Guidelines on management of congenital hypothyroidism in Sri Lanka
... Suggested procedure for re-evaluation is as follows: • Reduce dose of L-T4 by 30%. • Check TSH/ fT4 after 3 weeks. • Repeat an USS of the thyroid gland. • If TSH >10mIU/L, CH is confirmed and lifelong treatment needs to be given. • If CH is not confirmed, reduce L-T4 dose gradually with repeat TFTs ...
... Suggested procedure for re-evaluation is as follows: • Reduce dose of L-T4 by 30%. • Check TSH/ fT4 after 3 weeks. • Repeat an USS of the thyroid gland. • If TSH >10mIU/L, CH is confirmed and lifelong treatment needs to be given. • If CH is not confirmed, reduce L-T4 dose gradually with repeat TFTs ...
Slide 1
... mykiss). The ovaries of fishes and other non-mammalian vertebrates readily concentrate iodide in the oocytes. The control ovary at the left exhibits a size range of developing oocytes. The ovary at the right is from a fish that accumulated radiodide (131I) shortly after hatching. Although the radioa ...
... mykiss). The ovaries of fishes and other non-mammalian vertebrates readily concentrate iodide in the oocytes. The control ovary at the left exhibits a size range of developing oocytes. The ovary at the right is from a fish that accumulated radiodide (131I) shortly after hatching. Although the radioa ...
Chapter 36
... Blood & hormones flow to 2nd capillary bed in anterior pituitary where TRH and CRH bind to receptors in anterior pituitary ...
... Blood & hormones flow to 2nd capillary bed in anterior pituitary where TRH and CRH bind to receptors in anterior pituitary ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... By what pathway does stress stimulate the secretion of cortisol above basal values? How is negative feedback involved in maintaining cortisol levels after destruction of on of the adrenal glands? What is the difference in long-loop and short-loop negative feedback? Use the TRH-TSH-TH system an examp ...
... By what pathway does stress stimulate the secretion of cortisol above basal values? How is negative feedback involved in maintaining cortisol levels after destruction of on of the adrenal glands? What is the difference in long-loop and short-loop negative feedback? Use the TRH-TSH-TH system an examp ...
Histology of Endocrine System
... • Hormone produced by cells in endocrine glands or organs • Hormone is released into the circulation • Hormone affects function of target cells – Target cells have receptors – Receptors begin a process called signal ...
... • Hormone produced by cells in endocrine glands or organs • Hormone is released into the circulation • Hormone affects function of target cells – Target cells have receptors – Receptors begin a process called signal ...
cme reviewarticle - e
... pregnancy can be especially troubling in young women. The single most important diagnostic test is measurement of serum thyrotropin (TSH). The overwhelming majority of patients with hypothyroidism are treated with a single daily dose of synthetic levothyroxine with the goal of therapy being restorat ...
... pregnancy can be especially troubling in young women. The single most important diagnostic test is measurement of serum thyrotropin (TSH). The overwhelming majority of patients with hypothyroidism are treated with a single daily dose of synthetic levothyroxine with the goal of therapy being restorat ...
The Endocrine System
... What can go wrong if there is a loss of hormonal control? • Dwarfism (Hypopitutiary dwarfism) – GH= Growth hormone – When inadequate amounts are secreted. – Short, underdeveloped, lack full adult sexual features. – Treatment: Hormone therapy if diagnosed early ...
... What can go wrong if there is a loss of hormonal control? • Dwarfism (Hypopitutiary dwarfism) – GH= Growth hormone – When inadequate amounts are secreted. – Short, underdeveloped, lack full adult sexual features. – Treatment: Hormone therapy if diagnosed early ...
Basal Metabolic Temperature Test
... your body will be working below par, which in turn can have a profound effect on how efficiently your cells - and hence your body – are able to function. It’s actually as simple – but fundamental - as that. Chronic low body temperature = poor body function, which can end up causing a plethora of sym ...
... your body will be working below par, which in turn can have a profound effect on how efficiently your cells - and hence your body – are able to function. It’s actually as simple – but fundamental - as that. Chronic low body temperature = poor body function, which can end up causing a plethora of sym ...
