thyroid gland cells and its enzymes as nonself or invaders and attacks them. After destruction by immune system, not enough thyroid cells and its enzymes left that leads to hypothyroidism. It can begin suddenly or can follow a slow long-term course. Most common f ...
Parathyroid tumors
... calcium levels. The calcium in the blood is regulated by PTH (increases blood calcium) and calcitonin (a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland to decrease calcium) in order to keep it within a normal range. When the calcium gets too high or too low, symptoms arise. The most common symptoms of high c ...
... calcium levels. The calcium in the blood is regulated by PTH (increases blood calcium) and calcitonin (a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland to decrease calcium) in order to keep it within a normal range. When the calcium gets too high or too low, symptoms arise. The most common symptoms of high c ...
Why the European Association of Nuclear Medicine has declined to
... should not routinely be given to any patient who is considered ATA low-risk^. This includes both patients with classical unifocal microcarcinoma, in whom it has for a long time been established that 131I ablation offers no advantage, and patients with larger tumour sizes up to 4 cm. In patients with ...
... should not routinely be given to any patient who is considered ATA low-risk^. This includes both patients with classical unifocal microcarcinoma, in whom it has for a long time been established that 131I ablation offers no advantage, and patients with larger tumour sizes up to 4 cm. In patients with ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.