Pathology of the Endocrine System
... Figure 20–21 (Mescher) Thyroid follicular cell functions. The diagram shows the multistep process by which thyroid hormones are produced via the stored thyroglobulin intermediate. In an exocrine phase of the process, the glycoprotein thyroglobulin is made and secreted into the follicular lumen and i ...
... Figure 20–21 (Mescher) Thyroid follicular cell functions. The diagram shows the multistep process by which thyroid hormones are produced via the stored thyroglobulin intermediate. In an exocrine phase of the process, the glycoprotein thyroglobulin is made and secreted into the follicular lumen and i ...
Specific Endocrine Glands
... 5. when thyroid function is being measured by blood work, it is the TSH which is measured 6. it is a more direct barometer of thyroid activity 7. these two hormones elevate metabolic rate 8. Increase rate of glucose, fat, protein metabolism in many tissues thus increasing body temperature 9. Normal ...
... 5. when thyroid function is being measured by blood work, it is the TSH which is measured 6. it is a more direct barometer of thyroid activity 7. these two hormones elevate metabolic rate 8. Increase rate of glucose, fat, protein metabolism in many tissues thus increasing body temperature 9. Normal ...
PDF
... incubation (Hashimoto & Wilt, 1966; Manwell, Baker & Betz, 1966). Normal thyroid development can be seen on the second day in the chick embryo, appearing as a medial outgrowth from the pharyngeal floor. By the sixth day, when AHb is first recognized electrophoretically, the thyroid concentrates 131I ...
... incubation (Hashimoto & Wilt, 1966; Manwell, Baker & Betz, 1966). Normal thyroid development can be seen on the second day in the chick embryo, appearing as a medial outgrowth from the pharyngeal floor. By the sixth day, when AHb is first recognized electrophoretically, the thyroid concentrates 131I ...
Topic: Endocrine system Reading: Chapter 37 Main concepts
... Part of stress response, increase blood glucose levels and decrease immune response. ...
... Part of stress response, increase blood glucose levels and decrease immune response. ...
Figure 1. - journal of evidence based medicine and healthcare
... clinically diagnosed cases of fibromyalgia in NEIGRIHMS shilling from September 2013 to March 2014. Data from the cases when compared with 25 numbers of age matched control revealed a non significance of growth hormone in fibromyalgia with p value >0.05. The study also showed a significant differenc ...
... clinically diagnosed cases of fibromyalgia in NEIGRIHMS shilling from September 2013 to March 2014. Data from the cases when compared with 25 numbers of age matched control revealed a non significance of growth hormone in fibromyalgia with p value >0.05. The study also showed a significant differenc ...
Management
... Insulin activity prevents buildup of ketones. Sustained hyperglycemia results in marked dehydration. • Often related to dialysis, infection, and medications. Very high mortality rate. ...
... Insulin activity prevents buildup of ketones. Sustained hyperglycemia results in marked dehydration. • Often related to dialysis, infection, and medications. Very high mortality rate. ...
hormones - Avon Community School Corporation
... kidneys conserve sodium and excrete potassium, maintaining blood pressure Cortisol – glucocortoid, keeps blood glucose levels stable Adrenal Sex Hormones - androgens (male) and estrogens (female) ...
... kidneys conserve sodium and excrete potassium, maintaining blood pressure Cortisol – glucocortoid, keeps blood glucose levels stable Adrenal Sex Hormones - androgens (male) and estrogens (female) ...
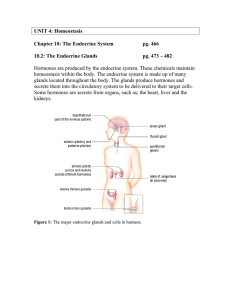
Note 10.2 - Endocrine Gland
... Thyroid gland – is an endocrine gland located in the throat that is regulated by the hypothalamus-pituitary system. Parathyroid hormone – is a hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands hat controls calcium and phosphate levels in the blood. The thyroid is located in the front of the throat, and it ...
... Thyroid gland – is an endocrine gland located in the throat that is regulated by the hypothalamus-pituitary system. Parathyroid hormone – is a hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands hat controls calcium and phosphate levels in the blood. The thyroid is located in the front of the throat, and it ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System - Linn
... stimulates it to secrete thyroid hormone • ACTH—stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and stimulates it to secrete glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol) • FSH—initiates growth of ovarian follicles each month in the ovary and stimulates one or more follicles to develop to the stage of maturity and ovul ...
... stimulates it to secrete thyroid hormone • ACTH—stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and stimulates it to secrete glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol) • FSH—initiates growth of ovarian follicles each month in the ovary and stimulates one or more follicles to develop to the stage of maturity and ovul ...
Lecture 11: Thyroid and Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands: Learning
... Inferior thyroid arteries primarily supply the posterior thyroid, where the parathyroid glands are located May also be supplied by branches from the superior thyroid arteries, the thyroid ima artery, or the laryngeal, tracheal, and esophageal arteries Parathyroid Veins Parathyroid veins drai ...
... Inferior thyroid arteries primarily supply the posterior thyroid, where the parathyroid glands are located May also be supplied by branches from the superior thyroid arteries, the thyroid ima artery, or the laryngeal, tracheal, and esophageal arteries Parathyroid Veins Parathyroid veins drai ...
Chapter 11 • The Endocrine System • What you absolutely need to
... Abnormal secretion of (or sensitivity to) melatonin may produce seasonal affective disorder (SAD) or winter depression, a form of depression that occurs when exposure to sunlight is low and melatonin levels are high ...
... Abnormal secretion of (or sensitivity to) melatonin may produce seasonal affective disorder (SAD) or winter depression, a form of depression that occurs when exposure to sunlight is low and melatonin levels are high ...
Endocrine System Revision Notes
... Ductless glands – hormones diffuse directly into the bloodstream Hormones are then carried by the blood to target tissues and organs – they influence cellular growth and metabolism Homeostasis of the internal environment is maintained partly by the autonomic nervous system and partly by the en ...
... Ductless glands – hormones diffuse directly into the bloodstream Hormones are then carried by the blood to target tissues and organs – they influence cellular growth and metabolism Homeostasis of the internal environment is maintained partly by the autonomic nervous system and partly by the en ...
ENDOCRINE: Endocrine glands Ductless Act with nervous system to
... 7. Lysosomal enzymes cleave T4/T3 from thyroglobulin and hormones diffuse into bloodstream o T3 is ten times more active than T4 o They both bind to target receptors o Peripheral tissues convert T4 to T3 if needed o Increases metabolic rate and heat production/energy release o Plays a role in: main ...
... 7. Lysosomal enzymes cleave T4/T3 from thyroglobulin and hormones diffuse into bloodstream o T3 is ten times more active than T4 o They both bind to target receptors o Peripheral tissues convert T4 to T3 if needed o Increases metabolic rate and heat production/energy release o Plays a role in: main ...
18-1 The Endocrine System
... – secrete products (hormones) into bloodstream – pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal – other organs secrete hormones as a 2nd function • hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas,ovaries,testes, kidneys, stomach, liver, small intestine, skin, heart & placenta ...
... – secrete products (hormones) into bloodstream – pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal – other organs secrete hormones as a 2nd function • hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas,ovaries,testes, kidneys, stomach, liver, small intestine, skin, heart & placenta ...
The Endocrine System
... darkened skin in armpits, widely spaced teeth, oily, tough skin, skin pigmentation changes, excessive hair growth in females, high blood pressure, goiter (enlarged thyroid), kyphosis or loss of disc spaces of the spine, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis • Laboratory findings-growth hormone level is high ...
... darkened skin in armpits, widely spaced teeth, oily, tough skin, skin pigmentation changes, excessive hair growth in females, high blood pressure, goiter (enlarged thyroid), kyphosis or loss of disc spaces of the spine, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis • Laboratory findings-growth hormone level is high ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.